Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
>> Applications of Tungsten Carbide
● Methods for Identifying Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Visual Inspection
>> 2. Weight Test
>> 3. Magnet Test
>> 4. Scratch Test
>> 5. Spark Test
● Practical Tips for Identification
● Common Misconceptions About Tungsten Carbide
● Environmental Impact and Recycling of Tungsten Carbide
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What is tungsten carbide used for?
>> 2. How can I tell if my jewelry is made from tungsten carbide?
>> 3. Is tungsten carbide magnetic?
>> 4. Can I recycle tungsten carbide?
>> 5. What are common markings found on tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is a highly durable and dense material commonly used in various industrial applications, including cutting tools, jewelry, and wear-resistant parts. Identifying tungsten carbide can be essential for recycling, manufacturing, and quality control processes. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to identify tungsten carbide, covering its properties, identification methods, practical tips, and applications.
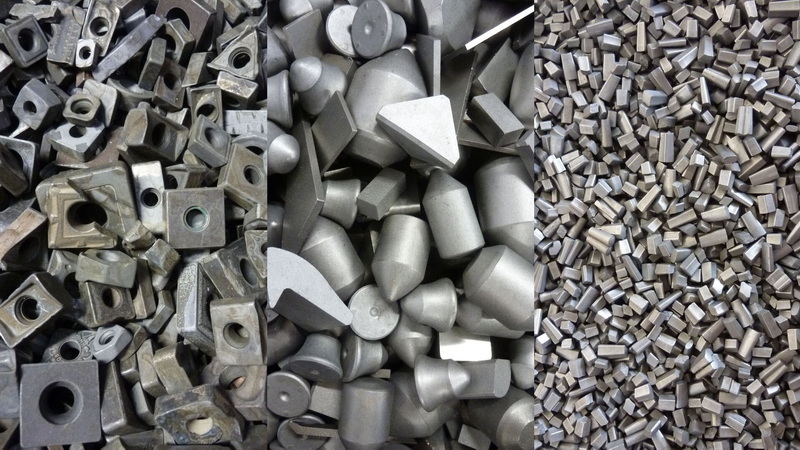

Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a chemical compound composed of equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. It is known for its remarkable hardness, ranking between 9 and 9.5 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available. Tungsten carbide is approximately three times as stiff as steel and is significantly denser, with a density of about 15.63 g/cm³, which is higher than that of steel and aluminum.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Density: Tungsten carbide is exceptionally dense, making it feel heavier than most metals.
- Hardness: It exhibits extreme hardness and can scratch glass easily.
- Color: Typically has a grayish metallic appearance.
- Non-Magnetic: Unlike ferrous metals, tungsten carbide is not magnetic.
- Durability: Resistant to scratching and wear, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it suitable for various applications:
- Cutting Tools: Widely used in the manufacturing of drill bits, end mills, and saw blades due to its hardness and wear resistance.
- Jewelry: Increasingly popular in rings and watches because of its scratch resistance and modern aesthetic.
- Industrial Machinery: Utilized in parts that require high durability and resistance to wear.
- Mining and Drilling: Employed in mining tools like rock drills due to its ability to withstand extreme conditions.
Methods for Identifying Tungsten Carbide
Identifying tungsten carbide can be done through several practical tests. Here are the most effective methods:
1. Visual Inspection
Begin with a visual inspection of the material:
- Color and Appearance: Look for a grayish metallic color typical of tungsten carbide. Cemented carbide may appear darker or black.
- Texture: Check for any textured surfaces that may indicate the presence of cobalt or other binding agents.
2. Weight Test
Tungsten carbide is significantly heavier than most metals:
- Comparison: Hold the material in your hand. If it feels unusually heavy compared to steel or aluminum pieces of similar size, it may be tungsten carbide.
3. Magnet Test
Conducting a magnet test can help differentiate tungsten carbide from ferrous metals:
- Procedure: Bring a magnet close to the material. If the magnet does not attract the material strongly (or at all), it is likely tungsten carbide since it is non-magnetic.
4. Scratch Test
The hardness of tungsten carbide allows it to scratch softer materials:
- Testing: Use a known piece of tungsten carbide to scratch the surface of the material in question. If it leaves little to no mark, it is likely tungsten carbide.
5. Spark Test
When ground against a high-speed wheel, tungsten carbide produces distinct sparks:
- Observation: Grind the material against a wheel and observe the sparks. Tungsten carbide emits short, dark-red sparks compared to bright white sparks from steel.
Practical Tips for Identification
- Always conduct multiple tests to confirm your findings.
- Be aware that some carbides may contain other metals that can affect their magnetic properties.
- Keep in mind that rust or corrosion indicates that the material is not tungsten carbide.
Common Misconceptions About Tungsten Carbide
Despite its popularity, there are several misconceptions surrounding tungsten carbide that are important to clarify:
- Misconception 1: Tungsten Carbide Is Indestructible
While tungsten carbide is extremely hard, it is not indestructible. It can chip or break under extreme impact or stress conditions.
- Misconception 2: All Tungsten Carbide Is Created Equal
There are different grades of tungsten carbide depending on its composition and intended use. Higher grades contain more tungsten content and are more durable.
- Misconception 3: Tungsten Carbide Jewelry Cannot Be Resized
While resizing tungsten carbide rings can be challenging due to their hardness, it is not impossible; specialized equipment must be used by professionals.
Environmental Impact and Recycling of Tungsten Carbide
Recycling tungsten carbide is both environmentally beneficial and economically advantageous due to its high value:
- Recycling Process: The recycling process involves collecting scrap materials from manufacturing processes or worn-out tools and then processing them to recover tungsten for reuse.
- Environmental Benefits: Recycling reduces waste in landfills and conserves natural resources by minimizing the need for new raw materials.
Conclusion
Identifying tungsten carbide requires a combination of visual inspection and practical tests such as weight, magnetism, scratching ability, spark characteristics, and advanced methods like XRF analysis. By familiarizing yourself with these methods and understanding common misconceptions surrounding this valuable material, you can confidently determine whether a piece of scrap or tool is made from tungsten carbide. Its unique properties make it indispensable across various industries while also presenting opportunities for sustainable practices through recycling.

FAQs
1. What is tungsten carbide used for?
Tungsten carbide is commonly used in cutting tools, industrial machinery parts, jewelry, and wear-resistant applications due to its hardness and durability.
2. How can I tell if my jewelry is made from tungsten carbide?
You can perform a weight test (it should feel heavier than similar-sized pieces), check for scratches (it should not scratch easily), and look for rust (tungsten carbide does not rust).
3. Is tungsten carbide magnetic?
No, tungsten carbide is generally non-magnetic; however, some binding agents used in its production may exhibit slight magnetic properties.
4. Can I recycle tungsten carbide?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled effectively due to its valuable composition; proper identification ensures efficient recycling processes.
5. What are common markings found on tungsten carbide?
Markings may include "WC" or "TC," indicating tungsten carbide content along with manufacturer codes or logos that provide information about its grade.
Citations:
[1] https://carbidescrapbuyers.com/carbide-scrap-identification/
[2] https://bansalcarbidebuyer.com/identify-carbide-scrap/
[3] https://www.carbide-usa.com/tungsten-carbide-testing-resources/
[4] https://www.thermalspray.com/how-to-distinguish-real-tungsten-carbide-from-fakes/
[5] https://www.gardnermetals.com/what-is-tungsten-carbide/
[6] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[7] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FuZ_vvgGOs4
[8] https://completecarbide.com/how-to-identify-carbide-scraps-from-other-metals/
[9] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cT1uKBo8lSA
[10] https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21205
[11] https://www.basiccarbide.com/tungsten-carbide-grade-chart/
[12] https://www.generalcarbide.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/GeneralCarbide-Designers_Guide_TungstenCarbide.pdf
[13] https://www.canadiancim.com/post/design-a-stunning-blog
[14] http://news.chinatungsten.com/en/tungsten-news/smart-glass/46-tungsten-news-en/tungsten-information/12980-ti-524.html
[15] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358849072_Crack_Identification_in_Tungsten_Carbide_Using_Image_Processing_Techniques
[16] https://www.shutterstock.com/search/tungsten-metal
















