Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Will Tungsten Carbide Tarnish?
>> Jewelry-Grade vs. Industrial-Grade Tungsten Carbide
● Factors Influencing Tarnishing
● Caring for Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Regular Cleaning:
>> 2. Avoid Harsh Chemicals:
>> 3. Storage:
>> 4. Inspection:
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
● Comparison with Other Materials
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Can all tungsten carbide tarnish?
>> 2. How do I clean my tungsten carbide ring?
>> 3. Is it safe to wear tungsten carbide rings while swimming?
>> 4. What should I avoid when caring for my tungsten carbide jewelry?
>> 5. How can I tell if my tungsten ring is high quality?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is a popular material known for its exceptional hardness and durability. It is widely used in various applications, including jewelry, cutting tools, and industrial machinery. However, many people wonder whether tungsten carbide can tarnish or rust over time. This article will explore the properties of tungsten carbide, the factors that influence its tarnishing potential, and how to care for tungsten carbide items to maintain their appearance.

Understanding Tungsten Carbide
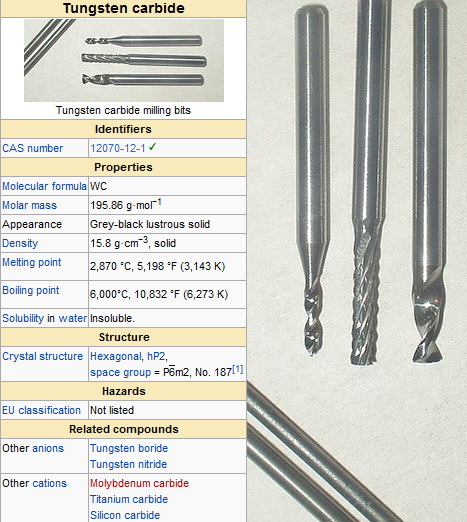
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a chemical compound composed of equal parts tungsten and carbon atoms. It is known for its remarkable hardness, ranking between 8.5 and 9 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond. Tungsten carbide is often used in various applications due to its high resistance to wear and corrosion, making it an ideal choice for cutting tools and industrial components.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Hardness: Tungsten carbide is extremely hard, making it resistant to scratches and wear.
- Density: It has a high density, which contributes to its durability.
- Chemical Inertness: Tungsten carbide is chemically inert under normal conditions, meaning it does not easily react with other substances.
- High Melting Point: It has a melting point of approximately 2,870 °C (5,200 °F), which allows it to maintain its integrity under extreme heat.
- Impact Resistance: Tungsten carbide exhibits high impact resistance due to its rigidity.
- Thermal Conductivity: It has thermal conductivity that is significantly higher than that of steel.
Will Tungsten Carbide Tarnish?
The short answer is that high-quality tungsten carbide does not tarnish under normal conditions. However, there are important distinctions between different grades of tungsten carbide that can affect its tarnishing potential.
Jewelry-Grade vs. Industrial-Grade Tungsten Carbide
1. Jewelry-Grade Tungsten Carbide:
- Typically mixed with a nickel binder.
- Chemically inert and resistant to oxidation.
- Will not rust or tarnish under normal wear conditions.
2. Industrial-Grade Tungsten Carbide:
- Often contains cobalt as a binder.
- More susceptible to oxidation and corrosion when exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals.
- May develop discoloration or tarnish over time.
Factors Influencing Tarnishing
Several factors can contribute to the tarnishing of tungsten carbide:
- Environmental Exposure: Prolonged exposure to moisture, humidity, or chemicals (such as bleach or chlorine) can lead to tarnishing.
- Quality of Material: The grade of tungsten carbide plays a significant role in its resistance to tarnishing. Higher-quality jewelry-grade tungsten carbide is less likely to tarnish compared to lower-grade industrial options.
- Alloy Composition: The presence of binders such as cobalt can increase the likelihood of oxidation and discoloration.
Caring for Tungsten Carbide
To maintain the appearance of tungsten carbide items, especially jewelry, proper care is essential:
1. Regular Cleaning:
- Use mild soap and warm water for cleaning.
- Soak the item for about 15 minutes and gently scrub with a soft brush if needed.
2. Avoid Harsh Chemicals:
- Keep tungsten carbide away from harsh cleaning agents such as bleach or ammonia.
- Remove rings before engaging in activities that may expose them to chemicals (e.g., swimming pools).
3. Storage:
- Store tungsten carbide items in a soft pouch or box when not in use to prevent scratches and exposure to moisture.
4. Inspection:
- Regularly inspect your tungsten carbide items for any signs of discoloration or damage.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it suitable for various applications beyond jewelry:
- Cutting Tools: Widely used in manufacturing due to its hardness and wear resistance.
- Mining Equipment: Utilized in drill bits and other tools that require extreme durability.
- Ammunition: Employed in armor-piercing projectiles due to its density and hardness.
- Construction Tools: Used in saw blades and drill bits designed for tough materials like concrete and asphalt.
Comparison with Other Materials
When comparing tungsten carbide with other materials such as titanium carbide or steel, several key differences emerge:
| Property | Tungsten Carbide | Titanium Carbide | Steel |
| Hardness | 8.5 - 9 | 9 - 9.5 | 4 - 8 |
| Density | High | Lower than WC | Lower |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Very Good | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher | Lower |
This table illustrates that while tungsten carbide offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, titanium carbide may provide slightly better hardness at a higher cost. Steel remains a more economical option but lacks the durability found in both types of carbide.
Conclusion
In summary, high-quality tungsten carbide does not tarnish under normal conditions due to its chemical inertness and durability. However, lower-grade industrial tungsten carbide may be more susceptible to tarnishing due to the presence of cobalt binders. By taking proper care of your tungsten carbide items through regular cleaning and avoiding harsh chemicals, you can ensure they maintain their shine and integrity over time.

FAQ
1. Can all tungsten carbide tarnish?
Not all tungsten carbide tarnishes; jewelry-grade tungsten carbide mixed with nickel will not tarnish, while industrial-grade with cobalt may tarnish over time.
2. How do I clean my tungsten carbide ring?
Clean your tungsten carbide ring with mild soap and warm water; soak it for 15 minutes and gently scrub with a soft brush if necessary.
3. Is it safe to wear tungsten carbide rings while swimming?
It's best to remove tungsten carbide rings before swimming in chlorinated pools as chlorine can cause discoloration over time.
4. What should I avoid when caring for my tungsten carbide jewelry?
Avoid using harsh chemicals like bleach or ammonia when cleaning your tungsten carbide jewelry as they can lead to tarnishing.
5. How can I tell if my tungsten ring is high quality?
High-quality tungsten rings are usually made from jewelry-grade tungsten carbide with nickel binders; they should come with warranties from reputable jewelers.
Citations:
[1] https://carbideprocessors.com/pages/carbide-parts/tungsten-carbide-properties.html
[2] https://theringshop.com/pages/tungsten-carbide-care
[3] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/79_tungsten-carbide-vs-titanium-carbide.html
[4] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[5] https://tymbergear.com/blogs/news/maintaining-your-tungsten-ring-easy-care-tips
[6] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/why-use-tungsten-carbide-over-other-metals/
[7] https://www.carbide-usa.com/top-5-uses-for-tungsten-carbide/
[8] https://www.larsonjewelers.com/pages/how-to-clean-tungsten-rings-in-5-easy-steps
[9] https://www.syalons.com/2024/07/08/silicon-carbide-vs-tungsten-carbide-wear-applications/
[10] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/features.html
[11] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[12] https://www.larsonjewelers.com/pages/how-to-properly-clean-and-care-for-your-tungsten-ring
[13] https://forums.tripwireinteractive.com/index.php
[14] https://www.sollex.se/en/blog/post/about-cemented-tungsten-carbide-applications-part-1
[15] https://www.bluenile.com/education/metal/tungsten
[16] https://urbandesigner.co/blogs/news/how-to-clean-tungsten-rings-a-step-by-step-guide
[17] https://www.gwstoolgroup.com/understanding-the-different-types-of-carbide-in-cutting-tools/
















