Content Menu
● What is Tungsten Carbide?
● The Casting Process of Tungsten Carbide
>> 1. Preparation of Raw Materials
>> 2. Mixing
>> 3. Melting
>> 4. Casting
● Applications of Cast Tungsten Carbide
>> Detailed Applications
● Advantages of Casting Tungsten Carbide
● Challenges in Casting Tungsten Carbide
● Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Casting
● Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Casting
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What are the main components used in casting tungsten carbide?
>> 2. Why is tungsten carbide so hard?
>> 3. Can tungsten carbide be machined after casting?
>> 4. What industries benefit from using cast tungsten carbide?
>> 5. How does the casting process affect the properties of tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a compound made from tungsten and carbon, known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. This article explores the casting of tungsten carbide, its properties, applications, and the methods involved in its production. We will also delve into the advantages and challenges associated with this process, providing a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable material.

What is Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide is a dense, metallic compound composed of equal parts tungsten and carbon. It is characterized by its high hardness, making it one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond. The material has a molecular weight of 195.85 and is often used in industrial applications due to its unique properties.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide:
- Hardness: Comparable to diamond.
- Density: Approximately double that of steel.
- Thermal Stability: Can withstand high temperatures without losing structural integrity.
- Wear Resistance: Highly resistant to abrasion and wear.
- Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to many acids and chemicals.
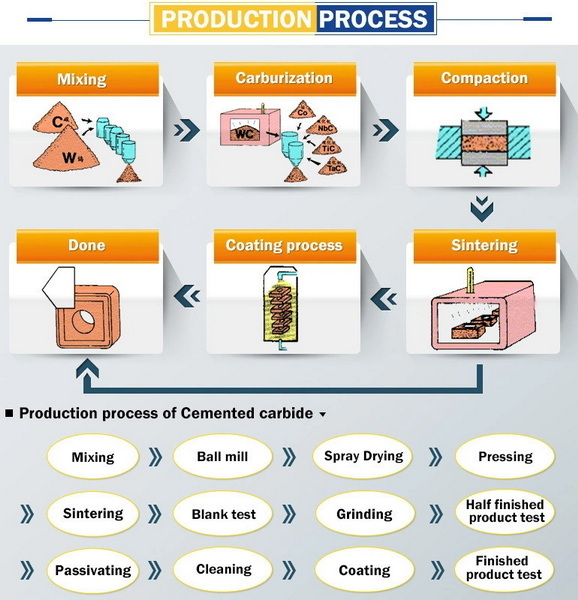
The Casting Process of Tungsten Carbide
Casting tungsten carbide involves several steps, which include mixing tungsten powder with carbon, melting the mixture, and then casting it into molds. The process can vary depending on the desired properties of the final product.
1. Preparation of Raw Materials
The first step in casting tungsten carbide is preparing the raw materials. This involves:
- Tungsten Powder: Typically 95-96 wt% of the mixture.
- Carbon Powder: About 3.95-4.10 wt% to ensure proper carbide formation.
The quality of these raw materials significantly impacts the final product's performance characteristics. High-purity tungsten and carbon powders are preferred to minimize impurities that could affect hardness and wear resistance.
2. Mixing
The tungsten and carbon powders are thoroughly mixed to achieve a homogeneous blend. This step is crucial for ensuring consistent properties throughout the cast product. Various mixing techniques can be employed, including mechanical mixing or ball milling, which helps achieve a uniform particle size distribution.
3. Melting
The mixed powders are then subjected to high temperatures (ranging from 2700°C to 3100°C) in a smelting furnace. This process transforms the powders into molten tungsten carbide. The melting process requires specialized equipment capable of reaching such high temperatures while maintaining a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
4. Casting
Once melted, the tungsten carbide is poured into molds where it cools and solidifies. The cooling process can be controlled to achieve specific microstructures that enhance performance characteristics. Different cooling rates can lead to variations in hardness and toughness in the final product.
Applications of Cast Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Cutting Tools: Used in manufacturing drills, milling cutters, and saw blades due to its hardness and wear resistance.
- Mining Equipment: Essential for drill bits and other tools used in harsh environments.
- Jewelry: Its durability makes it popular for wedding bands and other jewelry items.
- Industrial Machinery: Components that require high wear resistance benefit from tungsten carbide coatings or inserts.
- Aerospace Components: Used in parts that must withstand extreme conditions.
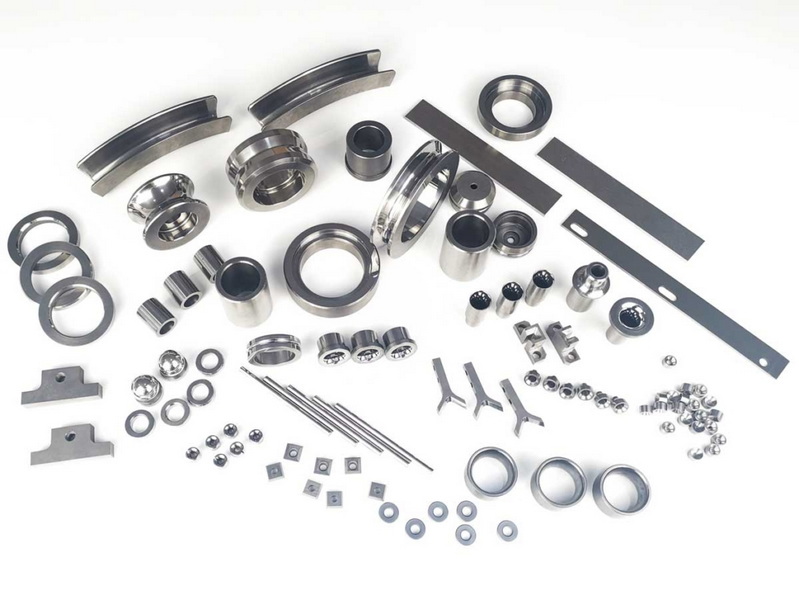

Detailed Applications
1. Cutting Tools:
Tungsten carbide cutting tools are widely used in machining operations due to their ability to maintain sharp edges longer than traditional steel tools. They are utilized in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and metalworking.
2. Mining Equipment:
In mining operations, tungsten carbide is used for drill bits that penetrate hard rock formations. Its wear resistance ensures longer tool life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
3. Jewelry:
Tungsten carbide has gained popularity in the jewelry market for wedding bands and fashion rings due to its scratch-resistant surface and modern aesthetic appeal.
4. Industrial Machinery:
Components like bearings, valves, and nozzles made from tungsten carbide exhibit superior performance under extreme conditions, making them ideal for heavy machinery applications.
5. Aerospace Components:
In aerospace engineering, tungsten carbide is used for components that require high strength-to-weight ratios while maintaining durability under stress.
Advantages of Casting Tungsten Carbide
Casting tungsten carbide offers several advantages over other manufacturing methods:
- High Precision: The casting process can produce intricate shapes with tight tolerances.
- Enhanced Properties: Controlled cooling allows for tailored microstructures that improve hardness and wear resistance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Large-scale production can reduce costs compared to machining solid tungsten carbide blocks.
- Versatility: The ability to cast complex geometries expands design possibilities for engineers and designers.
Challenges in Casting Tungsten Carbide
Despite its advantages, casting tungsten carbide presents some challenges:
- Brittleness: Pure tungsten carbide can be brittle; thus, additives like cobalt or titanium are often included to improve toughness.
- Cobalt acts as a binder that enhances toughness while maintaining hardness.
- Titanium can refine grain structure, further improving performance characteristics.
- Complexity of Process: The high temperatures required for melting demand specialized equipment and safety precautions.
- Operators must be trained to handle hazardous materials safely.
- Environmental controls are necessary to manage emissions during melting.
Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Casting
Recent advancements in technology have led to innovations in the casting process of tungsten carbide:
1. Additive Manufacturing:
- Techniques like 3D printing are being explored for creating complex shapes using tungsten carbide composites.
- This method allows for rapid prototyping and reduced waste during production.
2. Powder Metallurgy:
- Combining powder metallurgy techniques with traditional casting methods enhances the material properties of tungsten carbide.
- This approach allows for better control over particle size distribution and composition.
3. Recycling:
- With growing environmental concerns, recycling scrap tungsten carbide has become increasingly important.
- Recycling processes enable manufacturers to reclaim valuable materials while reducing waste.
Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Casting
As industries continue to evolve, several trends are likely to shape the future of tungsten carbide casting:
1. Sustainability Initiatives:
- Manufacturers will focus on sustainable practices by minimizing waste during production processes.
- The development of eco-friendly binders may gain traction as environmental regulations become stricter.
2. Smart Manufacturing:
- The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology into manufacturing processes will enhance monitoring capabilities.
- Real-time data collection can lead to improved quality control during casting operations.
3. Customization:
- As customer demands shift towards personalized products, manufacturers may offer customized solutions utilizing advanced casting techniques.
- Tailored formulations could lead to unique properties suited for specific applications.
Conclusion
Casting tungsten carbide is a complex yet rewarding process that leverages the unique properties of this material to create high-performance products across various industries. Its applications range from cutting tools to aerospace components, showcasing its versatility and importance in modern manufacturing. Despite challenges such as brittleness and the complexity of processes involved, ongoing innovations promise a bright future for tungsten carbide casting.
FAQs
1. What are the main components used in casting tungsten carbide?
The main components are tungsten powder (95-96 wt%) and carbon powder (3.95-4.10 wt%).
2. Why is tungsten carbide so hard?
Tungsten carbide's hardness comes from its strong covalent bonds between tungsten and carbon atoms, forming a rigid crystal structure.
3. Can tungsten carbide be machined after casting?
Yes, but it requires specialized tools due to its hardness.
4. What industries benefit from using cast tungsten carbide?
Industries such as mining, manufacturing, aerospace, and jewelry benefit significantly from cast tungsten carbide due to its durability and wear resistance.
5. How does the casting process affect the properties of tungsten carbide?
The casting process allows for controlled cooling rates which can enhance hardness and tailor microstructures for specific applications.
Citations:
[1] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN1546713A/en
[2] https://www.refractorymetal.org/tungsten-carbide-uses-properties.html
[3] https://www.samaterials.com/tungsten-carbide/1106-casting-tungsten-carbide-powder.html
[4] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[5] https://patents.google.com/patent/US5089182A/en
[6] https://www.sollex.se/en/blog/post/about-cemented-tungsten-carbide-applications-part-1
[7] https://rocklinmanufacturing.com/resources/files/yr/2020/Die_Casting_Engineer_Editorial_-_Sept_2020.pdf
[8] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[9] https://eurobalt.net/blog/2022/03/28/all-the-applications-of-tungsten-carbide/
















