Content Menu
● What is Super Fine Powder Silicon Carbide?
● Industrial Abrasives and Machining
>> Grinding and Polishing
>> Water-Jet Cutting and Sandblasting
● High-Temperature Refractory Materials
>> Kiln Shelving and Furnace Linings
>> Steelmaking and Casting
● Advanced Ceramics and Composites
>> Armor and Ballistic Protection
>> Automotive Brake Systems
>> Wear-Resistant Components
● Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
>> Wafer Processing and Heating Elements
>> LED and Optoelectronic Devices
● Renewable Energy and Aerospace
>> Solar Wafer Cutting
>> Aerospace Components
>> High-Performance Coatings
● Metallurgical Applications
>> Deoxidizing and Alloying
>> Sintering Aids
● Emerging Applications and Future Prospects
>> Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
>> Energy Storage and Batteries
>> Environmental and Filtration Technologies
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What makes super fine silicon carbide powder ideal for abrasive applications?
>> 2. How does China contribute to the global supply of super fine SiC powder?
>> 3. Can silicon carbide be used in high-temperature environments?
>> 4. What are the advantages of using SiC in semiconductor manufacturing?
>> 5. How is super fine SiC powder utilized in renewable energy technologies?
● Citations:
Silicon carbide (SiC) super fine powder is a cornerstone material in modern industrial and technological advancements. With exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability, it serves critical roles across industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, energy, and electronics. China has emerged as a global leader in producing high-quality super fine silicon carbide products, offering tailored solutions for abrasive, refractory, and high-performance applications. This article explores the diverse applications of super fine SiC powder, emphasizing its transformative impact on innovation and efficiency.

What is Super Fine Powder Silicon Carbide?
Super fine powder silicon carbide refers to SiC particles with diameters typically below 1 micron, with some advanced grades reaching nanometer scales. This ultra-fine particle size unlocks unique physical and chemical properties, such as increased surface area, enhanced reactivity, and improved sintering behavior. These characteristics make super fine SiC powder a vital ingredient in advanced ceramics, composites, and high-performance coatings.
China super fine powder silicon carbide products are manufactured through advanced techniques such as carbothermal reduction, chemical vapor deposition, and plasma synthesis. These processes ensure precise control over particle size distribution, purity, and morphology, meeting the stringent requirements of high-tech industries.
Industrial Abrasives and Machining
Grinding and Polishing
Super fine SiC powder is widely used in abrasive machining due to its Mohs hardness of 9.5, second only to diamond. It is integral to grinding wheels, sandpapers, and lapping compounds, enabling precision finishing of metals, ceramics, and composites. For example, green SiC powder (99% purity) is preferred for polishing semiconductor wafers and optical glass, while black SiC (97–98% purity) grinds cast iron and non-ferrous metals.
Water-Jet Cutting and Sandblasting
SiC's sharp-edged particles enhance the efficiency of water-jet cutting systems, slicing through thick metals and ceramics with minimal wear. In sandblasting, it removes rust and coatings from surfaces more effectively than aluminum oxide.
China's super fine powder silicon carbide products dominate this sector, with manufacturers like Huamao and Antelisic providing grades optimized for grit size (F12–F3000) and purity (up to 99.9%). These products are tailored to meet the needs of global customers seeking high-performance abrasives for demanding industrial applications.
High-Temperature Refractory Materials
Kiln Shelving and Furnace Linings
SiC's ability to withstand temperatures up to 1,600°C makes it ideal for kiln shelves, crucibles, and furnace linings. Its low thermal expansion prevents cracking, while high thermal conductivity ensures even heat distribution. These properties are crucial in industries such as ceramics, glass, and metallurgy, where thermal cycling and chemical attack are common.
Steelmaking and Casting
In metallurgy, SiC acts as a deoxidizer, replacing ferrosilicon to reduce impurities in steel. Chinese suppliers offer metallurgical-grade SiC (88% purity, 1–5mm grains) at competitive prices, lowering production costs while improving steel quality.
The addition of super fine SiC powder in the production of cast iron and steel enhances the mechanical properties of the final product, such as tensile strength and wear resistance. This makes it a valuable additive in the manufacturing of automotive parts, machinery, and construction materials.
Advanced Ceramics and Composites
Armor and Ballistic Protection
SiC ceramics are key components in bulletproof vests and vehicle armor. Their high hardness and lightweight properties dissipate kinetic energy effectively, outperforming traditional materials like alumina. Super fine SiC powder enables the production of dense, uniform ceramic plates with superior ballistic performance.
Automotive Brake Systems
Ceramic brake discs made from SiC composites offer superior heat resistance and durability, reducing wear in high-performance sports cars. The use of super fine SiC powder in these composites ensures a homogeneous microstructure, resulting in predictable friction behavior and extended service life.
Wear-Resistant Components
SiC's exceptional hardness and chemical inertness make it ideal for producing wear-resistant components such as seals, bearings, and pump parts. These components are used in harsh environments, including chemical processing, oil and gas extraction, and mining.
China's engineering ceramics sector relies on super fine SiC powder (D50 <0.8μm) for sintering reaction-bonded and pressureless SiC components. The fine particle size enhances densification and mechanical properties, making these components highly reliable in demanding applications.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Wafer Processing and Heating Elements
SiC's semiconducting properties and thermal stability make it indispensable in electronics. It is used to cut solar wafers with wire saws and manufacture heating elements for industrial furnaces. The super fine powder ensures clean, precise cuts with minimal material loss, which is critical for the cost-effective production of photovoltaic cells.
SiC-based semiconductors operate at higher voltages and temperatures than silicon, enabling faster switching in electric vehicle inverters and renewable energy systems. Devices such as Schottky diodes and MOSFETs made from SiC offer higher efficiency, reduced heat generation, and smaller form factors compared to their silicon counterparts.
China super fine powder silicon carbide products are essential for producing high-purity SiC substrates and epitaxial layers used in advanced electronic devices. These products are driving the next generation of power electronics, enabling the development of more efficient electric vehicles, smart grids, and renewable energy systems.
LED and Optoelectronic Devices
SiC substrates are also used in the production of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and other optoelectronic devices. The super fine powder is used to create defect-free, high-purity wafers that enhance the performance and longevity of these devices.
Renewable Energy and Aerospace
Solar Wafer Cutting
China's solar industry uses green SiC powder (JIS1000–JIS2000) for slicing silicon ingots into wafers. Its uniform particle distribution ensures minimal material loss and high efficiency. The adoption of super fine SiC powder in this process has contributed to the rapid growth of China's photovoltaic industry, making it a global leader in solar energy production.
Aerospace Components
SiC's lightweight and thermal shock resistance make it suitable for rocket nozzles and turbine blades. Nano-SiC composites are being tested for radiation shielding in space applications. The use of super fine SiC powder in these composites allows for precise control over microstructure and mechanical properties, resulting in components that can withstand the extreme conditions of space and high-speed flight.
High-Performance Coatings
Super fine SiC powder is used to formulate protective coatings for aerospace, automotive, and industrial equipment. These coatings offer exceptional resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and high temperatures, extending the service life of critical components.
Metallurgical Applications
Deoxidizing and Alloying
SiC reduces oxygen content in molten steel, improving mechanical properties. Chinese products (88% SiC, 0–10mm grains) are cost-effective alternatives to ferrosilicon. The use of super fine powder ensures rapid dissolution and uniform distribution in the melt, enhancing process efficiency.
Sintering Aids
In powder metallurgy, super fine SiC powder is used as a sintering aid to promote densification and grain growth control. This results in stronger, more durable metal-matrix composites used in cutting tools, dies, and structural components.
Emerging Applications and Future Prospects
Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
The rise of additive manufacturing has opened new avenues for super fine SiC powder. It is used as a feedstock for producing complex ceramic and composite parts via selective laser sintering (SLS) and binder jetting. The fine particle size enables high resolution and intricate geometries, paving the way for customized components in aerospace, medical, and energy sectors.
Energy Storage and Batteries
Research is underway to utilize super fine SiC powder as an additive in lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. Its high thermal conductivity and chemical stability can enhance electrode performance, improve safety, and extend battery life.
Environmental and Filtration Technologies
SiC membranes and filters produced from super fine powder are used for water purification, gas separation, and industrial wastewater treatment. Their high porosity, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance make them ideal for harsh operating environments.
Conclusion
Super fine silicon carbide powder is a versatile material driving innovation across industries. From abrasives and refractories to cutting-edge electronics and aerospace, its unique properties address challenges in durability, efficiency, and performance. China's robust manufacturing ecosystem supplies tailored SiC solutions, cementing its role as a global leader in advanced materials. As industries push toward higher temperatures, miniaturization, and sustainability, super fine SiC powder will remain indispensable, powering the next wave of technological progress.
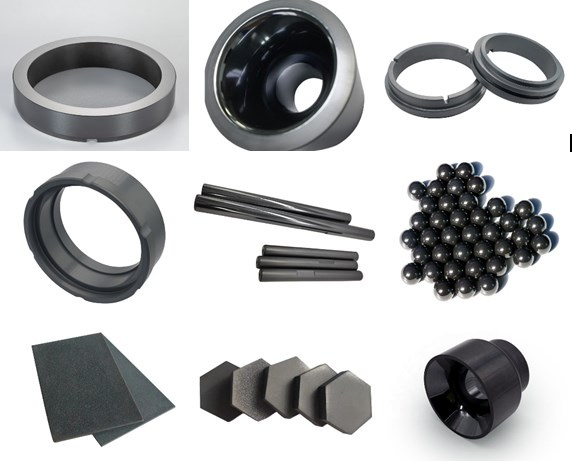

FAQ
1. What makes super fine silicon carbide powder ideal for abrasive applications?
SiC's extreme hardness (9.5 Mohs) and sharp grain edges enable efficient material removal. Chinese products offer customizable grit sizes (F12–F3000) and high purity (up to 99.9%) for precision grinding.
2. How does China contribute to the global supply of super fine SiC powder?
China produces over 70% of the world's SiC, with companies like Huamao and Antelisic offering grades for refractories, abrasives, and electronics. Their cost-effective, high-purity products dominate sectors like solar wafer cutting.
3. Can silicon carbide be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes. SiC retains strength up to 1,600°C, making it ideal for kiln shelving, furnace linings, and aerospace components. Its oxidation resistance ensures longevity in extreme conditions.
4. What are the advantages of using SiC in semiconductor manufacturing?
SiC's wide bandgap and high thermal conductivity allow devices to operate at higher voltages and temperatures, reducing energy loss in power electronics.
5. How is super fine SiC powder utilized in renewable energy technologies?
It cuts solar wafers with minimal waste and forms durable coatings for wind turbine components. SiC semiconductors also enhance efficiency in EV charging systems.
Citations:
[1] https://www.fishersci.no/shop/products/silicon-carbide-powder-superfine-600-grit-thermo-scientific-chemicals/11400064
[2] https://www.nanoshel.com/product/silicon-carbide-fine-powder
[3] https://www.antelisic.com/chinese-wholesale-super-fine-powder-silicon-carbide-products-granulated-powder-green-anteli-product/
[4] https://am-printing.com/sic-powder-20240925/
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicon_carbide
[6] https://huamaosic01.en.made-in-china.com/product/QGHRiEKvOYhX/China-Ultra-Fine-Silicon-Carbide-Powder-Black-Sic-Grit-for-Refractory-Applications-Ect.html
[7] http://www.sicah.cn/sicpowder.html
[8] https://shop.nanografi.com/blog/silicon-carbide-sic-micron-and-nano-powder/
[9] https://www.hwnanoparticles.com/superfine-sic-particle-green-beta-silicon-carbide-1-15um-product/
[10] https://www.hongfeng-abrasives.com/silicon-carbide/
[11] https://xinliabrasive.en.made-in-china.com/product/pESRltbuVQrN/China-Super-Fine-Sic-Green-Silicon-Carbide-Powder-Used-in-Polishing-Ceramic-Tube.html
[12] https://www.samaterials.com/black-silicon-carbide-ultra-fine-powder.html
[13] https://carbosystem.com/en/silicon-carbide-properties-applications/
[14] https://eastmatecarbon.en.made-in-china.com/product/UFfTHKBbfMAw/China-High-Purity-Fine-Powder-Black-Silicon-Carbide-for-Industrial-Applications.html
[15] https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/de/en/A16601.0E
[16] https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/tw/zt/A13561.36
[17] https://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/132127883074
[18] https://xinliabrasive.en.made-in-china.com/product/pESRltbuVQrN/China-Super-Fine-Sic-Green-Silicon-Carbide-Powder-Used-in-Polishing-Ceramic-Tube.html
[19] https://www.semicorex.com/silicon-carbide-sic-
[20] https://www.alibaba.com/showroom/silicon-carbide-powder-suppliers.html
[21] https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/tw/zt/A13561.0C
[22] https://www.malvernpanalytical.com/en/learn/knowledge-center/insights/highlights-from-the-future-days-semiconductor-qa-discover-key-insights-into-silicon-carbide
[23] https://pr.vwr.com/store/product/9876745/silicon-carbide-powder-superfine-600-grit
[24] https://www.goodfellow.com/global/material/compounds/carbides/silicon-carbide-powder
[25] https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/silicon-carbide-fine-powder-market-report
[26] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN1911798A/en
[27] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN100417591C/en
[28] https://www.fishersci.no/shop/products/silicon-carbide-powder-superfine-600-grit-thermo-scientific-chemicals/11400064
[29] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0272884221014772
[30] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0955221921005069
[31] https://www.nanoshel.com/product/silicon-carbide-fine-powder
[32] https://www.suoyi-group.com/product-category/carbide-powder/













