Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Radioactivity of Tungsten Carbide
>> Thoriated Tungsten Electrodes
>> Natural Radioactivity of Tungsten
● Health Implications
>> Acute Health Effects
>> Chronic Health Effects
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
>> Industrial Applications
● Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
● Comparative Analysis with Other Materials
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. Is pure tungsten carbide radioactive?
>> 2. What makes thoriated tungsten electrodes potentially hazardous?
>> 3. Are there any health risks associated with tungsten carbide?
>> 4. Can tungsten carbide be used for radiation shielding?
>> 5. What are the main applications of tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a composite material renowned for its exceptional hardness and strength, primarily utilized in industrial applications such as cutting tools, mining equipment, and jewelry. A common question arises regarding its radioactivity: Is tungsten carbide radioactive? This article will explore the properties of tungsten carbide, its composition, potential radioactivity, health implications, and its applications across various fields.

Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a chemical compound formed from tungsten and carbon in equal parts. It is a dense, hard material that is approximately three times stiffer than steel. The compound is produced through a process called sintering, where tungsten powder is mixed with carbon at high temperatures. The resulting product is a fine gray powder that can be molded into various shapes for different applications.
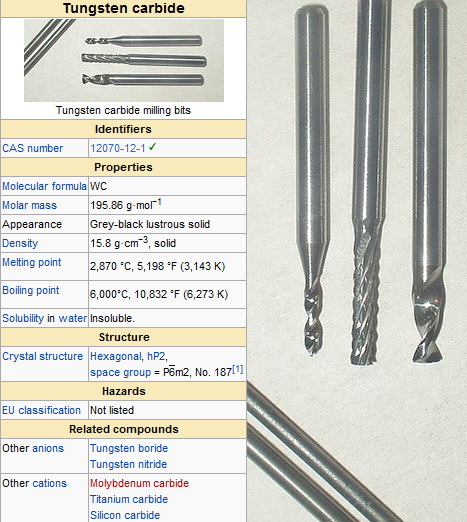
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Hardness: Tungsten carbide ranks between 9 and 9.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, making it one of the hardest materials available.
- Density: It has a specific gravity ranging from 1.5 to 2 times that of carbon steel, contributing to its effectiveness in applications requiring heavy-duty performance.
- Thermal Stability: Tungsten carbide can withstand high temperatures without losing its structural integrity, making it suitable for high-performance tools.
- Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to acids and bases, although it can be affected by hydrofluoric acid/nitric acid mixtures.
Radioactivity of Tungsten Carbide
The question of whether tungsten carbide is radioactive primarily hinges on its composition. Pure tungsten carbide (WC) itself is not radioactive. However, there are specific forms of tungsten that contain radioactive elements.
Thoriated Tungsten Electrodes
One notable example involves thoriated tungsten electrodes, which are often used in welding applications. These electrodes typically contain about 2% thorium, a naturally radioactive element. When used in welding processes, these electrodes can emit alpha radiation due to the presence of thorium. However, the radiation emitted from these electrodes is minimal because the thorium is encapsulated within the tungsten matrix, limiting exposure to external radiation.
Natural Radioactivity of Tungsten
Tungsten itself has isotopes that can exhibit low levels of radioactivity. For instance:
- Isotope Composition: Naturally occurring tungsten consists of stable isotopes and one long-lived radioactive isotope, $$^{180}W$$, which has an extremely long half-life (approximately $$1.8 \times 10^{18}$$ years). The decay rate of this isotope is negligible and poses no significant health risks.
- Artificial Isotopes: There are also artificial isotopes of tungsten that can be radioactive; however, these are not typically found in commercial products or natural deposits.
Health Implications
While tungsten carbide itself does not pose significant radioactivity risks, there are health concerns associated with exposure to tungsten carbide dust and its alloys:
- Inhalation Risks: Inhalation of tungsten carbide dust can lead to respiratory issues similar to silicosis. Prolonged exposure may result in chronic lung diseases.
- Skin Contact: Contact with tungsten carbide dust can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions.
- Cobalt Concerns: Many tungsten carbide products contain cobalt as a binder. Cobalt exposure has been associated with potential carcinogenic effects and lung diseases.
Acute Health Effects
Short-term exposure to tungsten carbide can lead to:
- Skin allergies or burns
- Eye irritation
- Gastrointestinal issues
Chronic Health Effects
Long-term exposure may result in:
- Permanent lung issues such as scarring or respiratory diseases
- Occupational asthma
- Interstitial fibrosis
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide's unique properties make it suitable for various applications:
- Cutting Tools: Its hardness allows for faster cutting speeds and longer tool life compared to traditional materials.
- Mining Equipment: Used in drill bits and mining tools due to its wear resistance.
- Jewelry: Increasingly popular in wedding bands and fashion jewelry for its durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Radiation Shielding: Recent studies suggest that tungsten carbide can serve as an effective lead-free material for radiation shielding due to its density and attenuation properties against gamma radiation.

Industrial Applications
Tungsten carbide powder finds extensive use in manufacturing cutting tools, wear-resistant components, and high-performance coatings.
- In the aerospace industry, it is utilized for specialized coating applications on engine components and landing gear systems due to its resistance to deterioration under extreme conditions.
- The automotive sector employs tungsten carbide for producing abrasion-resistant components and high-performance engine parts that enhance vehicle longevity by reducing friction and wear.
- In energy sectors, tungsten carbide-based materials are used in power generation equipment and renewable energy systems exposed to harsh environmental conditions or high mechanical stress.
Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
The production process of tungsten carbide involves several key stages:
1. Material Mixing: Tungsten powder is mixed with carbon black in a ball mill for uniformity.
2. Carburization: The mixture undergoes carburization at high temperatures (1300–1600°C) in a controlled environment.
3. Compacting: The blended powder is compacted into desired shapes using hydraulic presses.
4. Sintering: The compacted powder is heated around 1500°C to fuse the particles into a dense structure.
This meticulous process ensures the production of high-quality tungsten carbide with exceptional mechanical properties suitable for various demanding applications.
Comparative Analysis with Other Materials
When comparing tungsten carbide with traditional metals like gold and platinum used in jewelry:
| Property | Tungsten Carbide | Gold | Platinum |
| Hardness | 8.5 - 9 | 2.8 | 4.5 |
| Density | 15.63 g/cm³ | 12.42 g/cm³ | 21.45 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 2,870°C | 1,064°C | 1,768°C |
| Scratch Resistance | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Tungsten carbide offers superior strength and scratch resistance compared to traditional metals used in jewelry. Its ability to maintain its shine over time makes it an attractive option for consumers seeking durable yet stylish pieces.
Conclusion
In summary, pure tungsten carbide is not radioactive. However, certain forms containing thorium or other radioactive elements may pose minimal radiation risks in specific contexts like welding. The primary health concerns related to tungsten carbide arise from inhalation of dust or exposure to cobalt-containing alloys rather than radioactivity itself. Tungsten carbide remains a vital material across various industries due to its remarkable physical properties and versatility in applications ranging from cutting tools to jewelry manufacturing.
FAQs
1. Is pure tungsten carbide radioactive?
No, pure tungsten carbide is not radioactive.
2. What makes thoriated tungsten electrodes potentially hazardous?
Thoriated tungsten electrodes contain about 2% thorium, which is radioactive and can emit alpha radiation during use.
3. Are there any health risks associated with tungsten carbide?
Yes, inhalation of tungsten carbide dust can lead to respiratory issues while skin contact may cause irritation or allergic reactions.
4. Can tungsten carbide be used for radiation shielding?
Yes, recent studies indicate that tungsten carbide can effectively replace lead as a radiation shielding material due to its density and attenuation properties.
5. What are the main applications of tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is widely used in cutting tools, mining equipment, jewelry manufacturing, and radiation shielding materials.
Citations:
[1] https://www.linde-amt.com/resource-library/articles/tungsten-carbide-powder
[2] https://int-enviroguard.com/blog/tungsten-carbide-exposure-are-your-workers-at-risk/
[3] https://www.nobbier.com/blogs/editorial/tungsten-in-jewelry-everything-you-need-to-know/
[4] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-49842-3
[5] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/90_how-is-tungsten-carbide-made-.html
[6] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[7] http://metalpedia.asianmetal.com/metal/tungsten/health.shtml
[8] https://tiara.com.sg/blogs/tungsten-carbide-rings/why-tungsten-carbide-rings-are-dominating-the-jewelry-scene
[9] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38228643/
[10] https://grafhartmetall.com/en/sinter-process-of-tungsten-carbide/
[11] https://www.itia.info/applications-markets/
[12] https://nj.gov/health/eoh/rtkweb/documents/fs/1960.pdf
[13] https://redwoodrings.com/blogs/redwood-rings-blog/how-are-tungsten-rings-made-an-in-depth-exploration-1
[14] https://marshield.com/shielding-options-lead-vs-tungsten
[15] https://todaysmachiningworld.com/magazine/how-it-works-making-tungsten-carbide-cutting-tools/
[16] https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/80/Drill_bit_2-italy.JPG/220px-Drill_bit_2-italy.JPG?sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwidxefAlKCLAxWpJ0QIHTcoHNUQ_B16BAgIEAI
[17] https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/PHS/PHS.aspx?phsid=804&toxid=157
[18] https://jewelrybyjohan.com/en-de/blogs/metals-and-materials/the-pros-and-cons-of-tungsten-rings
[19] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/375053636_Tungsten_carbide_for_radiation_shielding_A_comprehensive_review
[20] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/process.html
















