Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Methods for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Diamond Saw Blades
>> 2. Abrasive Wheel Grinding
>> 3. Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)
>> 4. Electrolytic Machining (ECM)
>> 5. Wire Cutting
● Tools Required for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
● Safety Precautions
● Practical Applications of Tungsten Carbide Cutting
● Challenges in Cutting Tungsten Carbide
● Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Cutting Technologies
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What tools are best for cutting tungsten carbide?
>> 2. Is it safe to cut tungsten carbide at home?
>> 3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
>> 4. How does heat affect cutting tungsten carbide?
>> 5. What industries commonly use tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is one of the hardest materials known, making it a popular choice in various industrial applications, including cutting tools, mining machinery, and jewelry. However, its extreme hardness also poses challenges when it comes to cutting or shaping this material. This article will explore the methods for cutting tungsten carbide, the tools required, safety precautions, and practical applications.
Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a compound made from tungsten and carbon atoms. It is known for its exceptional hardness (8.5 to 9.5 on the Mohs scale), wear resistance, and durability. These properties make tungsten carbide ideal for use in cutting tools and other applications where high strength and resistance to wear are essential.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Hardness: Tungsten carbide is four times harder than titanium and twice as hard as steel.
- Wear Resistance: It maintains sharpness longer than other materials.
- Brittleness: While very hard, tungsten carbide is also brittle, which can lead to cracking or shattering if not handled properly.
- Corrosion Resistance: Tungsten carbide exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it suitable for harsh environments.
- Thermal Conductivity: It has good thermal conductivity, which helps in dissipating heat during machining processes.
Methods for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
Cutting tungsten carbide requires specialized techniques and tools due to its hardness. Here are the most common methods:
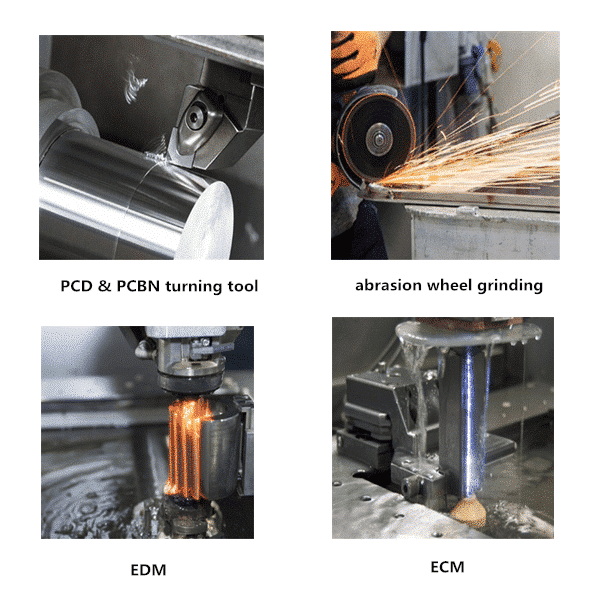
1. Diamond Saw Blades
Diamond saw blades are specifically designed to cut through hard materials like tungsten carbide. Their exceptional hardness allows them to make clean and accurate cuts.
- Application: Ideal for making straight cuts in larger pieces of tungsten carbide.
- Usage Tip: Ensure the blade is properly cooled during cutting to prevent overheating. A water-cooled system can be beneficial in maintaining optimal temperatures.
- Limitations: While effective, diamond blades can be expensive and may require frequent replacement depending on usage.
2. Abrasive Wheel Grinding
Abrasive wheels, particularly those coated with diamond or silicon carbide, can grind down tungsten carbide effectively.
- Application: Suitable for shaping and finishing surfaces.
- Usage Tip: Use a slow feed rate to avoid excessive heat buildup. Regularly check the wheel for wear and replace it when necessary.
- Advantages: This method allows for precise control over the amount of material removed and can achieve fine surface finishes.
3. Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM uses electrical discharges to erode material away from the workpiece. This method is highly precise and does not rely on mechanical cutting forces.
- Application: Best for complex shapes and fine details.
- Usage Tip: Requires specialized equipment and setup. Ensure that the dielectric fluid is adequately maintained for optimal performance.
- Benefits: EDM can produce intricate designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional cutting methods.
4. Electrolytic Machining (ECM)
ECM involves using an electrolyte solution to dissolve the tungsten carbide without generating heat. This method is effective for maintaining the integrity of the material during cutting.
- Application: Used for intricate designs where heat damage must be avoided.
- Usage Tip: Ensure proper setup of electrolyte flow for optimal results. The concentration of the electrolyte solution should be carefully controlled.
- Pros: ECM allows for high precision and can machine complex geometries without mechanical stress on the material.
5. Wire Cutting
Wire cutting techniques utilize thin wires that can cut through tungsten carbide with high precision.
- Application: Commonly used in mold making and precision engineering.
- Usage Tip: Select the appropriate wire thickness based on the desired cut quality. Regularly monitor wire tension during operation.
- Advantages: Wire cutting provides excellent accuracy and surface finish while minimizing material waste.
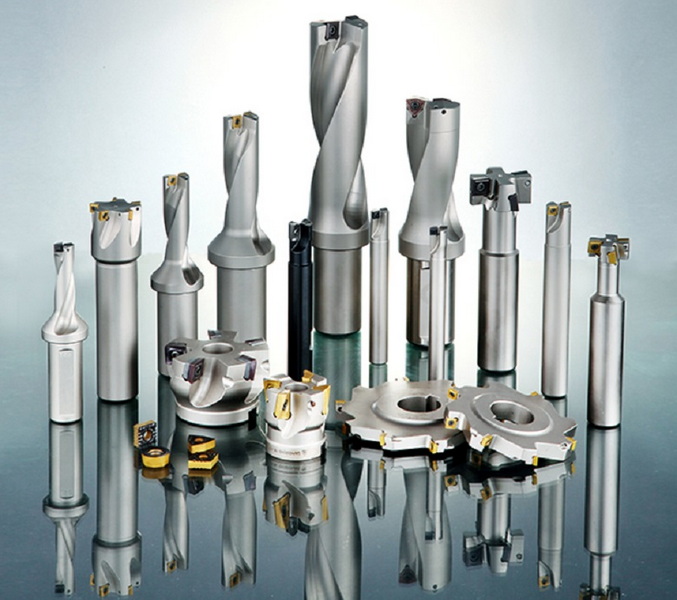

Tools Required for Cutting Tungsten Carbide
When cutting tungsten carbide, having the right tools is crucial:
- Diamond Saw Blades: For straight cuts.
- Dremel Tool with Carbide Wheel: For detailed work or small sections.
- Abrasive Wheels: For grinding and finishing surfaces.
- EDM Equipment: For high precision cutting.
- ECM Setup: For non-contact machining.
- Wire Cutting Machine: For intricate shapes and designs.
Safety Precautions
Cutting tungsten carbide can produce hazardous dust and debris. Therefore, safety precautions are essential:
- Protective Gear: Always wear safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask to protect against flying particles and inhalation of dust.
- Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation in the workspace to minimize inhalation risks. Using a fume extractor can help reduce airborne particles.
- Tool Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain tools to ensure they are in good working condition. Dull blades or worn wheels can create more friction and heat, increasing risks during operation.
Practical Applications of Tungsten Carbide Cutting
Tungsten carbide is used in various industries due to its hardness and durability:
- Cutting Tools: Manufacturing drill bits, milling cutters, saw blades, and inserts for lathes.
- Mining Equipment: Components that require high wear resistance such as drill bits used in oil drilling or geological exploration.
- Jewelry Making: Tungsten carbide rings are popular due to their scratch resistance and durability; they maintain their polish longer than traditional gold or silver rings.
- Industrial Machinery Parts: Used in components that require high strength under extreme conditions, such as wear plates or bushings in heavy machinery.
Challenges in Cutting Tungsten Carbide
Despite its advantages, there are challenges associated with cutting tungsten carbide:
- Cost of Tools: The specialized tools required for cutting tungsten carbide can be expensive compared to standard cutting tools used for softer materials.
- Brittleness Issues: The brittleness of tungsten carbide means that improper handling or excessive force during cutting can lead to chipping or breaking.
- Heat Management: Managing heat during the cutting process is crucial; excessive heat can lead to tool wear or damage to both the tool and workpiece.
Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Cutting Technologies
As industries continue to evolve, so do the technologies used for cutting tungsten carbide:
- Advanced Coatings: New coatings on cutting tools are being developed to enhance performance and longevity when working with tough materials like tungsten carbide.
- Automation & Robotics: The integration of automation in machining processes promises increased efficiency and precision when cutting hard materials.
- Innovative Cooling Techniques: Research into advanced cooling methods aims to improve heat management during machining operations, thereby extending tool life and improving cut quality.
Conclusion
Cutting tungsten carbide is challenging due to its extreme hardness but can be accomplished using specialized methods such as diamond saw blades, abrasive grinding, EDM, ECM, and wire cutting techniques. Each method has its advantages depending on the application requirements. Proper safety measures must be observed during the cutting process to ensure a safe working environment. As technology advances, new methods may further enhance our ability to work with this remarkable material efficiently.

FAQ
1. What tools are best for cutting tungsten carbide?
The best tools include diamond saw blades, Dremel tools with carbide wheels, abrasive wheels, EDM machines, ECM setups, and wire cutting machines.
2. Is it safe to cut tungsten carbide at home?
While it is possible to cut tungsten carbide at home using appropriate tools like a Dremel with a diamond wheel, safety precautions must be strictly followed due to flying debris and dust hazards.
3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled by reclaiming worn-out tools and scrap material for reuse through specialized recycling processes that recover both tungsten and carbon components.
4. How does heat affect cutting tungsten carbide?
Excessive heat can damage both the tungsten carbide workpiece and the cutting tool; therefore, cooling methods should be employed during cutting processes to prevent thermal degradation of both materials involved.
5. What industries commonly use tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is widely used in manufacturing cutting tools (like drill bits), mining equipment (for wear-resistant components), jewelry making (for durable rings), industrial machinery parts (for high-strength applications), and more due to its exceptional properties.
Citations:
[1] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/carbiderod-how-cut-tungsten-carbide-rod-shijin-lei
[2] https://shop.machinemfg.com/how-to-cut-tungsten-carbide-rods-an-overview/
[3] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/tungsten-carbide.html
[4] https://www.dreamstime.com/photos-images/tungsten-carbide.html
[5] https://tronex-tools.com/products/carbide-hard-wire-taper-head-cutters-medium-long-ergonomic-handle
[6] https://www.model-engineer.co.uk/forums/topic/how-to-cut-tungsten-carbide/
[7] https://www.carbide-part.com/blog/how-to-cut-carbide/
[8] https://www.retopz.com/57-frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-tungsten-carbide/
[9] https://www.practicalmachinist.com/forum/threads/machining-tungsten-carbide-advice-needed.351332/
[10] https://todaysmachiningworld.com/magazine/how-it-works-making-tungsten-carbide-cutting-tools/
[11] http://derbytalk.com/viewtopic.php?t=2378
[12] https://www.stepcraft-systems.com/forum/milling/4349-cutting-tungsten-carbide
[13] https://www.mmc-carbide.com/us/technical_information/tec_guide/tec_guide_carbide
[14] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MqupCjkNqUk
[15] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zk3ZiVOvwFg
[16] https://www.reddit.com/r/EngineeringPorn/comments/q3sc8w/milling_tungsten_carbide/
[17] https://www.ringrescue.com/blog/cutting-tungsten-rings-are-there-risks
[18] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LxvVUvUBqag
[19] https://www.practicalmachinist.com/forum/threads/carbide-vs-tungsten-carbide-in-tool-realm.336544/
[20] https://www.larsonjewelers.com/pages/can-tungsten-rings-be-cutoff
[21] https://www.reddit.com/r/metalworking/comments/1e9xttj/cutting_tungsten/
[22] https://forums.anandtech.com/threads/is-it-true-that-you-cant-cut-off-a-tungsten-ring-easily.53714/
[23] https://www.istockphoto.com/de/bot-wall?returnUrl=%2Fde%2Fphotos%2Ftungsten-carbide-drill-bits
[24] https://stock.adobe.com/search?k=tungsten+carbide
[25] https://stock.adobe.com/search?k=carbide
[26] https://eternaltools.com/blogs/tutorials/tungsten-carbide-an-informative-guide
[27] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-questions-tungsten-carbide-burrs-shijin-lei
[28] https://www.cnczone.com/forums/metalwork-discussion/226048-quot-machine-quot-tungsten-carbide.html
[29] https://www.carbidetek.com/faqs/
[30] https://www.everlastgenerators.com/forums/showthread.php/2772-Plasma-Cutting-Tungsten
[31] https://www.practicalmachinist.com/forum/threads/turning-tungsten.84677/
[32] https://tuncomfg.com/about/faq/
[33] https://www.7leaders.com/blog/tungsten-carbide
[34] http://www.titaniumkay.com/tungsten-rings/can-you-cut-a-tungsten-carbide-ring/
[35] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/tungsten-carbide-tool.html
[36] https://www.istockphoto.com/de/bot-wall?returnUrl=%2Fde%2Fphotos%2Ftungsten-carbide
[37] https://www.betalentcarbide.com/what-are-the-basic-requirements-for-tungsten-carbide-cutter-materials.html
















