Content Menu
● The Origins of Tungsten
>> Historical Context
● The Chemical Structure of Tungsten Carbide
>> Molecular Characteristics
● The Production Process of Tungsten Carbide
>> Mining and Preparation of Tungsten Ore
>> Reduction of Tungsten Oxide
>> Carburization
>> Sintering
>> Quality Control and Finishing
● Properties of Tungsten Carbide
>> Comparison with Other Materials
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
>> Cutting Tools
>> Jewelry
>> Industrial Machinery
>> Military Applications
● Environmental Considerations
>> Mining Impact
>> Recycling Potential
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is tungsten carbide used for?
>> 2. How is tungsten carbide made?
>> 3. Where does tungsten come from?
>> 4. What are the properties of tungsten carbide?
>> 5. Why is tungsten carbide popular for jewelry?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide, a compound made from equal parts of tungsten and carbon, is renowned for its exceptional hardness and durability. This material is widely used in various applications, including industrial machinery, cutting tools, jewelry, and even armor-piercing ammunition. Understanding the origins and production processes of tungsten carbide is essential to appreciate its significance in modern technology and industry.
The Origins of Tungsten
Tungsten was discovered in 1783 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele in the form of tungsten oxide. The name "tungsten" comes from the Swedish words "tung sten," meaning "heavy stone." Tungsten is a naturally occurring element found in minerals such as wolframite and scheelite. These minerals are primarily mined in countries like China, Canada, and Portugal, where large deposits exist.
Historical Context
The history of tungsten mining dates back to the late 18th century, but it gained significant importance during World War II due to its use in military applications. The strategic importance of tungsten led to increased mining efforts and technological advancements in extraction methods.
The Chemical Structure of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide (WC) is formed when tungsten metal reacts with carbon at high temperatures, typically between 1400°C and 2000°C. This reaction creates a fine gray powder that can be further processed into various forms. The chemical formula for tungsten carbide indicates a 1:1 ratio of tungsten to carbon atoms, which contributes to its unique properties.
Molecular Characteristics
The molecular structure of tungsten carbide consists of a crystalline lattice that provides its hardness. The strong covalent bonds between tungsten and carbon atoms contribute to its exceptional strength and resistance to deformation.
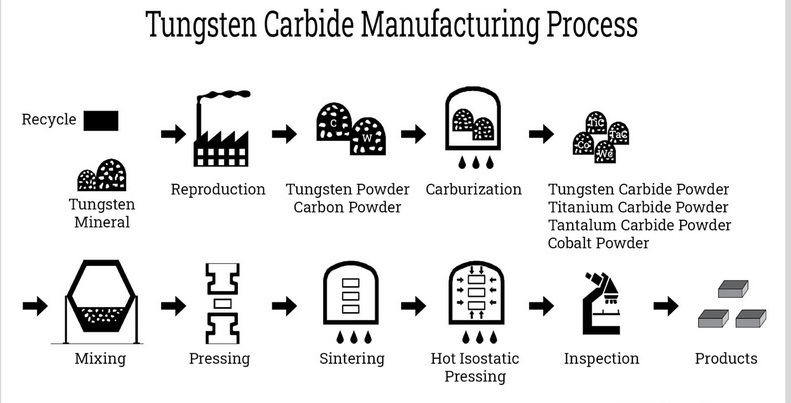
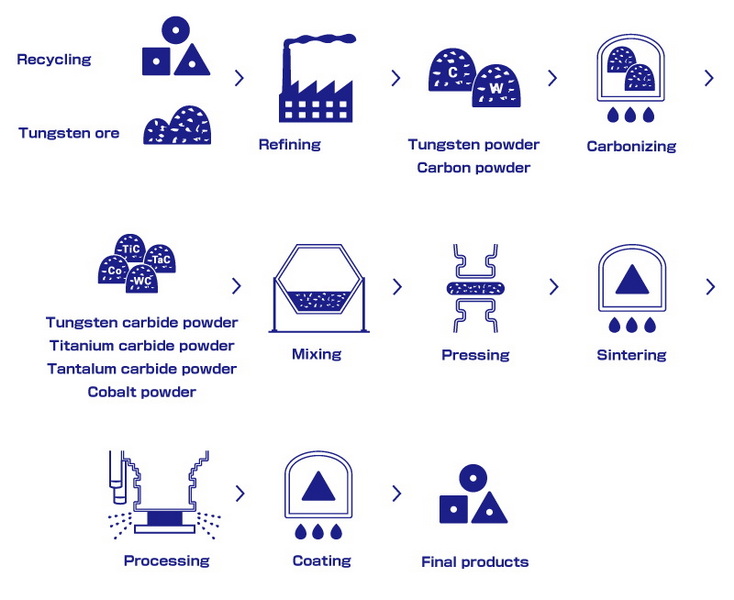
The Production Process of Tungsten Carbide
The production of tungsten carbide involves several key steps:
Mining and Preparation of Tungsten Ore
The first step in producing tungsten carbide is the extraction of tungsten from its ore. The ore is crushed and treated with chemicals to produce tungsten oxide (WO₃). This process involves several stages:
- Crushing: The ore is crushed into smaller pieces.
- Chemical Treatment: Chemicals are used to extract tungsten oxide from the crushed ore.
- Calcination: The tungsten oxide is heated to remove impurities.
Reduction of Tungsten Oxide
Once tungsten oxide is obtained, it undergoes a reduction process to produce tungsten metal. This involves heating the oxide in the presence of hydrogen or carbon, which removes the oxygen and leaves behind pure tungsten.
WO3+3H2→W+3H2O
Carburization
The next step is carburization, where pure tungsten metal is mixed with carbon at high temperatures:
- Mixing: Tungsten powder is mixed with carbon black or graphite.
- Heating: The mixture is heated in a furnace at temperatures ranging from 1400°C to 2000°C.
- Reaction: A chemical reaction occurs that combines the tungsten with carbon to form tungsten carbide.
W+C→WC
Sintering
After carburization, the tungsten carbide powder undergoes sintering:
- Pressing: The powder is pressed into desired shapes.
- Heating: The pressed shapes are heated in a furnace at around 1500°C to fuse the particles together, creating a dense material.
Quality Control and Finishing
Once sintered, the tungsten carbide products undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet industry standards. This may include testing for hardness, density, and structural integrity. After passing quality checks, the products can be ground or polished to achieve specific finishes required for their applications.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide possesses several remarkable properties:
- Hardness: It ranks between 8 and 9 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available.
- Density: It is approximately twice as dense as steel.
- Wear Resistance: Its resistance to wear makes it ideal for cutting tools and industrial applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Tungsten carbide exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion, which extends its lifespan in various environments.
Comparison with Other Materials
When compared to other hard materials like ceramics or steel alloys, tungsten carbide stands out due to its superior toughness combined with hardness. While ceramics may be harder than tungsten carbide, they are also more brittle; thus, they can fracture under stress.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it suitable for various applications:
Cutting Tools
One of the most significant uses of tungsten carbide is in cutting tools such as drills, saw blades, and milling cutters. Its hardness allows these tools to maintain sharp edges longer than those made from other materials.
Jewelry
Tungsten carbide has become increasingly popular in jewelry making, especially for wedding bands and fashion rings due to its scratch-resistant nature and modern appearance.
Industrial Machinery
In industrial settings, tungsten carbide is used for various components that require high wear resistance, such as bearings, valves, and nozzles.
Military Applications
Due to its density and hardness, tungsten carbide is employed in military applications like armor-piercing ammunition and protective gear.
Environmental Considerations
As with many industrial processes, the mining and production of tungsten carbide have environmental implications:
Mining Impact
Mining operations can lead to habitat destruction and pollution if not managed responsibly. Efforts are being made within the industry to adopt more sustainable practices.
Recycling Potential
Tungsten carbide has excellent recycling potential; worn-out tools can be recycled back into usable raw materials through specialized processes that recover both tungsten and cobalt (if present).
Conclusion
In conclusion, tungsten carbide originates from the mining of tungsten ore followed by a series of chemical processes that convert it into this incredibly durable material. Its unique combination of hardness, density, wear resistance, and versatility makes it invaluable across multiple industries—from manufacturing cutting tools to creating stylish jewelry pieces. As technology advances and industries evolve, the demand for high-performance materials like tungsten carbide will continue to grow.

FAQ
1. What is tungsten carbide used for?
Tungsten carbide is primarily used for cutting tools, industrial machinery components, jewelry (especially rings), and military applications due to its hardness and durability.
2. How is tungsten carbide made?
Tungsten carbide is made by heating tungsten metal with carbon at high temperatures (1400°C to 2000°C), followed by sintering to form a solid material.
3. Where does tungsten come from?
Tungsten comes from minerals such as wolframite and scheelite, primarily mined in countries like China, Canada, and Portugal.
4. What are the properties of tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is known for its exceptional hardness (8-9 on the Mohs scale), high density (twice that of steel), excellent wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
5. Why is tungsten carbide popular for jewelry?
Tungsten carbide is popular for jewelry because it is extremely durable and scratch-resistant compared to traditional metals like gold or silver.
Citations:
[1] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/90_how-is-tungsten-carbide-made-.html
[2] https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/tungsten-carbide
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[4] https://edu.rsc.org/magnificent-molecules/tungsten-carbide/3008556.article
[5] https://todaysmachiningworld.com/magazine/how-it-works-making-tungsten-carbide-cutting-tools/
[6] https://scienceinfo.com/tungsten-carbide-properties-applications/
[7] https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/24896/03chapter3.pdf?sequence=4
[8] https://konecarbide.com/what-is-tungsten-carbide/
[9] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wQwc5-mg4B4
















