Content Menu
● Industrial Applications of Carbide Products
● Carbide Production Process
● Market Drivers and Economic Impact
● Investment and Operational Considerations
● Environmental and Safety Measures
● Technological Innovations in Carbide Production
● Global Market Trends and Future Outlook
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What raw materials are used in carbide production?
>> 2. How does a carbide plant ensure product quality?
>> 3. What industries benefit most from carbide products?
>> 4. Can carbide production be environmentally sustainable?
>> 5. How long does carbide equipment last compared to steel tools?
● Citations:
Carbide production plants play a pivotal role in meeting the diverse needs of modern industries, from manufacturing cutting-edge tools to enabling chemical synthesis. These facilities produce critical materials like calcium carbide (CaC₂) and tungsten carbide (WC), which are indispensable in sectors such as metallurgy, construction, mining, electronics, and agriculture. By converting raw materials into high-performance compounds, carbide plants ensure the steady supply of components that drive industrial efficiency, innovation, and sustainability.

Industrial Applications of Carbide Products
Carbide materials are engineered to meet specific industrial demands due to their exceptional properties:
1. Metalworking and Tool Manufacturing
- Cutting tools: Tungsten carbide, with a Mohs hardness of 8.5–9, is widely used in drills, milling cutters, and lathe tools due to its wear resistance and ability to maintain sharpness under stress.
- Dies and molds: Carbide components enhance precision in stamping, forging, and injection molding processes, reducing downtime and improving product consistency.
2. Mining and Construction
- Drill bits and excavation tools: Carbide-tipped equipment withstands extreme abrasion in rock drilling and tunneling, extending tool life in harsh environments.
- Wear-resistant coatings: Carbide layers protect machinery parts from erosion in mining operations.
3. Chemical Production
- Acetylene synthesis: Calcium carbide reacts with water to produce acetylene gas (C₂H₂), a key feedstock for PVC, solvents, and synthetic rubber.
- Fertilizer manufacturing: Heating calcium carbide with nitrogen yields calcium cyanamide, a nitrogen-rich fertilizer.
4. Electronics and Energy
- Semiconductors: Silicon carbide (SiC) is critical for high-temperature, high-voltage electronic devices like LEDs and power inverters.
- Thermal management: Carbide materials dissipate heat efficiently in aerospace and automotive systems.
5. Steel and Metallurgy
- Desulfurization: Calcium carbide removes sulfur impurities from molten iron, improving steel quality.
- Alloy additives: Tungsten carbide enhances the hardness and durability of specialty steels.
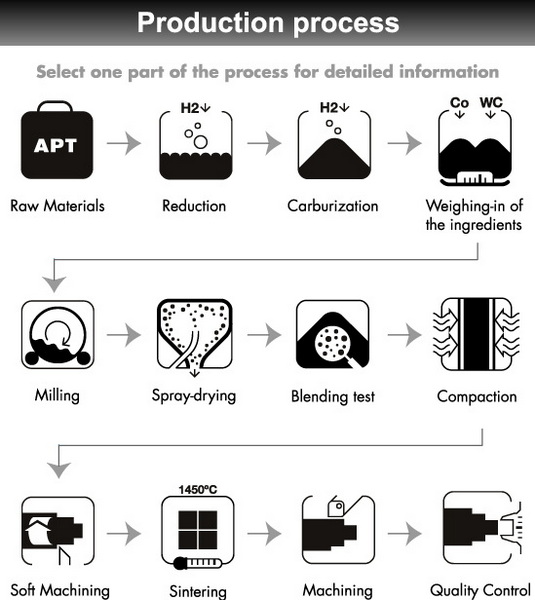
Carbide Production Process
Carbide manufacturing involves advanced techniques tailored to material type:
Calcium Carbide Production
1. Raw materials: Lime (CaO) and coke (carbon) are mixed in a 1:3 ratio.
2. Electric arc furnace: Heated to 2,200–2,400°C, the reaction `CaO + 3C → CaC₂ + CO` produces molten calcium carbide.
3. Crushing and grading: The cooled product is processed into lumps or powder for industrial use.
Tungsten Carbide Production
1. Powder metallurgy: Tungsten carbide powder is blended with cobalt binder (6–20%).
2. Compaction and sintering: The mixture is pressed into shapes and heated at 1,400–1,600°C to form dense, hard components.
Market Drivers and Economic Impact
Key factors fueling demand for carbide plants include:
- Steel industry growth: Rising global steel production (1.95 billion metric tons in 2024) necessitates calcium carbide for desulfurization and alloying.
- Infrastructure development: Mining and construction sectors require durable carbide tools for projects like tunnel boring and oil drilling.
- Electronics innovation: Silicon carbide demand grows with electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
| Sector | Carbide Application | Market Share (2025) |
| Metalworking | Cutting tools, dies | 38% |
| Mining | Drill bits, wear plates | 27% |
| Chemicals | Acetylene, PVC production | 19% |
| Electronics | Semiconductors, LEDs | 11% |
| Agriculture | Fertilizers, fruit ripening | 5% |
Investment and Operational Considerations
Establishing a carbide production plant requires strategic planning:
Capital Costs
- Equipment: Electric arc furnaces ($2M–$5M), crushers, and sintering machines.
- Facilities: Specialized infrastructure for high-temperature processes and waste management.
Operational Costs
- Energy: 3,000–4,000 kWh per ton of calcium carbide.
- Raw materials: Lime ($50–$80/ton), coke ($200–$300/ton).
ROI Analysis
- Plants achieve breakeven within 5–7 years, with profit margins of 15–25% post-commissioning.
Environmental and Safety Measures
- Waste management: Calcium hydroxide slurry from acetylene production is neutralized before disposal.
- Recycling: Tungsten carbide scrap is reclaimed to reduce mining dependency.
- Safety protocols: Automated systems monitor acetylene generation to prevent explosions.
Technological Innovations in Carbide Production
Advancements in carbide manufacturing are focused on efficiency and sustainability:
1. Energy Efficiency
- Advanced furnace designs: Improved insulation and heat recovery systems reduce energy consumption by up to 20%.
- Renewable energy integration: Solar or wind power can supplement traditional energy sources for furnace operation.
2. Material Recycling
- Closed-loop systems: Tungsten carbide scrap is recycled into new products, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Recycled content: Incorporating recycled carbide into new tools enhances their environmental profile.
3. Digitalization and Automation
- Predictive maintenance: AI-driven monitoring systems predict equipment failures, minimizing downtime.
- Quality control: Real-time monitoring ensures consistent product quality, reducing defects and waste.
Global Market Trends and Future Outlook
The global carbide market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% by 2027, driven by:
- Increasing demand for durable tools: In mining and construction, where carbide tools offer significant cost savings through extended lifespan.
- Electronics sector expansion: Silicon carbide's role in high-power electronics will continue to drive demand.
- Sustainability initiatives: Recycling and energy-efficient production methods will become more prevalent.
Conclusion
Carbide production plants are the backbone of industrial advancement, supplying materials that enable precision manufacturing, energy efficiency, and chemical innovation. By integrating advanced metallurgical processes with sustainable practices, these facilities ensure industries meet evolving demands while minimizing environmental impact. As global infrastructure and technology sectors expand, carbide plants will remain critical to maintaining competitive and resilient supply chains.

FAQs
1. What raw materials are used in carbide production?
Calcium carbide requires lime and coke, while tungsten carbide uses tungsten powder and cobalt binder. Recycled scrap is also increasingly utilized.
2. How does a carbide plant ensure product quality?
Strict control of furnace temperatures (2,200–2,400°C for CaC₂) and sintering conditions (1,400–1,600°C for WC) ensures consistent hardness and purity.
3. What industries benefit most from carbide products?
Metalworking, mining, chemicals, and electronics rely heavily on carbide components for durability and performance.
4. Can carbide production be environmentally sustainable?
Yes, through energy-efficient furnaces, slurry neutralization, and recycling programs for tungsten scrap.
5. How long does carbide equipment last compared to steel tools?
Carbide tools last 5–10 times longer than high-speed steel in abrasive applications, reducing replacement frequency.
Citations:
[1] https://enterclimate.com/calcium-carbide-manufacturing-unit-setup
[2] https://nanografi.com/blog/carbides-from-atomic-structure-to-industrial-applications-nanografi-/
[3] https://www.tjtywh.com/a-the-role-of-calcium-carbide-manufacturers-in-industrial-processes.html
[4] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/calcium-carbide.html
[5] https://www.tjtywh.com/a-the-role-of-calcium-carbide-in-industrial-applications.html
[6] https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/calcium-carbide
[7] https://www.retopz.com/57-frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-tungsten-carbide/
[8] https://www.acetylenegasplant.com/faq.php
[9] https://www.tjtywh.com/a-the-role-of-calcium-carbide-in-industrial-applications1.html
[10] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/calcium-carbide-manufacturing-plant-report-cost-model-amit-sharma-exxmc
[11] https://www.imarcgroup.com/calcium-carbide-manufacturing-plant-project-report
[12] https://www.tjtywh.com/a-the-role-of-acetylene-calcium-carbide-in-industrial-applications.html
[13] https://www.rroij.com/open-access/the-benefits-of-using-carbide-tools-in-manufacturing.php?aid=92754
[14] https://www.carbidellc.com/solutions.html
[15] https://www.manufacturingtomorrow.com/article/2019/08/5-ways-carbide-metal-compound-is-used-in-the-manufacturing-industry/13794
[16] https://www.chemanalyst.com/industry-report/calcium-carbide-market-2850
[17] https://www.gettyimages.in/photos/union-carbide-factory
[18] https://www.greenearthchem.com/important-carbide-chemicals-industrial-application.html
[19] https://www.gettyimages.in/photos/union-carbide-factory-in-bhopal
[20] https://tuncomfg.com/about/faq/
[21] https://www.sandvik.coromant.com/en-gb/services/recycling/faq-carbide-recycling
[22] https://www.mmc-carbide.com/in/technical_information/tec_guide/tec_guide_carbide
[23] https://www.istockphoto.com/photos/carbide
[24] https://www.vecteezy.com/free-photos/carbide
[25] https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/carbide/2
[26] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/frequently-asked-questions-used-tungsten-carbide-inserts/
[27] https://rexarc.com/blog/six-methods-of-carbide-lime-processing/
















