Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
● Raw Material Preparation
● Mixing with Binder
● Shaping
● Sintering
● Finishing Processes
● Quality Control
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide Tools
● Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Tool Manufacturing
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What makes tungsten carbide tools superior compared to other materials?
>> 2. Can tungsten carbide tools be recycled?
>> 3. How does sintering affect the properties of tungsten carbide?
>> 4. What types of coatings are applied to tungsten carbide tools?
>> 5. Why is cobalt used as a binder in tungsten carbide production?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide tools are renowned for their exceptional hardness and durability, making them a preferred choice in various industrial applications, particularly in cutting and machining. This article delves into the intricate process of manufacturing tungsten carbide tools, exploring each step from raw material preparation to the final product.
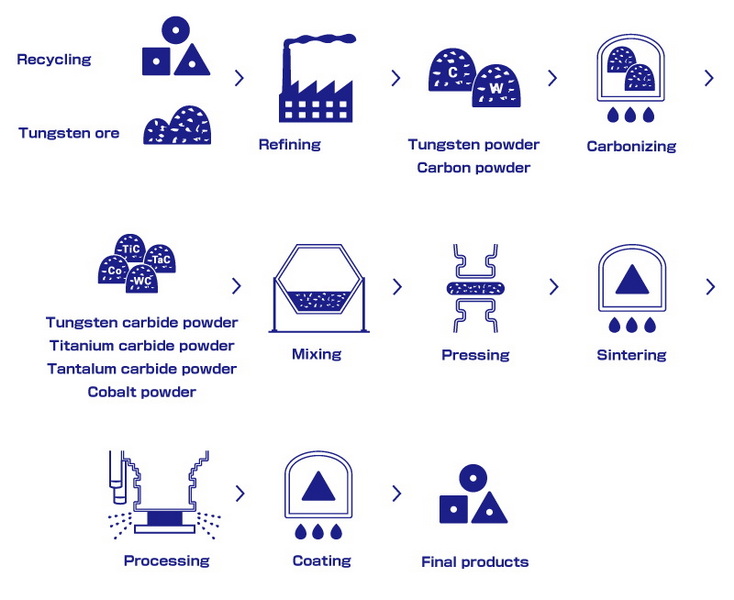
Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a compound made from tungsten and carbon, forming a dense and hard material. It is primarily used in the production of cutting tools due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist wear. The typical hardness of tungsten carbide ranks between 8.5 to 9 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond.
The unique properties of tungsten carbide arise from its microstructure and the bonding between tungsten and carbon atoms. This compound is not only hard but also possesses excellent compressive strength, making it suitable for applications where resistance to deformation is critical.
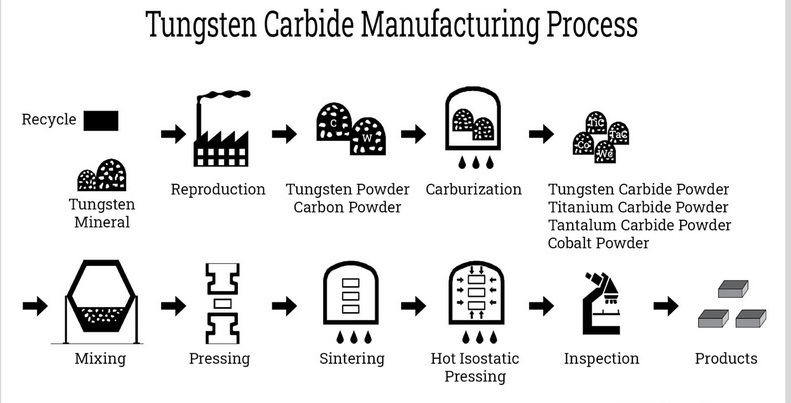
Raw Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the preparation of raw materials:
- Tungsten Ore: The primary source is tungsten ore, which is crushed and chemically treated to produce tungsten oxide.
- Carburization: The tungsten oxide is mixed with carbon (usually in the form of graphite) and heated to high temperatures (over 1200°C) in a controlled environment. This process converts tungsten oxide into tungsten carbide through a chemical reaction that removes oxygen and combines carbon with tungsten.
- Powder Production: The resulting tungsten carbide is ground into a fine powder, which will later be blended with a binder material.
This initial stage is crucial as the purity and quality of the raw materials directly affect the performance characteristics of the final tools. Impurities can lead to defects that compromise tool integrity.
Mixing with Binder
After producing the tungsten carbide powder, it is mixed with a metallic binder, typically cobalt or nickel. This step is crucial as it enhances the mechanical properties of the final product:
- Mixing Process: The powders are combined in specific ratios using a ball mill or similar equipment to ensure uniform distribution. This mixture is often blended with solvents to facilitate processing.
- Granulation: The mixed powder may undergo granulation to achieve desired particle sizes, which significantly impacts the final tool's performance.
The choice of binder material influences not only the toughness but also the thermal stability of the tools. Cobalt is commonly favored due to its ability to enhance toughness without significantly compromising hardness.
Shaping
Once the mixing process is complete, the next step involves shaping the powder into desired forms:
- Pressing: The granulated mixture is placed into molds and subjected to high pressure (up to 20 tons) to create "green" compacts that resemble chalk in consistency.
- Extrusion: In some cases, extrusion methods are used to produce rods or other complex shapes that may be required for specific applications.
The shaping process must be carefully controlled to ensure uniform density throughout the compacted material. Variations in density can lead to inconsistencies in performance during machining operations.
Sintering
Sintering is one of the most critical steps in the manufacturing process:
- Heating: The pressed compacts are heated in a sintering furnace at temperatures ranging from 1400°C to 1500°C under controlled atmospheres (usually vacuum or inert gas). This heating allows the binder metal (cobalt or nickel) to melt and bond the tungsten carbide particles together.
- Shrinkage: During sintering, the components shrink significantly (up to 50%), leading to a denser final product. This reduction must be accounted for during the pressing stage to ensure that final dimensions meet specifications.
The sintering process not only enhances density but also improves mechanical properties such as hardness and toughness. Proper control over temperature and atmosphere during this stage is essential for achieving optimal results.
Finishing Processes
After sintering, additional finishing processes may be employed:
- Grinding: The sintered tools are often ground using diamond wheels to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. This step ensures that cutting edges are sharp and meet stringent tolerances required for effective machining.
- Coating: Many tungsten carbide tools receive surface coatings (such as titanium nitride) that enhance their wear resistance and reduce friction during operation.
Finishing processes play a vital role in determining how well a tool performs under operational conditions. A well-finished tool can significantly improve cutting efficiency and prolong tool life.
Quality Control
Quality control is integral throughout the manufacturing process:
- Testing: Samples from each batch are tested for hardness, wear resistance, and other mechanical properties to ensure they meet industry standards.
- Inspection: Final products undergo rigorous inspection before packaging and shipping to customers.
Quality control measures include non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing, which helps identify internal defects without damaging the product. Consistent quality assurance ensures reliability in performance across various applications.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Tools
Tungsten carbide tools find applications across various industries due to their durability and performance characteristics:
- Cutting Tools: Used extensively in machining operations for metals, plastics, and wood.
- Mining Tools: Employed in drilling applications due to their ability to withstand abrasive conditions.
- Construction Tools: Utilized for cutting and shaping materials in construction projects.
- Oil & Gas Industry: Used for drilling equipment where extreme durability is required due to harsh environmental conditions.
- Aerospace Applications: Essential for manufacturing components that require precision machining under stringent tolerances.
The versatility of tungsten carbide tools makes them indispensable across multiple sectors, driving demand for continuous innovation in their manufacturing processes.
Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Tool Manufacturing
As technology evolves, so does the manufacturing process for tungsten carbide tools:
- Additive Manufacturing: Techniques such as 3D printing are being explored for creating complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve efficiently.
- Advanced Coatings: Research into new coating materials aims at further enhancing wear resistance while reducing friction even more than current solutions allow.
- Smart Manufacturing Technologies: The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices allows manufacturers to monitor production processes in real-time, ensuring higher consistency and quality control throughout production runs.
These innovations not only improve efficiency but also open new avenues for application where traditional tooling methods may fall short.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of tungsten carbide tools involves multiple stages, each critical for producing high-quality products capable of performing under extreme conditions. From raw material preparation through shaping, sintering, finishing, and quality control, every step contributes significantly to the tool's overall performance and longevity. As industries continue to evolve, so too will the technologies used in producing these essential tools. With ongoing advancements in manufacturing techniques and materials science, we can expect even more robust solutions tailored for specific applications in various sectors.
FAQ
1. What makes tungsten carbide tools superior compared to other materials?
Tungsten carbide tools are superior due to their extreme hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain sharpness under high-stress conditions, making them ideal for cutting hard metals.
2. Can tungsten carbide tools be recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled. Worn-out tools can be reclaimed and reused in new manufacturing processes.
3. How does sintering affect the properties of tungsten carbide?
Sintering bonds the tungsten carbide particles together under heat and pressure, resulting in a denser material with enhanced mechanical properties such as hardness and strength.
4. What types of coatings are applied to tungsten carbide tools?
Common coatings include titanium nitride (TiN) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which enhance wear resistance and reduce friction during machining operations.
5. Why is cobalt used as a binder in tungsten carbide production?
Cobalt serves as an effective binder because it enhances toughness while allowing for sufficient bonding between tungsten carbide grains during sintering.
Citations:
[1] https://www.tool-tool.com/news/201202/cutting-tool-manufacturing-process/index.html
[2] https://www.zgcccarbide.com/news/The-Manufacturing-Process-of-Cemented-Carbide-Inserts:-A-Comprehensive-Guide-39.html
[3] https://www.mmc-carbide.com/in/technical_information/tec_guide/tec_guide_carbide
[4] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/tungsten-carbide.html
[5] https://eternaltools.com/blogs/tutorials/tungsten-carbide-an-informative-guide
[6] https://www.retopz.com/57-frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-tungsten-carbide/
[7] https://www.7leaders.com/blog/tungsten-carbide
[8] https://huanatools.com/how-to-make-tungsten-carbide-rods/
[9] https://www.tungstenman.com/tungsten-carbide-tools-the-pros-and-cons.html
[10] https://todaysmachiningworld.com/magazine/how-it-works-making-tungsten-carbide-cutting-tools/
[11] https://tuncomfg.com/about/faq/
[12] https://www.axismateria.co.jp/aml_en/technical/manufacturing-process-material-characteristic.html
[13] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=95yS7W66-BI
[14] https://www.mmc-carbide.com/in/technical_information/tec_guide/tec_guide_carbide
[15] https://www.everloy-cemented-carbide.com/en/process/
[16] https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/24896/03chapter3.pdf?sequence=4
[17] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0QrynzJ_lZ4
[18] https://www.psmindustries.com/yillik/tungsten-carbide-manufacturing-process
[19] https://todaysmachiningworld.com/magazine/how-it-works-making-tungsten-carbide-cutting-tools/
[20] https://www.7leaders.com/blog/tungsten-carbide
[21] https://www.istockphoto.com/de/bot-wall?returnUrl=%2Fde%2Fphotos%2Ftungsten-carbide
[22] https://www.mmc.co.jp/corporate/en/news/2024/news20240529.html
[23] https://www.gettyimages.hk/%E5%9C%96%E7%89%87/tungsten-carbide
[24] https://stock.adobe.com/search/images?k=carbide+cutting
[25] https://www.hit-tw.com/newsdetails.aspx?nid=298
[26] https://www.carbideburr.net/faq/
[27] https://huanatools.com/6-facts-about-tungsten-carbide-burrs-and-how-to-use-them/
[28] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/3-questions-tungsten-carbide-buttons-shijin-lei
[29] https://www.mtb2b.tw/en/articles/182
















