Content Menu
● Introduction
● Global Distribution of Tungsten Carbide Production
>> Leading Tungsten-Producing Countries
>> Geographic Concentration and Supply Risks
● The Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
>> Raw Material Preparation
>> Carburization and Powder Production
>> Binder Addition and Compaction
>> Sintering and Final Processing
● Industrial Applications and Market Trends
● Environmental Impact and Sustainability in Tungsten Carbide Production
● Recycling and Circular Economy
● Technological Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Production
● Future Trends and Market Outlook
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
>> 1. What is tungsten carbide and why is it important?
>> 2. Where is most of the world's tungsten carbide produced?
>> 3. What are the main steps in the tungsten carbide manufacturing process?
>> 4. What industries use tungsten carbide?
>> 5. What are the main challenges facing the tungsten carbide industry?
Introduction
Tungsten carbide stands as one of the most remarkable materials in modern industry, prized for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Its unique properties make it indispensable in a wide array of applications, from cutting tools and mining equipment to aerospace components and medical devices. As global demand for robust and reliable materials grows, understanding where tungsten carbide is produced, how it is manufactured, and the challenges facing its supply chain becomes increasingly important. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the global landscape of tungsten carbide production, the manufacturing process, major applications, and the industry's evolving future, illustrated throughout with relevant images.

Global Distribution of Tungsten Carbide Production
The production of tungsten carbide is closely tied to the availability of its primary raw material—tungsten ore. Mining and processing of tungsten are highly concentrated in a handful of countries, with China dominating the industry.
Leading Tungsten-Producing Countries
- China: China is the world's leading producer of tungsten, accounting for more than 80% of global output. In recent years, China has maintained its dominance despite export restrictions and stricter environmental regulations. In 2024, Chinese tungsten production reached approximately 67,000 metric tons, reflecting the country's pivotal role in the global supply chain.
- Vietnam: The Nui Phao mine in Vietnam is the largest tungsten-producing mine outside China. However, production has recently declined due to lower ore grades and operational challenges, highlighting the volatility of secondary sources.
- Other Notable Producers: Russia, North Korea, Bolivia, Rwanda, Australia, Austria, and Portugal also contribute to global tungsten supply, but their combined output is significantly smaller than China's.
- Emerging Sources: South Korea's Sangdong Tungsten Project is expected to become a major producer, potentially supplying up to 50% of the world's tungsten outside China once fully operational. This development could help diversify the global supply chain and reduce dependency on China.
Geographic Concentration and Supply Risks
The concentration of tungsten production in China introduces significant supply chain risks. Export restrictions, geopolitical tensions, and environmental policies have led to increased volatility in tungsten prices and availability. Many industries and governments are actively seeking to diversify their sources of tungsten to mitigate these risks and ensure a stable supply of this critical material.
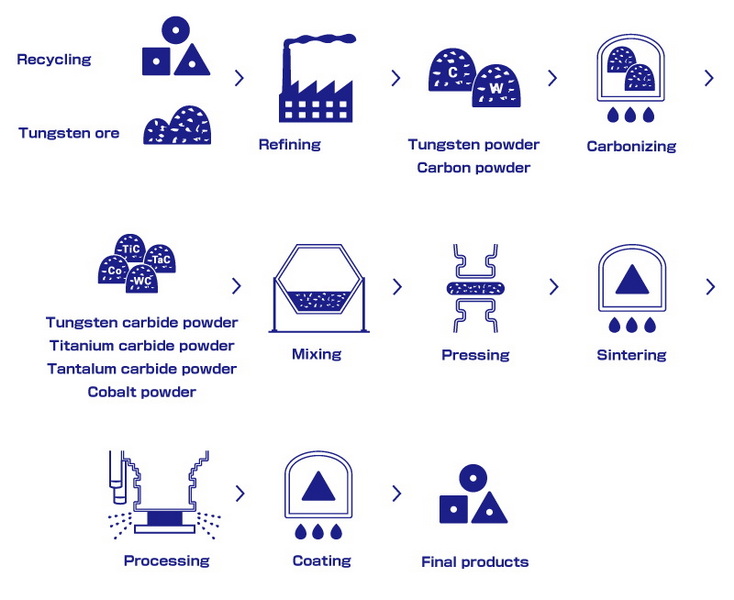
The Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is not simply mined; it is engineered through a sophisticated, multi-stage process that transforms raw tungsten ore into a versatile industrial material.
Raw Material Preparation
- Tungsten Ore: The process begins with the mining of tungsten ores, primarily wolframite and scheelite.
- Purification: The ore undergoes chemical processing to produce ammonium paratungstate (APT), which is then calcined to form tungsten oxide (WO₃).
- Reduction: Tungsten oxide is reduced in a hydrogen atmosphere to yield tungsten metal powder.
Carburization and Powder Production
- Mixing: Tungsten powder is mixed with carbon sources such as graphite or carbon black.
- Carburization: The mixture is heated in a furnace, typically between 1,400°C and 2,000°C, to form tungsten carbide powder (WC).
- Ball Milling: The tungsten carbide powder is further processed in a ball mill to achieve a uniform particle size and distribution.
Binder Addition and Compaction
- Binder Metals: Cobalt or nickel is added to the tungsten carbide powder to enhance toughness and ductility.
- Mixing: The powders are thoroughly mixed to ensure homogeneity.
- Compaction: The mixture is pressed into the desired shapes using uniaxial or isostatic pressing methods.
Sintering and Final Processing
- Sintering: The compacted "green" parts are sintered at high temperatures (1,400°C to 1,600°C) in a vacuum or inert atmosphere. The binder melts, binding the tungsten carbide particles into a dense, solid material.
- Machining: After sintering, the components may be machined to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes.
- Finishing: Surface treatments such as polishing or coating are applied to improve wear resistance and performance.
Industrial Applications and Market Trends
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it indispensable in a wide range of industries:
- Cutting Tools: Drills, milling cutters, and inserts for machining metals and composites.
- Mining and Construction: Wear-resistant parts for drilling, boring, and excavation equipment.
- Aerospace and Defense: Components requiring high strength and resistance to extreme conditions.
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments and implants due to biocompatibility and durability.
- Consumer Goods: Jewelry, watch components, and even self-defense tools.
The global market for tungsten carbide is expected to grow steadily, driven by increasing demand in advanced manufacturing, renewable energy, and defense sectors. However, supply chain disruptions and rising raw material costs present ongoing challenges.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability in Tungsten Carbide Production
The production of tungsten carbide, while essential for many industries, also poses environmental challenges. Mining tungsten ore can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water contamination if not managed responsibly. Additionally, the chemical processes involved in purifying tungsten and producing tungsten carbide powder generate waste products that require careful disposal to prevent environmental harm.
Sustainability efforts in the tungsten carbide industry are gaining momentum. Companies are increasingly adopting greener mining practices, such as reducing water usage and minimizing land disturbance. Advances in chemical processing aim to reduce hazardous waste and improve energy efficiency.
Recycling and Circular Economy
Recycling tungsten carbide is a critical component of sustainable production. Due to the high value and scarcity of tungsten, recycling scrap materials from manufacturing processes and end-of-life products helps conserve natural resources and reduce environmental impact.
Recycling involves collecting used tungsten carbide tools and components, crushing them into powder, and then reprocessing the material to produce new tungsten carbide products. This circular economy approach not only reduces the demand for newly mined tungsten but also lowers production costs and energy consumption.
Technological Innovations in Tungsten Carbide Production
Technological advancements continue to enhance the properties and manufacturing efficiency of tungsten carbide. Innovations include the development of nano-structured tungsten carbide powders, which offer improved hardness and toughness.
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) techniques are also being explored to create complex tungsten carbide components with reduced material waste and shorter production times. These technologies promise to expand the applications of tungsten carbide in industries such as aerospace and medical devices.
Future Trends and Market Outlook
Looking ahead, the tungsten carbide market is expected to evolve with increasing demand for high-performance materials in emerging technologies. The growth of electric vehicles, renewable energy infrastructure, and advanced manufacturing will drive demand for tungsten carbide components.
Efforts to diversify supply chains and invest in recycling will be crucial to ensuring a stable and sustainable supply of tungsten carbide. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, governments, and research institutions will play a key role in addressing challenges and fostering innovation.
Conclusion
The production of tungsten carbide is a complex, global endeavor that begins with the mining of tungsten ore and culminates in the creation of one of the hardest and most durable materials known to industry. China remains the dominant force in tungsten production, but the landscape is shifting as new sources emerge and supply chain risks prompt diversification. The future of tungsten carbide production will be shaped by technological innovation, geopolitical developments, and the ongoing quest for sustainable and secure supply chains.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is tungsten carbide and why is it important?
Tungsten carbide is a compound of tungsten and carbon, known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It is widely used in cutting tools, mining equipment, and industrial applications due to its durability and ability to withstand extreme conditions.
2. Where is most of the world's tungsten carbide produced?
Most tungsten carbide is produced in China, which accounts for over 80% of global tungsten output. Other significant producers include Vietnam, Russia, and, increasingly, countries like South Korea and Australia.
3. What are the main steps in the tungsten carbide manufacturing process?
The main steps include ore mining and purification, reduction to tungsten metal, carburization to form tungsten carbide powder, mixing with a binder (cobalt or nickel), pressing into shape, sintering at high temperatures, and final machining and finishing.
4. What industries use tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is used in manufacturing cutting tools, mining and construction equipment, aerospace and defense components, medical devices, and even consumer goods like jewelry and self-defense tools.
5. What are the main challenges facing the tungsten carbide industry?
Key challenges include supply chain vulnerability due to reliance on Chinese exports, price volatility, and environmental and ethical concerns related to mining practices. Diversification of supply sources and investment in recycling are important strategies to address these issues.
















