Content Menu
● Introduction
● Understanding Saw Tips: What Are They?
● Carbide Saw Tips: Composition and Features
>> Key Advantages of Carbide Saw Tips:
>> Limitations:
● Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips: Composition and Features
>> Key Advantages of Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips:
>> Limitations:
● Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips: The Ultimate Comparison
>> 1. Performance & Longevity
>> 2. Cost vs. Value
>> 3. Versatility
>> 4. Speed and Efficiency
>> 5. Maintenance and Sharpening
● Factors to Consider Before Choosing
● Ideal Applications
>> Carbide Saw Tip Applications:
>> Diamond-Tipped Saw Tip Applications:
● Conclusion
● FAQ: Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips
>> 1. What's the main difference between carbide saw tips and diamond-tipped saw tips?
>> 2. Are diamond-tipped saw blades better in all cutting applications?
>> 3. Can carbide saw tips handle heavy-duty industrial cutting?
>> 4. Is the longer life of diamond-tipped blades worth the higher cost?
>> 5. How can I determine which blade is best for my factory or OEM needs?
Introduction
In today's competitive manufacturing environment, the choice between Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips is a critical decision for precision cutting. Whether you're an OEM serving global clients with stainless steel capillary tubes, coiled piping systems, stainless plates, and carbon steel tubing—or a brand that demands high-quality and reliable tool performance—the efficiency and lifespan of your cutting tools matter.
This expert-level guide walks you through everything you need to know about the features, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of both carbide and diamond-tipped saw tips. By understanding the composition, behavior, and ideal usage scenarios for each, industry professionals can make informed decisions that boost productivity and reduce long-term costs.
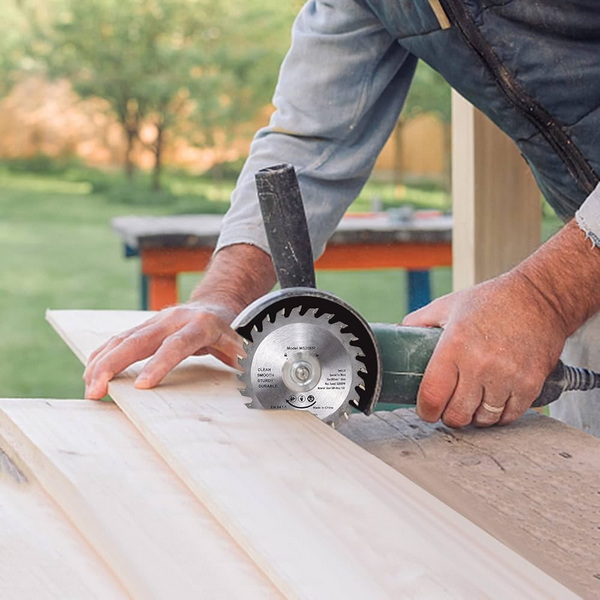

Understanding Saw Tips: What Are They?
Saw tips are specialized materials brazed onto the tips of saw blades, designed to enhance the blade's cutting capabilities, durability, and performance. Standard blades often fail quickly when subjected to hard or abrasive materials, whereas tipped saw blades with carbide or diamond inserts provide significantly improved wear resistance, cutting speed, and accuracy.
These tips are especially valuable in industries involving hard metals (like stainless steel and carbon steel), ceramics, fiberglass, and reinforced plastics. Modern production lines depend on saw tips that can handle high-volume applications without frequent sharpening or replacement.
Carbide Saw Tips: Composition and Features
Tungsten carbide is a compound of tungsten and carbon atoms, forming one of the hardest materials known to industrial cutting tools next to diamonds. It is manufactured through a sintering process, where fine powder is compacted and heated until it bonds into a solid, durable mass.
Key Advantages of Carbide Saw Tips:
- High Wear Resistance: Carbide is highly resistant to abrasion, making it capable of cutting through hard metals like stainless steel for extended periods without dulling.
- Heat Resistance: Ideal for high-speed cutting operations where heat generation can impair blade life.
- Cost Efficiency: Significantly more affordable than diamond-tipped blades, making it a practical choice for bulk materials or general-purpose manufacturing.
- Sharpenable: Carbide tips can be resharpened multiple times, extending the blade's usefulness and reducing waste.
Limitations:
- While extremely hard, carbide is still more brittle than steel and can chip if misused.
- Less effective than diamonds when dealing with ultra-hard or highly abrasive materials like ceramics, glass, or stone.
Carbide-tipped blades are commonly found in facilities manufacturing stainless steel tubing, coiled piping, structural steel components, and wood-based products. Their versatility makes them a staple in both general fabrication and precise material sizing operations.
Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips: Composition and Features
Diamond-tipped saw tips are produced using synthetic diamonds—industrially created under extreme pressure and heat—that are bonded onto a backing material, typically tungsten carbide. These synthetic diamonds possess the same molecular structure and hardness as natural diamonds but can be manufactured in controlled environments for optimal consistency.
Key Advantages of Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips:
- Supreme Hardness: Diamonds are the hardest known material, capable of cutting through virtually anything, including ceramics, glass, and highly abrasive composites with minimal friction.
- Extended Tool Life: Under the right conditions, diamond-tipped tools can last 20 to 50 times longer than carbide-tipped equivalents.
- Exceptional Surface Finish: Ideal for applications where chipping, micro-cracking, or delamination must be avoided, such as wafer cutting or composite fabrication.
- High-Speed Cutting: Diamond-tipped tools can operate at extremely high RPMs while maintaining sharpness and accuracy.
Limitations:
- Cost: Diamond tips are significantly more expensive, both in initial blade cost and in replacement or re-coating.
- Not Re-sharpenable: Once the diamond edge is worn, the blade or tip typically needs full replacement.
- Unsuitable for Ferrous Metals: Heat and friction from cutting iron or steel degrade diamonds quickly, which means they are best used on non-metallic materials or very specific use cases.
Diamond-tipped saw tips are the top choice in aerospace, electronics, ceramics, glass, and specialized composite manufacturing where superior finish and long-lasting performance outweigh the upfront investment.
Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips: The Ultimate Comparison
When comparing Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips, it's essential to evaluate various performance attributes in the context of application, cost, and desired end results.
1. Performance & Longevity
- Carbide performs well for most industrial tasks and can be resharpened multiple times. Expected blade life is reasonable, especially when working on materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, and wood.
- Diamond tips offer unbeatable durability for ultra-hard or abrasive materials but cannot be resharpened.
2. Cost vs. Value
- Carbide presents lower acquisition costs and is ideal for high-volume cutting where margins are tight.
- Diamond tips offer high value in precision applications where downtime or replacement would be more costly than the upfront investment.
3. Versatility
- Carbide tips are better for working with metals, especially stainless steel tubing and piping.
- Diamond tips shine in specialized environments, including cutting fragile or abrasive materials like glass, ceramics, and composite sheets.
4. Speed and Efficiency
- For metals, carbide enables quick, efficient cuts with acceptable tool wear.
- For ultra-hard composites or dense materials, diamonds maintain edge sharpness longer and allow faster feed rates without blade degradation.
5. Maintenance and Sharpening
- Carbide blades can be serviced, sharpened, and reused multiple times.
- Diamond-tipped blades require specialized tools or complete replacement, making them less flexible from a maintenance standpoint.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing
If your factory processes stainless steel capillary tubes or coiled piping systems, you most likely need carbide tips for their strength and compatibility with ferrous metals. However, if your operations involve more exotic materials like carbon fiber composites, glass, or ceramics, diamond tips will provide the superior cutting edge you need.
Other essential considerations include:
- Production Volume: For high-volume environments, carbide blades provide an ideal balance between cost and performance.
- Material Volume and Variety: If your workload includes both soft and hard materials, maintaining an inventory of both types of tips may be necessary.
- Tolerance and Finish Requirements: For high-tolerance sectors like electronics or aerospace, only diamond-tipped tools may meet specifications.
Ideal Applications
Carbide Saw Tip Applications:
- Cutting precision stainless steel tubes, pipes, and carbon steel bars
- High-speed automatic saw operations in manufacturing lines
- Cost-sensitive mass production environments
- General wood and plastic cutting
Diamond-Tipped Saw Tip Applications:
- Precision cutting of brittle materials like ceramics, PCB boards, and silicon wafers
- Aerospace fastener slots or structural composites
- Non-ferrous materials with abrasive properties
- Electronics, glass, automotive, and aerospace manufacturing
Conclusion
Choosing between Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips ultimately depends on your operational demands, materials processed, and production goals. Carbide tips are the backbone of industrial cutting due to their versatility and value. In contrast, diamond-tipped saw tips offer elite performance in precision environments—lasting longer and cutting cleaner when it counts most.
Both materials have earned their place in industrial environments, each excelling where the other may fall short. Carefully assessing your application's specific requirements—and balancing durability, cost, and precision—will lead you to the right saw tip for the job.

FAQ: Carbide Saw Tips vs. Diamond-Tipped Saw Tips
1. What's the main difference between carbide saw tips and diamond-tipped saw tips?
Answer: The core difference lies in material hardness and application. Carbide saw tips are suitable for metal and general-purpose cutting, while diamond-tipped saw tips excel in cutting hard, abrasive, or brittle materials. Diamonds offer much higher durability but come at a higher cost and are not well suited for cutting ferrous metals.
2. Are diamond-tipped saw blades better in all cutting applications?
Answer: Not necessarily. While diamond-tipped blades provide exceptional wear resistance, they are designed for specific materials such as ceramics, glass, and composites. They outperform carbide in those cases but are not suitable for cutting steel or iron.
3. Can carbide saw tips handle heavy-duty industrial cutting?
Answer: Yes. Carbide saw tips are widely used in high-speed automotive, construction, and metal fabrication environments. They're particularly effective for cutting stainless steel pipes, rods, and sheets—providing a balance of toughness, sharpenability, and cost-efficiency.
4. Is the longer life of diamond-tipped blades worth the higher cost?
Answer: In specialized applications that demand perfect cutting edges and durability—such as aerospace or electronics manufacturing—the longevity of diamond-tipped blades often justifies their cost. However, for general cutting of metals or wood, carbide remains the more economical choice.
5. How can I determine which blade is best for my factory or OEM needs?
Answer: Consider the types of materials you process, your production volume, desired surface finish, and budget. If your factory specializes in cutting stainless steel and carbon steel materials in bulk, carbide saw tips are usually sufficient. On the other hand, if your operations involve cutting advanced materials like printed circuit boards or reinforced composites, diamond-tipped saw blades will be more suitable.
















