Content Menu
● Introduction to Tungsten Carbide Recycling
>> Importance of Recycling
● Methods of Tungsten Carbide Recycling
>> 1. Electrolytic Method
>> 2. Zinc Smelting Method
>> 3. Chemical Recycling
● Role of Professional Manufacturers in Recycling
>> Advanced Technologies
>> Quality Assurance
>> Regulatory Compliance
● Environmental Impact and Sustainability
>> Environmental Benefits
>> Sustainability in Manufacturing
● Economic Benefits of Recycling
>> Cost Savings
>> Market Demand
● Challenges in Tungsten Carbide Recycling
>> Technological Challenges
>> Economic Challenges
● Future Developments in Recycling Technology
>> Emerging Technologies
>> Collaboration and Innovation
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What are the primary methods for recycling tungsten carbide?
>> 2. Why is recycling tungsten carbide important?
>> 3. What are the advantages of the electrolytic method?
>> 4. How does the zinc smelting method work?
>> 5. What role do professional manufacturers play in recycling?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide, known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, is widely used in cutting tools, wear parts, and other industrial applications. However, its recycling is crucial due to its significant environmental and economic impact. This article delves into the methods and importance of tungsten carbide recycling, highlighting the processes involved and the benefits they offer.
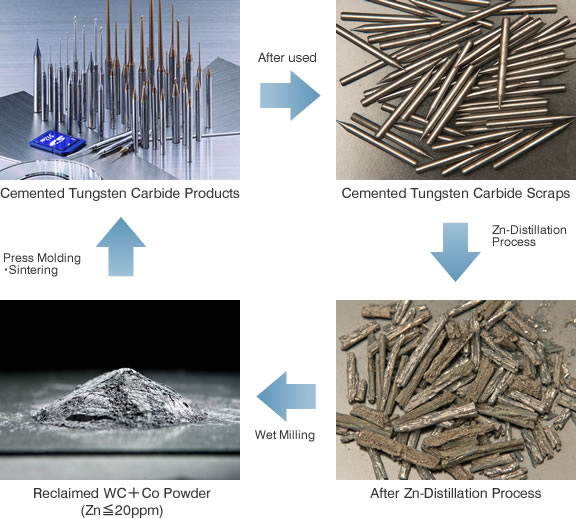
Introduction to Tungsten Carbide Recycling
Tungsten carbide recycling is essential for conserving resources and reducing environmental pollution. The process involves recovering tungsten and other valuable metals from scrap materials, which can then be reused in new products. This not only saves energy but also decreases the need for mining raw materials, thereby minimizing ecological damage.
Importance of Recycling
- Resource Conservation: Tungsten is a rare element, and recycling helps preserve natural resources by reducing the demand for new mining activities.
- Energy Savings: Recycling tungsten carbide requires less energy than producing it from raw materials, which helps lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Environmental Protection: Recycling prevents tungsten carbide from ending up in landfills, where it could contaminate soil and water.
Methods of Tungsten Carbide Recycling
Several methods are used to recycle tungsten carbide, each with its advantages and limitations.
1. Electrolytic Method
The electrolytic method is an efficient process that leverages the electrode potentials of different components within tungsten-containing waste. It is particularly effective for waste materials that include tungsten carbide and cobalt metal.
Process Overview:
1. Setup: A graphite anode and a nickel plate cathode are used in an acidic solution.
2. Electrolysis: Cobalt dissolves into the solution, forming CoCl2, while tungsten carbide is separated.
3. Recovery: The anode mud is processed to recover tungsten carbide, which can be reused.
Advantages:
- Low reagent and energy consumption.
- Simplicity of the process.
Limitations:
- Only applicable to waste with a cobalt content above 10%.
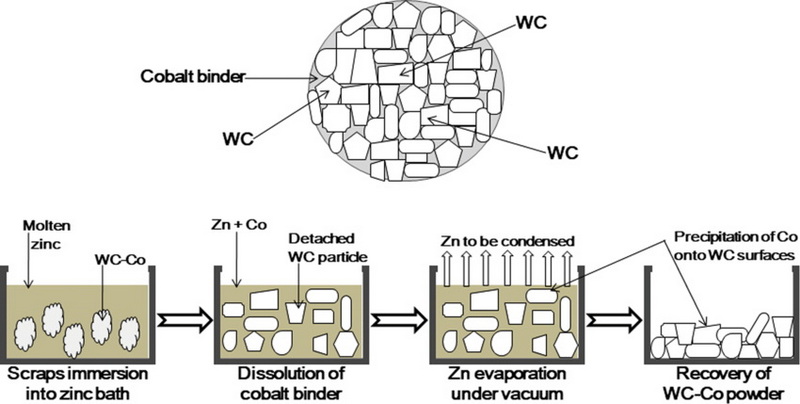
2. Zinc Smelting Method
This method involves using metallic zinc and high temperatures to recover tungsten carbide from waste materials. It is effective for waste with low cobalt content or those containing other metals like tantalum and titanium.
Process Overview:
1. Setup: Waste tungsten carbide and metallic zinc are placed in a crucible inside a vacuum furnace.
2. Heating: The mixture is heated to form a zinc-cobalt alloy.
3. Distillation: Zinc is removed by vacuum distillation, leaving behind tungsten carbide and cobalt powder.
Advantages:
- Short production process.
- Handles low-cobalt content waste.
Limitations:
- Requires specific equipment and high energy consumption.
- Generally more costly than the electrolytic method.
3. Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling involves oxidation followed by alkali leaching to convert scrap into sodium tungstate, from which raw tungsten can be recovered. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Process Overview:
1. Oxidation: Scrap is oxidized to form tungsten oxide.
2. Leaching: The oxide is converted into sodium tungstate.
3. Purification: The solution is purified to obtain high-purity tungsten.
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly.
- Cost-effective.
Limitations:
- Requires specialized equipment and chemicals.
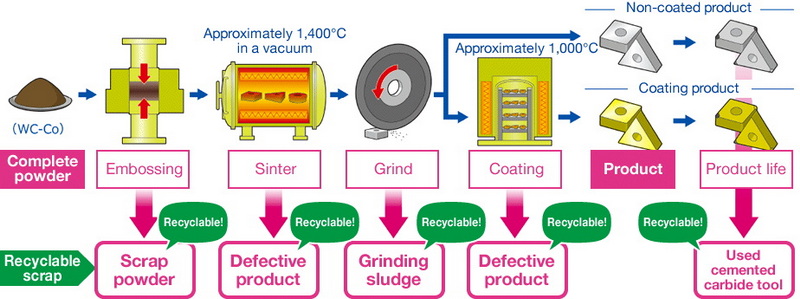
Role of Professional Manufacturers in Recycling
Experienced tungsten carbide manufacturers play a crucial role in recycling by using advanced technologies like chemical recycling and mechanical processing. They ensure that recycled materials retain their structural integrity and hardness, making them suitable for future industrial uses.
Advanced Technologies
- Chemical Recycling: Involves processes like oxidation and leaching to recover tungsten.
- Mechanical Processing: Includes crushing and milling to prepare materials for reuse.
Quality Assurance
Manufacturers ensure that recycled tungsten carbide meets quality standards, maintaining its hardness and durability for industrial applications. This involves rigorous testing to ensure that the recycled material performs as well as newly produced tungsten carbide.
Regulatory Compliance
Reputable manufacturers adhere to environmental regulations, ensuring that recycling practices are safe and legally compliant. This includes proper waste handling and disposal of by-products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tungsten carbide itself is not hazardous to the environment during production. However, improper disposal can lead to contamination. Recycling helps mitigate these risks by conserving resources and reducing waste.
Environmental Benefits
- Conservation of Resources: Recycling reduces the need for new mining activities.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower energy consumption compared to producing new materials.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizes landfill waste and potential environmental pollution.
Sustainability in Manufacturing
Manufacturing tungsten carbide from recycled materials supports sustainable practices by reducing the environmental footprint associated with raw material extraction and processing. This aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Economic Benefits of Recycling
Recycling tungsten carbide also offers significant economic benefits. By recovering valuable metals like tungsten and cobalt, companies can reduce their raw material costs. Additionally, recycling helps maintain a stable supply chain by reducing dependence on primary mining activities, which can be affected by geopolitical factors.
Cost Savings
- Raw Material Costs: Recycling reduces the need for purchasing raw materials.
- Stable Supply Chain: Minimizes risks associated with fluctuations in raw material availability.
Market Demand
The demand for recycled tungsten carbide is increasing as industries seek more sustainable and cost-effective solutions. This trend is expected to continue, driving innovation in recycling technologies and processes.
Challenges in Tungsten Carbide Recycling
Despite the benefits, there are challenges associated with recycling tungsten carbide. These include the complexity of the recycling process, high energy requirements, and the need for specialized equipment.
Technological Challenges
- Complexity of Processes: Requires advanced technologies and expertise.
- Energy Consumption: High energy costs can make recycling less economical.
Economic Challenges
- Initial Investment: Setting up recycling facilities requires significant capital.
- Market Fluctuations: Prices of raw materials can affect the economic viability of recycling.
Future Developments in Recycling Technology
Advancements in recycling technology are crucial for overcoming current challenges and improving the efficiency of tungsten carbide recycling. Research into new methods, such as plasma arc recycling and microwave-assisted processes, aims to reduce energy consumption and increase the purity of recovered materials.
Emerging Technologies
- Plasma Arc Recycling: Offers high-temperature processing with reduced energy consumption.
- Microwave-Assisted Processes: Enhances efficiency and reduces processing time.
Collaboration and Innovation
Collaboration between industries and research institutions is vital for driving innovation in recycling technologies. This includes developing more efficient processes and improving the quality of recycled materials.
Conclusion
Tungsten carbide recycling is vital for both environmental conservation and economic efficiency. Methods like electrolytic, zinc smelting, and chemical recycling offer effective ways to recover valuable materials, reducing the need for new mining and lowering energy consumption. As industries continue to adopt sustainable practices, the importance of tungsten carbide recycling will only grow.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the primary methods for recycling tungsten carbide?
The primary methods include the electrolytic method, zinc smelting method, and chemical recycling. Each method has its specific applications and advantages.
2. Why is recycling tungsten carbide important?
Recycling tungsten carbide is important for conserving resources, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing environmental pollution. It also helps recover valuable metals like tungsten and cobalt.
3. What are the advantages of the electrolytic method?
The electrolytic method offers low reagent and energy consumption and is simple to implement. However, it is limited to waste with high cobalt content.
4. How does the zinc smelting method work?
The zinc smelting method involves heating waste tungsten carbide with metallic zinc to form a zinc-cobalt alloy. Zinc is then removed by distillation, leaving behind tungsten carbide and cobalt powder.
5. What role do professional manufacturers play in recycling?
Professional manufacturers use advanced technologies to ensure the quality and integrity of recycled materials. They also comply with environmental regulations to ensure safe and sustainable recycling practices.
Citations:
[1] https://www.carbide-products.com/blog/tungsten-carbide-recycling/
[2] https://www.facebook.com/p/Tungsten-carbide-scrap-and-recycle-100040548562277/
[3] https://www.retopz.com/capabilities/tungsten-carbide-recycling/
[4] https://www.sohu.com/a/364716744_528671/
[5] https://patents.google.com/patent/EP2521799A1/en
[6] https://www.dreamstime.com/photos-images/carbide-recycling.html
[7] https://dormerpramet.com/carbide-recycling
[8] https://patents.google.com/patent/TW201144221A/en
[9] https://www.itia.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/ITIA_Newsletter_2019_08.pdf
[10] https://tungstencarbide42.wordpress.com/environmental-impact-and-sustainability/
[11] https://www.sohu.com/a/150966204_489486
















