Content Menu
● Introduction to Carbide Production
>> Tungsten Carbide Production
>> Calcium Carbide Production
● Economic Viability of Carbide Production
>> Tungsten Carbide Market
>> Calcium Carbide Market
● Environmental Challenges in Carbide Production
>> Environmental Solutions
>> Sustainable Practices
● Future Prospects
>> Technological Advancements
>> Emerging Markets
● Market Trends and Innovations
>> Carbide in Aerospace
>> Carbide in Automotive
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What are the primary applications of tungsten carbide?
>> 2. What are the environmental challenges faced by calcium carbide production?
>> 3. How does recycling impact carbide production?
>> 4. What technological advancements are enhancing carbide tool manufacturing?
>> 5. How do environmental regulations affect calcium carbide production costs?
● Citations:
Carbide production, encompassing various types of carbides such as tungsten carbide and calcium carbide, is a complex process with significant industrial applications. The profitability of carbide production depends on several factors, including raw material costs, production efficiency, market demand, and environmental regulations. This article will delve into the profitability of carbide production, exploring its economic viability, environmental challenges, and future prospects.
Introduction to Carbide Production
Carbides are compounds of carbon with metals or metalloids. Tungsten carbide, for instance, is renowned for its hardness and wear resistance, making it crucial in manufacturing cutting tools and medical instruments. Calcium carbide, on the other hand, is pivotal in acetylene production and steel desulfurization.
Tungsten Carbide Production
Tungsten carbide production involves the reaction of tungsten with carbon at high temperatures. This process is energy-intensive and requires careful control of raw materials and manufacturing conditions to ensure product quality.
Tungsten Carbide Production Process:
1. Raw Material Preparation: Tungsten and carbon are prepared in powder form.
2. Sintering: The powders are mixed and sintered at high temperatures to form tungsten carbide.
3. Shaping and Finishing: The carbide is then shaped into desired forms and finished for use in tools.
Tungsten Carbide Production
A[Raw Material Preparation] --> B[Sintering]
B --> C[Shaping and Finishing]
C --> D[Final Product]
Calcium Carbide Production
Calcium carbide production involves the electrolysis of lime with coke or coal, followed by mixing with water to create calcium oxide. This process is also energy-intensive and poses environmental challenges.
Calcium Carbide Production Process:
1. Electrolysis: Lime is electrolyzed with coke or coal to produce calcium carbide.
2. Mixing with Water: The carbide reacts with water to produce acetylene gas.
Calcium Carbide Production
A[Electrolysis] --> B[Mixing with Water]
B --> C[Acetylene Gas Production]
C --> D[Final Product]
Economic Viability of Carbide Production
The economic viability of carbide production is influenced by several factors:
- Raw Material Costs: The cost of raw materials such as tungsten and calcium significantly affects production costs.
- Market Demand: High demand for carbide tools and acetylene gas supports profitability.
- Production Efficiency: Efficient manufacturing processes reduce costs and enhance profitability.
Tungsten Carbide Market
The tungsten carbide market is driven by its use in cutting tools and medical instruments. The carbide tools market is projected to exceed $17.3 billion by 2032, with a significant portion attributed to tungsten carbide inserts.
Tungsten Carbide Market Growth
A[2023] --> B[2024]
B --> C[2032]
C --> D[Market Value: $17.3 Billion]
Calcium Carbide Market
Calcium carbide is crucial for acetylene production and steel desulfurization. However, environmental regulations and energy costs impact its profitability.
Calcium Carbide Production Costs
A[Raw Material Costs] --> B[Energy Costs]
B --> C[Environmental Compliance Costs]
C --> D[Total Production Costs]
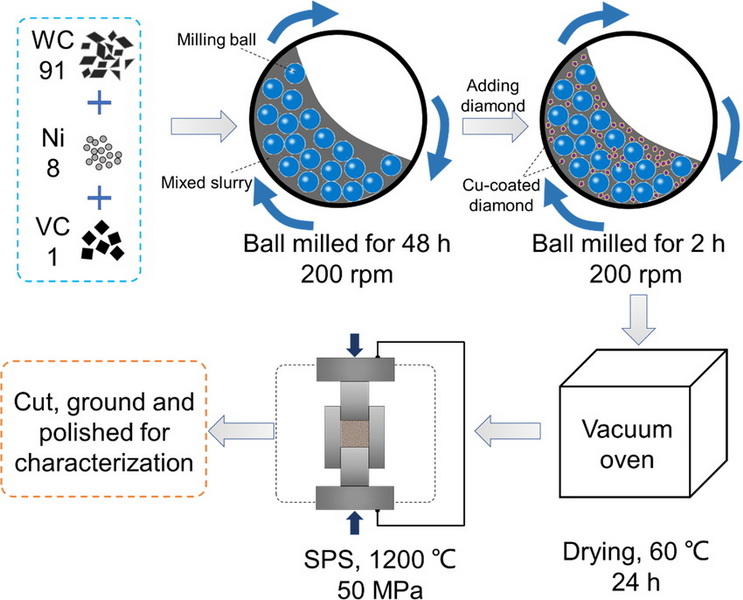
Environmental Challenges in Carbide Production
Both tungsten and calcium carbide production face environmental challenges:
- Energy Consumption: Both processes are energy-intensive, contributing to carbon emissions.
- Waste Management: Carbide production generates waste that requires proper disposal.
Environmental Solutions
Manufacturers are adopting strategies to reduce environmental impacts:
1. Recycling: Recycling carbide scrap reduces waste and energy consumption.
2. Advanced Technologies: Implementing dust control systems and moisture prevention measures in calcium carbide production.
Carbide Recycling Process
A[Carbide Scrap Collection] --> B[Recycling Process]
B --> C[Recovery of Tungsten and Cobalt]
C --> D[Reuse in New Products]
Sustainable Practices
To enhance sustainability, companies are focusing on:
- Renewable Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources to reduce carbon footprints.
- Circular Economy: Encouraging closed-loop production systems where materials are continuously cycled back into production.
Sustainable Carbide Production Model
A[Raw Material Extraction] --> B[Production]
B --> C[Product Use]
C --> D[Recycling and Reuse]
D --> A
Future Prospects
The future of carbide production is influenced by technological advancements and sustainability efforts:
- Smart Manufacturing: Integration of IoT technology enhances efficiency and reduces waste.
- Sustainability: Focus on recyclable materials and reduced carbon footprints.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in manufacturing technology, such as the use of sensors for real-time monitoring, improve tool performance and longevity.
Smart Carbide Tool Manufacturing
A[IoT Integration] --> B[Real-Time Monitoring]
B --> C[Enhanced Tool Performance]
C --> D[Increased Efficiency]
Emerging Markets
Emerging markets in Asia and Latin America are driving demand for carbide tools and acetylene gas, offering new opportunities for growth.
Emerging Markets for Carbide Products
A[Asia] --> B[Latin America]
B --> C[Market Growth Opportunities]
C --> D[Increased Demand]
Market Trends and Innovations
Recent trends include the development of new carbide materials with enhanced properties and the integration of carbides in advanced technologies such as aerospace and automotive industries.
Carbide in Aerospace
Tungsten carbide is used in aerospace for its high strength-to-weight ratio, contributing to lighter and more efficient aircraft components.
Aerospace Applications of Tungsten Carbide
A[Engine Components] --> B[Structural Parts]
B --> C[Weight Reduction]
C --> D[Improved Efficiency]
Carbide in Automotive
In the automotive sector, carbide is used in wear-resistant parts and fuel injectors, enhancing engine performance and durability.
Automotive Applications of Tungsten Carbide
A[Fuel Injectors] --> B[Wear-Resistant Parts]
B --> C[Improved Engine Performance]
C --> D[Increased Durability]
Conclusion
Carbide production, particularly tungsten and calcium carbide, is a profitable industry due to its critical applications in manufacturing and industrial processes. However, profitability is contingent upon efficient production processes, market demand, and compliance with environmental regulations. As the industry moves towards sustainability and technological advancements, the future of carbide production looks promising.

FAQs
1. What are the primary applications of tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is primarily used in manufacturing cutting tools, medical instruments, and wear-resistant parts due to its hardness and durability.
2. What are the environmental challenges faced by calcium carbide production?
Calcium carbide production faces challenges such as dust emissions, chemical risks, waste management, and high energy consumption leading to significant CO₂ emissions.
3. How does recycling impact carbide production?
Recycling carbide reduces the need for raw materials, lowers energy consumption, and minimizes waste, contributing to sustainable production practices.
4. What technological advancements are enhancing carbide tool manufacturing?
The integration of IoT technology and real-time monitoring systems improves tool performance, efficiency, and predictive maintenance.
5. How do environmental regulations affect calcium carbide production costs?
Environmental regulations increase production costs by requiring compliance with emission standards and energy efficiency measures, which can lead to fluctuations in calcium carbide prices.
Citations:
[1] https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/tungsten-carbide
[2] https://www.tjtywh.com/environmental-challenges-in-calcium-carbide-production-and-tywh-s-solutions.html
[3] https://www.ee.cityu.edu.hk/~gchen/pdf/Writing.pdf
[4] https://www.niir.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Manufacturing-Business-of-Calcium-Carbide-Calcium-Acetylide.-Investment-Opportunities-in-Chemical-Industry.-1.pdf
[5] https://dormerpramet.com/carbide-recycling
[6] https://jphe.amegroups.org/article/view/4265/10863
[7] https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/01/08/3006094/0/en/Carbide-Tools-Market-to-exceed-17-3-Bn-by-2032-Says-Global-Market-Insights-Inc.html
[8] https://www.tjtywh.com/how-environmental-regulations-impact-global-calcium-carbide-production-and-supply-chains.html















