Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Methods for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Diamond Saw Blades
>> 2. Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)
>> 3. Laser Cutting
>> 4. Abrasive Wheel Grinding
● Emergency Removal of Tungsten Carbide Rings
>> 1. Fracturing with Vice Grips
● Safety Precautions When Cutting Tungsten Carbide
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Cutting Tools
>> 2. Mining Industry
>> 3. Jewelry
>> 4. Aerospace Industry
>> 5. Medical Instruments
● Advanced Techniques in Cutting Tungsten Carbide
>> Cryogenic Treatment
>> Coatings
● Environmental Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Can tungsten carbide rings be cut off?
>> 2. What tools are best for cutting tungsten carbide?
>> 3. Is it safe to cut tungsten carbide?
>> 4. Why is tungsten carbide so hard?
>> 5. What happens if I try to cut a tungsten ring with regular tools?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is a highly durable material, often used in various industrial applications, jewelry, and cutting tools due to its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear. However, its hardness also presents challenges when it comes to cutting or machining. This article will explore the methods and considerations involved in cutting tungsten carbide, focusing on its properties, the tools required, and safety precautions.
Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a composite material made from tungsten and carbon. It is known for its incredible hardness, rated between 8.5 to 9.5 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available. This hardness makes tungsten carbide an ideal choice for manufacturing cutting tools, drill bits, and wear-resistant surfaces. However, this same property complicates cutting processes.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Hardness: Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and resistant to scratching.
- Brittleness: Despite its hardness, tungsten carbide is brittle. This means that while it can withstand high pressure and wear, it can crack or shatter under certain conditions.
- Heat Resistance: Tungsten carbide maintains its properties at high temperatures but can be affected by excessive heat during cutting.
Methods for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
Cutting tungsten carbide requires specialized tools and techniques due to its hardness and brittleness. Here are some of the most effective methods:
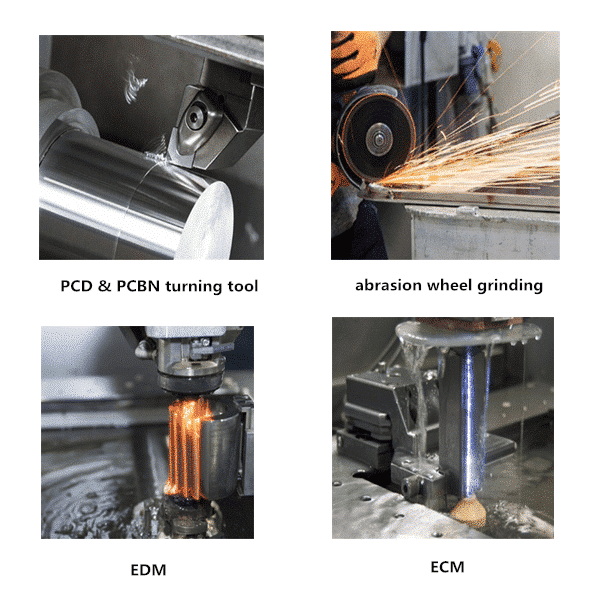
1. Diamond Saw Blades
Using diamond-coated saw blades is one of the most common methods for cutting tungsten carbide. These blades are designed to handle the material's hardness effectively.
- Advantages:
- High precision.
- Suitable for various shapes and sizes.
- Disadvantages:
- Can generate significant heat.
- Requires careful handling to avoid damaging the blade or workpiece.
2. Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM utilizes electrical discharges to remove material from the workpiece. This method is particularly useful for complex shapes and high precision.
- Advantages:
- Can achieve intricate designs.
- Does not apply mechanical force that could fracture the material.
- Disadvantages:
- Slower process compared to traditional cutting methods.
- Requires specialized equipment.
3. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is another effective technique for tungsten carbide. It uses a focused laser beam to melt or vaporize the material.
- Advantages:
- High precision with minimal material waste.
- Non-contact method reduces mechanical stress on the material.
- Disadvantages:
- Equipment can be expensive.
- Not suitable for all thicknesses of tungsten carbide.
4. Abrasive Wheel Grinding
This method involves using abrasive wheels that are often diamond-coated to grind away material gradually.
- Advantages:
- Effective for achieving smooth finishes.
- Versatile for various applications.
- Disadvantages:
- Slower than other methods.
- Requires cooling systems to manage heat buildup.

Emergency Removal of Tungsten Carbide Rings
One common concern with tungsten carbide jewelry, such as wedding bands, is their removal in emergencies (e.g., finger swelling). While these rings cannot be cut off easily due to their hardness, they can be safely removed using specific techniques:
1. Fracturing with Vice Grips
In emergencies, tungsten carbide rings can be fractured rather than cut off. This method involves using locking pliers (vice grips) to apply pressure until the ring breaks apart.
- Procedure:
- Place vice grips around the ring.
- Gradually tighten until a crack is heard.
This method is effective because it leverages the brittleness of tungsten carbide, allowing it to break instead of being cut through.
Safety Precautions When Cutting Tungsten Carbide
Cutting tungsten carbide poses several risks due to the nature of the material and the tools used. Here are essential safety precautions:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask to protect against debris and fine particles generated during cutting.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation when working with tungsten carbide to avoid inhaling harmful particles.
- Tool Handling: Use tools specifically designed for cutting tungsten carbide to prevent accidents and ensure efficiency.
- Heat Management: Monitor heat buildup during cutting processes; overheating can damage both the workpiece and cutting tools.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it invaluable across various industries. Its applications include:
1. Cutting Tools
Tungsten carbide is widely used in manufacturing cutting tools such as drill bits, end mills, saw blades, and lathe tools due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. These tools are crucial in metalworking, mining, and construction industries where durability is essential.
2. Mining Industry
In mining applications, tungsten carbide is integral for rock drilling tools, crusher components, and tunnel boring machines. Its ability to withstand harsh conditions makes it ideal for these demanding environments.
3. Jewelry
The jewelry industry has embraced tungsten carbide for wedding bands and other accessories due to its scratch resistance and durability compared to traditional metals like gold or silver.
4. Aerospace Industry
Tungsten carbide components are utilized in aerospace applications where reliability under extreme conditions is critical. This includes parts such as turbine blades that require high strength-to-weight ratios.
5. Medical Instruments
In medical applications, tungsten carbide's hardness allows for precise surgical instruments that maintain sharp edges longer than conventional materials.
Advanced Techniques in Cutting Tungsten Carbide
As technology evolves, so do methods for cutting tungsten carbide more efficiently:
Cryogenic Treatment
Recent advancements have introduced cryogenic treatment as a means of enhancing tungsten carbide's properties before machining. This process involves cooling the material to extremely low temperatures (-196°C) which alters its microstructure and improves wear resistance significantly[2].
Coatings
Applying advanced coatings like titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN) enhances the performance of tungsten carbide tools by increasing their thermal stability and prolonging tool life[24]. These coatings help reduce friction during machining processes while maintaining sharpness longer than uncoated counterparts.
Environmental Considerations
The production of tungsten carbide involves significant energy consumption; however, recycling efforts are gaining traction as about thirty percent of global tungsten supply comes from recycled sources[11]. This not only helps reduce waste but also mitigates some environmental impacts associated with mining new materials.
Conclusion
Cutting tungsten carbide is a complex process that requires specialized knowledge and tools due to its extreme hardness and brittleness. While various methods exist—from diamond saw blades to electric discharge machining—each has its advantages and drawbacks depending on the application at hand. In emergency situations involving tungsten carbide rings, fracturing rather than cutting may be necessary for safe removal. Understanding these methods and adhering to safety precautions will ensure effective handling of this challenging material.

FAQ
1. Can tungsten carbide rings be cut off?
No, tungsten carbide rings cannot be easily cut off due to their hardness; they are typically fractured using vice grips in emergencies.
2. What tools are best for cutting tungsten carbide?
Diamond saw blades, electric discharge machining (EDM), laser cutters, and abrasive wheel grinders are all effective for cutting tungsten carbide.
3. Is it safe to cut tungsten carbide?
Yes, but proper safety precautions must be taken, including wearing protective gear and ensuring adequate ventilation.
4. Why is tungsten carbide so hard?
Tungsten carbide's hardness comes from its composite nature; it combines tungsten with carbon atoms in a tightly bonded structure.
5. What happens if I try to cut a tungsten ring with regular tools?
Using regular tools may not only be ineffective but could also lead to injury or damage; specialized tools are necessary for safe cutting.
Citations:
[1] https://www.samaterials.com/content/application-of-tungsten-in-modern-industry.html
[2] https://ctpcryogenics.com/services/industrial/carbide/
[3] https://kindle-tech.com/faqs/what-is-a-substitute-for-tungsten-carbide
[4] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/features.html
[5] https://shop.machinemfg.com/how-to-cut-tungsten-carbide-rods-an-overview/
[6] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/five-tungsten-carbide-application-linda-tian
[7] https://monaghantooling.com/case-studies/solid-carbide-tooling-case-studies/
[8] https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/tungsten-carbide
[9] https://eurobalt.net/blog/2022/03/28/all-the-applications-of-tungsten-carbide/
[10] https://www.grinding.com/en/news-media/media-library/case-studies/ceratizit-tools-case-study/
[11] https://www.tungstenringsco.com/blog/2013/03/finding-alternative-sources-of-tungsten/
[12] https://carbideprocessors.com/pages/carbide-parts/tungsten-carbide-properties.html
[13] https://www.finescience.com/en-US/Products/Scissors/Standard-Scissors/Fine-Scissors-Tungsten-Carbide
[14] https://www.carbide-usa.com/top-5-uses-for-tungsten-carbide/
[15] https://www.synova.ch/images/Case%20Studies/Tools/TOOL04_Case_Study_-_PCD_and_CBN_tools.pdf
[16] https://naeco.net/tungsten-hm-2/
[17] https://www.makeitfrom.com/material-properties/Tungsten-Carbide-WC
[18] https://www.kennametal.com/us/en/resources/blog/metal-cutting/tungsten-carbide-versus-cobalt-drill-bits.html
[19] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[20] https://www.reddit.com/r/toolgifs/comments/17sgnz3/a_tungsten_carbide_tool_cutting_metal_under_a/
[21] https://www.eng-tips.com/threads/tungsten-amp-tungsten-carbide-alternatives.234870/
[22] https://www.azom.com/properties.aspx?ArticleID=1203
[23] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LxvVUvUBqag
[24] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[25]https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275016929_Selective_Laser_Sintering_A_Case_Study_of_Tungsten_Carbide_and_Cobalt_Powder_Sintering_by_Pulsed_NdYAG_Laser
[26] https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=17807
[27] https://www.imetra.com/tungsten-carbide-material-properties/
[28] https://www.techmet-carbide.com/techmet/saw-tips
[29] https://www.itia.info/applications-markets/
[30] https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/09544089241288939
[31] https://www.coorstek.com/en/materials/tungsten-carbide/
[32] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/use.html
[33] https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/manufacturingscience/article/93/4/1106/392931/Oxide-Treatment-of-Tungsten-Carbide-Tools-and-Its
[34] https://www.reddit.com/r/worldbuilding/comments/apwh29/alternative_sword_materials/
[35] https://www.kennametal.com/us/en/resources/blog/metal-cutting/selecting-carbide-inserts-for-metalworking.html
















