Content Menu
● Introduction to Bearings
● What is Tungsten Carbide?
● Advantages of Tungsten Carbide Ball Bearings
>> 1. Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
>> 2. High Temperature Resistance
>> 3. Corrosion Resistance
>> 4. Reduced Friction
>> 5. Longevity and Reliability
● Disadvantages of Tungsten Carbide Ball Bearings
>> 1. Higher Initial Cost
>> 2. Brittleness
>> 3. Limited Availability
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide Ball Bearings
● Comparison with Traditional Steel Bearings
>> Performance
>> Cost
>> Availability
● Conclusion
● Related Questions
>> 1. What are the specific applications where tungsten carbide bearings excel?
>> 2. How does the cost of tungsten carbide bearings compare to steel bearings?
>> 3. What are the maintenance requirements for each type of bearing?
>> 4. Can tungsten carbide bearings be used in all environments?
>> 5. How do I choose between tungsten carbide and steel bearings for my application?
Tungsten carbide ball bearings have gained significant attention in various industries due to their unique properties and advantages over traditional steel bearings. This article explores the differences between tungsten carbide and steel bearings, their applications, benefits, and limitations, providing a comprehensive understanding of why one might choose tungsten carbide over steel.

Introduction to Bearings
Bearings are crucial components in machinery, allowing for smooth rotation and reducing friction between moving parts. They come in various materials, with steel being the most common due to its strength and durability. However, advancements in materials science have introduced alternatives like tungsten carbide, which offer enhanced performance in specific applications.
What is Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide is a composite material made from tungsten and carbon atoms. It is known for its exceptional hardness, high wear resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. These properties make tungsten carbide an ideal choice for applications where traditional materials may fail.
Advantages of Tungsten Carbide Ball Bearings
1. Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of tungsten carbide ball bearings is their hardness. Tungsten carbide is nearly four times harder than steel, which means it can withstand greater loads and resist wear over time. This property is particularly beneficial in high-load applications, such as in heavy machinery and aerospace components.
2. High Temperature Resistance
Tungsten carbide can maintain its structural integrity at higher temperatures compared to steel. This makes it suitable for applications in environments where heat is a concern, such as in automotive engines or industrial machinery that generates significant heat during operation.
3. Corrosion Resistance
While steel bearings can rust and corrode over time, tungsten carbide is more resistant to chemical corrosion. This property is essential in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications, where exposure to moisture and chemicals is common.
4. Reduced Friction
Tungsten carbide bearings can provide lower friction coefficients than steel bearings, leading to improved efficiency in machinery. This reduction in friction can result in lower energy consumption and extended equipment life.
5. Longevity and Reliability
Due to their hardness and resistance to wear, tungsten carbide bearings often have a longer lifespan than their steel counterparts. This longevity translates to reduced maintenance costs and less frequent replacements, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Disadvantages of Tungsten Carbide Ball Bearings
Despite their many advantages, tungsten carbide bearings also have some drawbacks:
1. Higher Initial Cost
Tungsten carbide bearings are generally more expensive to produce than steel bearings. The initial investment can be a barrier for some businesses, especially those operating on tight budgets.
2. Brittleness
While tungsten carbide is incredibly hard, it is also more brittle than steel. This brittleness can lead to failure under shock loads or impact, making it less suitable for applications where sudden forces are common.
3. Limited Availability
Tungsten carbide bearings may not be as readily available as traditional steel bearings, which can lead to longer lead times for procurement.
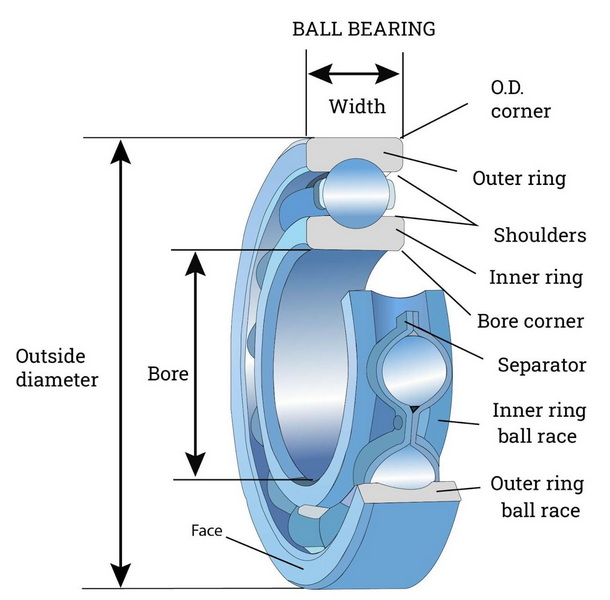
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Ball Bearings
Tungsten carbide ball bearings are used in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: In aircraft engines and landing gear, where high performance and reliability are critical.
- Automotive: In high-performance vehicles, where reduced weight and increased efficiency are desired.
- Manufacturing: In machinery that operates under high loads and temperatures, such as CNC machines and industrial robots.
- Medical Devices: In surgical instruments and implants, where precision and durability are paramount.
- Oil and Gas: In drilling equipment, where resistance to wear and corrosion is essential.
Comparison with Traditional Steel Bearings
When comparing tungsten carbide ball bearings to traditional steel bearings, several factors come into play:
Performance
Tungsten carbide bearings outperform steel in terms of hardness, wear resistance, and temperature tolerance. However, steel bearings may be more suitable for applications involving shock loads due to their toughness.
Cost
While tungsten carbide bearings offer long-term savings due to their durability, the initial cost is higher than that of steel bearings. Businesses must weigh the upfront investment against potential savings in maintenance and replacement costs.
Availability
Steel bearings are widely available and come in various sizes and specifications, making them easier to source. Tungsten carbide bearings may require specialized suppliers, which can affect lead times.
Conclusion
Tungsten carbide ball bearings present a compelling alternative to traditional steel bearings, particularly in applications requiring high performance, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. While they come with a higher initial cost and some limitations, the long-term benefits often justify the investment. As industries continue to evolve and demand more efficient and reliable components, tungsten carbide bearings are likely to play an increasingly important role.

Related Questions
1. What are the specific applications where tungsten carbide bearings excel?
Tungsten carbide bearings excel in high-load and high-temperature applications, such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery, where durability and performance are critical.
2. How does the cost of tungsten carbide bearings compare to steel bearings?
Tungsten carbide bearings typically have a higher initial cost than steel bearings, but their longevity and reduced maintenance needs can lead to cost savings over time.
3. What are the maintenance requirements for each type of bearing?
Steel bearings may require regular lubrication and inspection for rust, while tungsten carbide bearings generally require less maintenance due to their wear resistance.
4. Can tungsten carbide bearings be used in all environments?
While tungsten carbide bearings are resistant to corrosion and high temperatures, they may not be suitable for applications involving shock loads due to their brittleness.
5. How do I choose between tungsten carbide and steel bearings for my application?
Consider factors such as load requirements, operating temperature, environmental conditions, and budget. For high-performance needs, tungsten carbide may be the better choice, while steel may suffice for standard applications.
















