Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Tools Required for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
● Step-by-Step Guide to Cutting Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Preparation
>> 2. Marking the Material
>> 3. Securing the Material
>> 4. Cutting Techniques
>> 5. Cooling During Cutting
>> 6. Finishing Touches
● Advanced Techniques for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
>> Laser Cutting
>> Water Jet Cutting
>> Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
● Safety Precautions
● Common Challenges When Cutting Tungsten Carbide
>> Tool Wear
>> Cracking
>> Dust Management
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is tungsten carbide used for?
>> 2. Can I cut tungsten carbide at home?
>> 3. What are the best tools for cutting tungsten carbide?
>> 4. Is it safe to cut tungsten carbide without protective gear?
>> 5. How do I maintain my cutting tools when working with tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is a highly durable material known for its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, making it a popular choice in various industrial applications, including cutting tools, jewelry, and machinery parts. However, its toughness also makes it challenging to cut. This article will guide you through the methods, tools, and safety precautions necessary for effectively cutting tungsten carbide.
Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a composite material made from tungsten and carbon atoms. It typically ranks between 8.5 to 9.5 on the Mohs hardness scale, which indicates its superior hardness compared to most metals. Due to this hardness, tungsten carbide is often used in applications that require high wear resistance.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Hardness: As one of the hardest materials available, tungsten carbide can withstand significant wear and tear.
- Density: It has a high density, making it heavy and robust.
- Corrosion Resistance: Tungsten carbide is resistant to corrosion and oxidation, which enhances its durability in harsh environments.
- Brittleness: Despite its hardness, tungsten carbide can be brittle under certain conditions, necessitating careful handling during cutting.
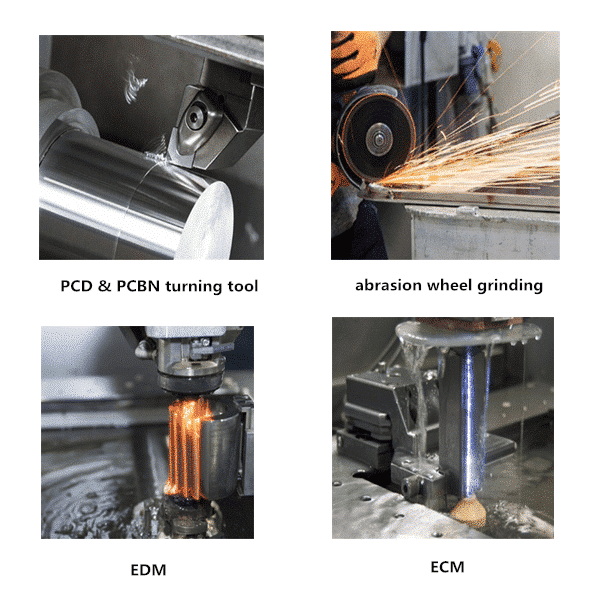
Tools Required for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
When cutting tungsten carbide, using the right tools is crucial for achieving clean cuts and maintaining tool integrity. Here are some commonly used tools:
- Diamond Saw Blades: These blades are specifically designed for cutting hard materials like tungsten carbide. They provide precision and durability.
- Carbide-Tipped Tools: These tools can handle the toughness of tungsten carbide and are suitable for rough cuts.
- Dremel Tool with Diamond Wheel: Ideal for small-scale or intricate tasks, providing control and precision.
- Angle Grinders with Diamond Grinding Wheels: Useful for shaping and cutting larger pieces of tungsten carbide.
- Electric Discharge Machining (EDM): A high-precision method that uses electrical discharges to cut through the material.
- Laser Cutters: For non-contact cutting that allows intricate shapes without damaging the material.
Step-by-Step Guide to Cutting Tungsten Carbide
1. Preparation
Before you begin cutting, ensure you have the necessary safety equipment:
- Safety Glasses: To protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Gloves: To prevent cuts and abrasions.
- Dust Mask: To avoid inhaling fine particles generated during cutting.
2. Marking the Material
Accurate marking is essential for precise cuts:
- Use a high-quality marker or scribe to outline the area where you intend to cut. Consider using a caliper for more precise measurements if needed.
3. Securing the Material
Stability during cutting is crucial:
- Secure the tungsten carbide rod or piece in a vise or clamp to prevent movement during the cutting process. Ensure that it is firmly held but not overly tightened, as this could lead to cracking.
4. Cutting Techniques
Depending on your specific needs, choose one of the following methods:
- Using Diamond Saw Blades:
- Set up your saw with a diamond blade.
- Apply moderate pressure while cutting; excessive force can cause cracking.
- Maintain a steady speed and avoid abrupt movements to ensure a clean cut.
- Dremel Tool Method:
- Attach a diamond wheel to your Dremel tool.
- Cut slowly along the marked line for precision.
- Use short bursts of power rather than continuous pressure to avoid overheating.
- Angle Grinder Method:
- Equip an angle grinder with a diamond grinding wheel.
- Ensure proper alignment and apply consistent pressure while moving along the cut line.
- Keep the grinder at a slight angle to reduce friction and heat buildup.
5. Cooling During Cutting
To prevent overheating:
- Use a coolant system (like clean water or specialized coolant) to dissipate heat during cutting. Applying coolant not only prolongs tool life but also reduces the risk of damaging the workpiece.
6. Finishing Touches
After cutting:
- Use abrasion wheels for grinding and smoothing edges. This step is essential if you need a polished finish or if there are any sharp edges left after cutting.

Advanced Techniques for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
For those looking to achieve even more precision or tackle complex shapes, consider these advanced techniques:
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting provides a non-contact method that can handle intricate designs without compromising the integrity of the material. This method is particularly beneficial when working with thin sheets of tungsten carbide or when high precision is required.
Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through materials without generating heat that can alter their properties. This method is ideal for thick pieces of tungsten carbide where traditional methods may struggle.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM is an advanced technique that uses electrical discharges (sparks) to remove material from conductive workpieces. This method allows for extremely precise cuts and is often used in manufacturing complex shapes or components that require tight tolerances.
Safety Precautions
Cutting tungsten carbide generates fine particles and debris that can be hazardous:
- Always work in a well-ventilated area.
- Ensure all safety gear is worn properly before starting any cutting operation.
Common Challenges When Cutting Tungsten Carbide
While cutting tungsten carbide can be accomplished successfully with proper techniques, several challenges may arise:
Tool Wear
Due to its hardness, tools can wear down quickly when cutting tungsten carbide. Regularly inspect your blades and wheels for signs of wear and replace them as necessary to maintain efficiency.
Cracking
Tungsten carbide can crack if subjected to excessive force or rapid temperature changes. Always apply steady pressure and use cooling methods when necessary.
Dust Management
The fine dust generated during cutting can pose health risks if inhaled. Using appropriate dust extraction systems or working in well-ventilated areas can mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
Cutting tungsten carbide requires specialized techniques and tools due to its extreme hardness and brittleness. By following proper procedures, utilizing appropriate tools, and adhering to safety guidelines, you can achieve clean cuts while minimizing risks associated with this challenging material. Whether you're working on industrial applications or crafting jewelry, understanding how to effectively cut tungsten carbide will enhance your skills and ensure successful outcomes in your projects.

FAQ
1. What is tungsten carbide used for?
Tungsten carbide is commonly used in industrial applications such as cutting tools, mining machinery, jewelry (like rings), and wear-resistant parts due to its hardness and durability.
2. Can I cut tungsten carbide at home?
Yes, you can cut tungsten carbide at home using appropriate tools like diamond blades or Dremel tools; however, ensure you follow safety precautions.
3. What are the best tools for cutting tungsten carbide?
The best tools include diamond saw blades, angle grinders with diamond wheels, Dremel tools with diamond wheels, electric discharge machining (EDM) setups, and laser cutters.
4. Is it safe to cut tungsten carbide without protective gear?
No, it is not safe. Always wear safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask when cutting tungsten carbide to protect against flying debris and inhalation of particles.
5. How do I maintain my cutting tools when working with tungsten carbide?
Ensure your cutting tools are equipped with diamond blades or tips designed for hard materials. Regularly cool them during use to prevent overheating and check for wear after each use.
Citations:
[1] https://shop.machinemfg.com/how-to-cut-tungsten-carbide-rods-an-overview/
[2] https://www.ideal-tek.com/catalogue/1/cutters-and-pliers/tungsten-carbide-cutters
[3] http://www.titaniumkay.com/tungsten-rings/can-you-cut-a-tungsten-carbide-ring/
[4] https://tuncomfg.com/engineered-solutions/cutting-solutions/
[5] https://www.reddit.com/r/metalworking/comments/1e9xttj/cutting_tungsten/
[6] https://www.gwstoolgroup.com/understanding-the-different-types-of-carbide-in-cutting-tools/
[7] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zk3ZiVOvwFg
[8] https://www.lindstromtools.com/us_en/tungsten-carbide-cutter
















