Content Menu
● Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
● Raw Materials
● Manufacturing Process Overview
● Detailed Steps in the Manufacturing Process
>> 1. Powder Preparation
>> 2. Mixing
>> 3. Compaction
>> 4. Sintering
>> 5. Machining
>> 6. Finishing
● Quality Control Measures
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
● Advantages of Tungsten Carbide
● Challenges in Manufacturing Tungsten Carbide
● Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Manufacturing
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What is tungsten carbide made of?
>> 2. How hard is tungsten carbide compared to other materials?
>> 3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
>> 4. What industries commonly use tungsten carbide?
>> 5. What are the benefits of using cobalt as a binder in tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a highly durable material known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it an essential component in various industrial applications, including cutting tools, mining equipment, and wear-resistant parts. This article delves into the intricate manufacturing process of tungsten carbide, detailing each step from raw material preparation to the final product.

Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a chemical compound formed from tungsten and carbon atoms. It is renowned for its hardness, ranking between 9 and 9.5 on the Mohs scale, making it nearly as hard as diamond. The typical composition of tungsten carbide consists of approximately 94% tungsten and 6% carbon by weight. This unique structure grants tungsten carbide its remarkable mechanical properties, including high density (about 15.6 g/cm³) and excellent thermal stability.
Raw Materials
The production of tungsten carbide involves several key raw materials:
- Tungsten Ore: The primary source of tungsten is typically found in ores such as wolframite or scheelite.
- Carbon Sources: Carbon is usually sourced from graphite or carbon black.
- Binder Metals: Cobalt or nickel is often used as a binder to enhance the toughness and ductility of the final product.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The manufacturing process of tungsten carbide can be broken down into several critical stages:
1. Powder Preparation
The first stage involves preparing tungsten powder through various methods:
- Reduction of Tungsten Oxide: Tungsten oxide (WO₃) is reduced in a hydrogen atmosphere to produce tungsten metal powder.
- Carburization: The tungsten metal powder is then mixed with carbon sources and subjected to high temperatures (typically between 1400°C to 2000°C) to form tungsten carbide through a chemical reaction.
2. Mixing
The tungsten carbide powder is mixed with binder metals (like cobalt) in a ball mill to ensure uniform distribution. This mixture may also include additives to improve specific properties.
3. Compaction
After mixing, the powder mixture is compacted into shapes using either uniaxial pressing or isostatic pressing methods. This step forms "green" parts that have sufficient strength for handling but are not yet fully dense.
4. Sintering
Sintering is a crucial step where the compacted parts are heated in a furnace at temperatures ranging from 1400°C to 1600°C in a vacuum or inert atmosphere. During this process, the binder melts and bonds the tungsten carbide particles together, resulting in a solid, dense material.
5. Machining
Post-sintering, the tungsten carbide components may undergo machining processes such as grinding, milling, or electrical discharge machining (EDM) to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes.
6. Finishing
Finally, surface treatments such as polishing or coating may be applied to enhance wear resistance and improve surface quality.
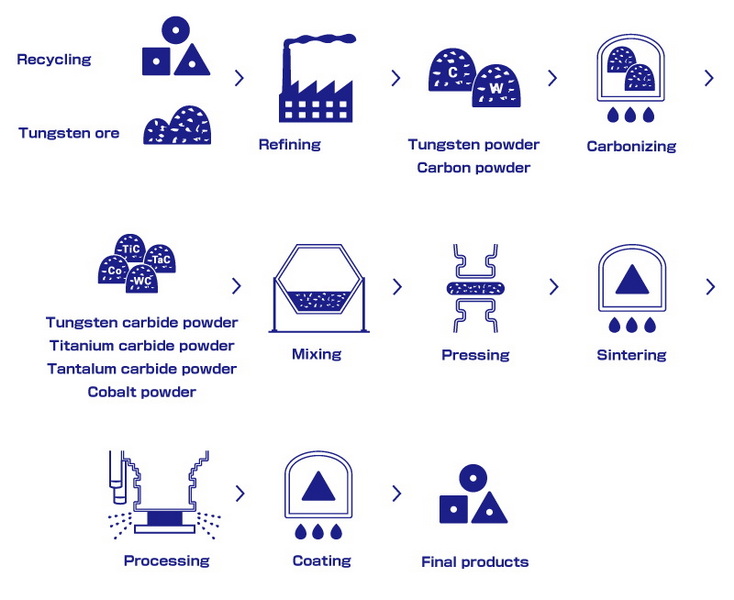
Detailed Steps in the Manufacturing Process
1. Powder Preparation
The preparation of tungsten carbide powder involves several methods:
- Carburization Reaction: Tungsten metal reacts with carbon at high temperatures to form WC:
W+C→WC
- Temperature Control: The temperature during this reaction significantly affects the grain size and properties of the resulting tungsten carbide. Higher temperatures tend to produce finer grains, which can enhance hardness but may also lead to brittleness if not controlled properly.
2. Mixing
In this stage:
- Ball Milling: The mixed powders are placed in a ball mill with additives like paraffin wax to improve green strength.
- Uniformity Check: Ensuring that the mixture is homogeneous is crucial for consistent quality in the final product. Inadequate mixing can lead to weak spots in the final component.
3. Compaction
This process involves:
- Pressing Techniques: Using mechanical or hydraulic presses to compact the powder into desired shapes.
- Green Density Measurement: Monitoring green density helps predict how well the part will sinter. A higher green density typically correlates with better sintering outcomes.
4. Sintering
Key aspects include:
- Controlled Atmosphere: Sintering occurs in a controlled environment to prevent oxidation and ensure proper bonding.
- Temperature Profile: A gradual increase in temperature helps burn off any binders before reaching sintering temperatures. This careful control minimizes defects and ensures uniform density throughout the component.
5. Machining
Due to its extreme hardness:
- Specialized Tools: Diamond-tipped tools are often required for machining tungsten carbide.
- Precision Techniques: High precision is necessary to achieve tight tolerances and desired surface finishes. Techniques such as CNC machining are commonly employed for this purpose.
6. Finishing
Finishing processes may involve:
- Polishing: Achieving a smooth surface finish using diamond polishing compounds.
- Coating Treatments: Applying coatings like PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) enhances wear resistance further.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount throughout the manufacturing process of tungsten carbide. Various techniques are employed to ensure that each batch meets stringent specifications:
- Particle Size Analysis: Ensures that the powder used for manufacturing has consistent particle sizes, which affects sintering behavior and final properties.
- Density Testing: Both green density and sintered density are measured using techniques like Archimedes' principle or X-ray computed tomography (CT) scans.
- Microstructural Examination: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can be used to analyze grain structure and detect any defects within the material.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it suitable for various applications:
- Cutting Tools: Used extensively in drills, end mills, and saw blades due to its hardness.
- Mining Equipment: Components like drill bits and mining tips benefit from its wear resistance.
- Industrial Machinery Parts: Used in parts that require high durability under extreme conditions.
- Jewelry Making: Tungsten carbide's scratch resistance makes it popular for wedding bands and other jewelry items.
Advantages of Tungsten Carbide
The advantages of using tungsten carbide over other materials include:
1. Exceptional Hardness: Its hardness allows for longer tool life compared to standard steel tools.
2. Wear Resistance: Tungsten carbide components can withstand significant wear from abrasive materials, making them ideal for harsh environments.
3. High Density: The high density contributes to stability during operation, reducing vibrations in cutting applications.
4. Thermal Stability: Tungsten carbide maintains its properties at elevated temperatures better than many other materials.
5. Versatility: It can be used in various forms—powdered, solid blocks, or coated surfaces—making it adaptable for numerous applications.
Challenges in Manufacturing Tungsten Carbide
Despite its advantages, manufacturing tungsten carbide presents challenges:
1. Brittleness: While hard, tungsten carbide can be brittle; thus, careful design considerations must be made to avoid fractures during use.
2. Cost of Raw Materials: The cost of tungsten ore can fluctuate significantly based on market demand and geopolitical factors.
3. Environmental Concerns: The mining processes involved in extracting tungsten ore can have environmental impacts that need addressing through sustainable practices.
4. Complex Manufacturing Process: Each step requires precision; any deviation can result in defects that compromise performance.
Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Manufacturing
Looking ahead, several trends are emerging in the manufacturing of tungsten carbide:
1. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Advances in additive manufacturing techniques are beginning to allow for more complex geometries that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
2. Sustainable Practices: Efforts are being made towards more sustainable mining practices and recycling processes for used tungsten carbide tools.
3. Nanostructured Materials: Research into nanostructured versions of tungsten carbide could lead to even harder materials with improved toughness and wear resistance properties.
4. Smart Manufacturing Technologies: The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies into manufacturing processes could enhance monitoring and control over production parameters, leading to improved quality assurance.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of tungsten carbide combines advanced materials science with precise engineering techniques. From raw material preparation through sintering and finishing, each step plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets rigorous performance standards required by various industries. As technology advances, innovations such as additive manufacturing are beginning to revolutionize how tungsten carbide components are produced, offering new possibilities for design and application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is tungsten carbide made of?
Tungsten carbide is composed primarily of equal parts tungsten (W) and carbon (C), forming a chemical compound with exceptional hardness.
2. How hard is tungsten carbide compared to other materials?
Tungsten carbide ranks between 9 and 9.5 on the Mohs hardness scale, making it one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond.
3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled effectively; worn-out tools can be reclaimed and reused in new products.
4. What industries commonly use tungsten carbide?
Industries such as mining, manufacturing (cutting tools), aerospace, and oil drilling frequently utilize tungsten carbide due to its durability and performance under stress.
5. What are the benefits of using cobalt as a binder in tungsten carbide?
Cobalt enhances toughness and ductility while maintaining high hardness levels in cemented carbides, making them more resilient against fracture during use.
Citations:
[1] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/90_how-is-tungsten-carbide-made-.html
[2] https://www.bangerter.com/en/tungsten-carbide/manufacturing-process
[3] https://www.carbide-part.com/blog/tungsten-carbide-machining-process/
[4] https://www.gettyimages.hk/%E5%9C%96%E7%89%87/tungsten-carbide
[5] https://shop.machinemfg.com/tungsten-carbide-an-overview/
[6] https://www.retopz.com/57-frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-tungsten-carbide/
[7] https://www.zgcccarbide.com/news/The-Manufacturing-Process-of-Cemented-Carbide-Inserts:-A-Comprehensive-Guide-39.html
[8] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[9] https://www.kovametalli-in.com/manufacturing.html
[10] https://www.linde-amt.com/resource-library/articles/tungsten-carbide
[11] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=95yS7W66-BI
[12] https://eternaltools.com/blogs/tutorials/tungsten-carbide-an-informative-guide
[13] https://www.tool-tool.com/news/201202/cutting-tool-manufacturing-process/index.html
[14] http://www.tungsten-carbides.com/News/Carbide_manufacturing_process.html
[15] https://todaysmachiningworld.com/magazine/how-it-works-making-tungsten-carbide-cutting-tools/
[16] https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/24896/03chapter3.pdf?sequence=4
[17] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/process.html
[18] https://huanatools.com/how-to-make-tungsten-carbide-rods/
[19] https://patents.google.com/patent/US4008090A/en
[20] https://www.xa-blt.com/en/news/revolutionizing-tungsten-carbide-manufacturing-blts-additive-manufacturing-technology-approach-unveiled-at-tct-asia-2023/
[21] https://ceramics.org/ceramic-tech-today/tungsten-carbide-made-easy-government-industry-academia-investigate-additively-manufacturing-cemented-carbide-parts/
[22] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/tungsten-carbide.html
[23] https://generalcarbide.com
[24] https://www.everloy-cemented-carbide.com/en/process/
[25] https://create.vista.com/photos/tungsten-carbide/
[26] https://www.carbide-part.com/blog/tungsten-carbide-machining-process/
[27] https://consolidatedresources.com/blog/10-facts-about-tungsten-carbide/
[28] https://generalcarbide.com/pdf/General-Carbide-Designers-Guide-Tungsten-Carbide.pdf
[29] https://www.researchgate.net/topic/Tungsten
[30] https://www.yatechmaterials.com/en/news/production-process-and-equipment-of-tungsten-carbide-powder/
[31] https://www.hit-tw.com/newsdetails.aspx?nid=298
[32] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/frequently-asked-questions-used-tungsten-carbide-inserts/
















