Content Menu
● Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
>> Raw Materials for Tungsten Carbide Production
● Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide Powder
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide Powder
● Challenges and Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Production
● Environmental Considerations
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is Tungsten Carbide Made Of?
>> 2. Why is Tungsten Carbide So Hard?
>> 3. What are the Main Applications of Tungsten Carbide?
>> 4. How is Tungsten Carbide Powder Manufactured?
>> 5. What are the Raw Materials Used to Produce Tungsten Carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide powder is renowned for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it a crucial material in various industrial applications, including cutting tools, wear-resistant parts, and abrasives. The production of tungsten carbide involves a complex process known as powder metallurgy, which requires precise control over raw materials and manufacturing conditions. In this article, we will delve into the details of how tungsten carbide powder is made, exploring the raw materials, manufacturing processes, and applications of this versatile material.

Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide, with the chemical formula WC, is composed of equal parts tungsten and carbon atoms. It is a fine gray powder that can be pressed and formed into shapes through sintering. Tungsten carbide has a density of about 15.6 g/cm³, significantly denser than other carbides like silicon carbide, which has a density of around 3.21 g/cm³. Its hardness is comparable to diamond, making it an excellent material for cutting tools and abrasives.
Raw Materials for Tungsten Carbide Production
The primary raw materials for producing tungsten carbide include:
- Tungsten Ore: The most widely known source of tungsten is black ore, also known as wolframite. Tungsten is extracted from this ore through a series of chemical processes.
- Ammonium Paratungstate (APT): A purified chemical compound derived from tungsten ore, serving as an intermediate in the production of tungsten metal and tungsten carbide. APT is produced by dissolving tungsten ore in a strong alkaline solution.
- Tungsten Oxide: Produced by calcinating APT at high temperatures, which is then reduced to tungsten metal powder in a hydrogen atmosphere. This process involves heating APT in a rotary kiln to produce tungsten trioxide (WO3), which is further reduced to tungsten metal.
- Carbon Sources: Such as soot or graphite, used to convert tungsten metal powder into tungsten carbide through a high-temperature carburization process. The choice of carbon source can affect the final properties of the tungsten carbide.
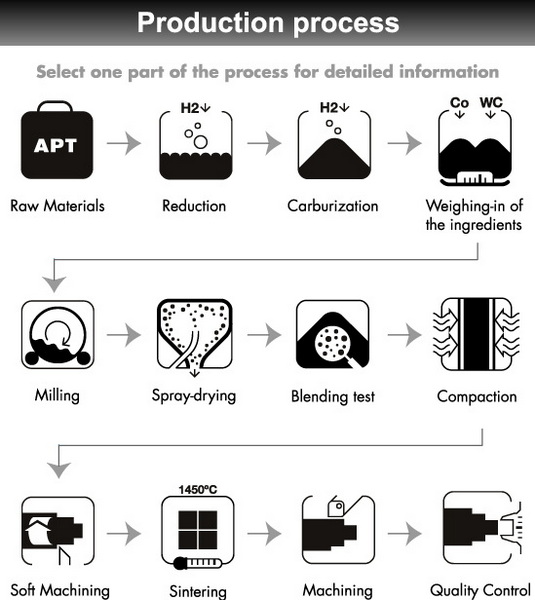
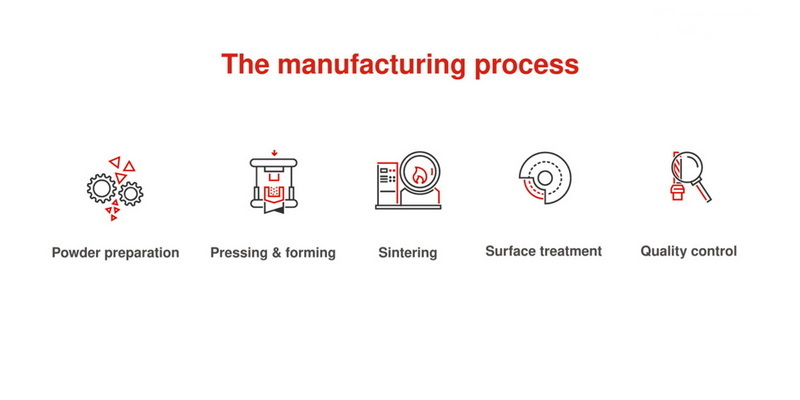
Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide Powder
The manufacturing process of tungsten carbide powder involves several key steps:
1. Material Mixing: Tungsten powder is mixed with carbon black in a ball mill for 2-4 hours to ensure uniformity. The mixture is considered uniform when no stratification is observed with the naked eye. This step is crucial to ensure that the tungsten and carbon are evenly distributed, which affects the final hardness and wear resistance of the carbide.
2. Material Carburization: The carburization of tungsten powder typically occurs in a graphite carbon tube furnace. The carburization temperature for fine tungsten powder is 1300-1350°C, while for coarse powder, it is 1600°C. The carburization time ranges from 1-2 hours. During this process, the tungsten reacts with carbon to form tungsten carbide.
3. Ball Milling: After carburization, the material is further processed in a ball mill. The duration of ball milling is determined by the specific process, usually around 2 hours. The material is then sieved under closed conditions to achieve uniform particle sizes. This step ensures that the tungsten carbide powder is fine enough for various applications.
4. Sintering: The blended powder is compacted into a desired shape and then heated around 1500°C, causing the particles to fuse and form a homogeneous and dense cemented carbide body. Cobalt is often added as a binder to improve the sintering process and enhance the mechanical properties of the final product.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten carbide powder is widely used in various industries due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Some of the key applications include:
- Cutting Tools: Tungsten carbide is used in cutting tools for machining metals due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain sharpness. It is particularly effective in high-speed machining operations.
- Wear-Resistant Parts: It is used in machinery parts that require high wear resistance, such as nozzles and drill bits. Tungsten carbide components are often used in environments where abrasive wear is a significant concern.
- Aerospace and Energy: Tungsten carbide is used in aerospace and energy industries for its high strength and resistance to corrosion. It is also used in rocket nozzles and other components that require high thermal resistance.
- Jewelry and Watchmaking: Tungsten carbide is used in making rings and other jewelry due to its durability and scratch resistance.
- Medical Applications: Tungsten carbide is used in medical implants and surgical instruments due to its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion.
Challenges and Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Production
Despite its widespread use, the production of tungsten carbide faces several challenges. One of the main challenges is the high energy consumption during the carburization and sintering processes. Additionally, the use of cobalt as a binder has raised environmental concerns due to its toxicity. To address these challenges, researchers are exploring alternative binders and more efficient production methods, such as using advanced sintering techniques like spark plasma sintering (SPS) to reduce energy consumption.
Furthermore, innovations in nanotechnology have led to the development of nanostructured tungsten carbide, which exhibits improved mechanical properties compared to conventional tungsten carbide. This advancement opens up new possibilities for applications in high-performance cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
Environmental Considerations
The production of tungsten carbide also involves environmental considerations. The extraction of tungsten ore can have environmental impacts, such as soil pollution and water contamination. Moreover, the use of cobalt as a binder poses health risks to workers involved in the manufacturing process. Efforts are being made to develop more sustainable production methods and to reduce the reliance on cobalt by exploring alternative binders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the production of tungsten carbide powder involves a sophisticated process that requires precise control over raw materials and manufacturing conditions. Its unique properties make it indispensable in various industrial applications. As industries continue to demand high-performance materials, the innovation in tungsten carbide production persists, ensuring its relevance for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Tungsten Carbide Made Of?
Tungsten carbide is made by mixing tungsten powder with carbon powder in a process called carburization. The resulting material is extremely hard and wear-resistant.
2. Why is Tungsten Carbide So Hard?
Tungsten carbide's hardness results from the unique interatomic bonding where carbon atoms fit into interstices between tungsten atoms, forming an incredibly hard and stable crystal lattice structure.
3. What are the Main Applications of Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide is primarily used in cutting tools, wear-resistant parts, and in industries such as aerospace and energy due to its high strength and resistance to corrosion.
4. How is Tungsten Carbide Powder Manufactured?
Tungsten carbide powder is manufactured through a process involving mixing tungsten and carbon powders, carburization, ball milling, and sintering to form a dense and homogeneous material.
5. What are the Raw Materials Used to Produce Tungsten Carbide?
The raw materials include tungsten ore, ammonium paratungstate (APT), tungsten oxide, and carbon sources such as soot or graphite.
Citations:
[1] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/90_how-is-tungsten-carbide-made-.html
[2] https://www.kennametal.com/us/en/products/Metal-Powders-Materials-Consumables/tungsten-carbide-powders.html
[3] https://www.kovametalli-in.com/manufacturing.html
[4] https://www.hoganas.com/en/powder-technologies/carbide-powders/
[5] https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/24896/03chapter3.pdf?sequence=4
[6] https://www.gettyimages.hk/%E5%9C%96%E7%89%87/tungsten-carbide
[7] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/process.html
[8] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Scanning-electron-microscopy-images-of-A-tungsten-carbide-powder-B-cobalt-powder-and-C_fig3_374723250
[9] https://www.bangerter.com/en/tungsten-carbide/manufacturing-process
[10] https://am-material.com/news/tungsten-carbide-powder-20231218/
















