Content Menu
● Understanding Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● The Magnetic Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Why Is This Important?
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
● Comparison with Other Materials
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Is pure tungsten magnetic?
>> 2. What affects the magnetism of tungsten carbide?
>> 3. Can tungsten carbide be used safely in MRI environments?
>> 4. What are the main applications of tungsten carbide?
>> 5. How does cobalt affect the properties of tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide, a compound formed from tungsten and carbon, is renowned for its exceptional hardness and durability. However, a common question arises regarding its magnetic properties: Is tungsten carbide magnetic? This article delves into the nature of tungsten carbide, its composition, the factors that influence its magnetism, and its various applications.

Understanding Tungsten Carbide
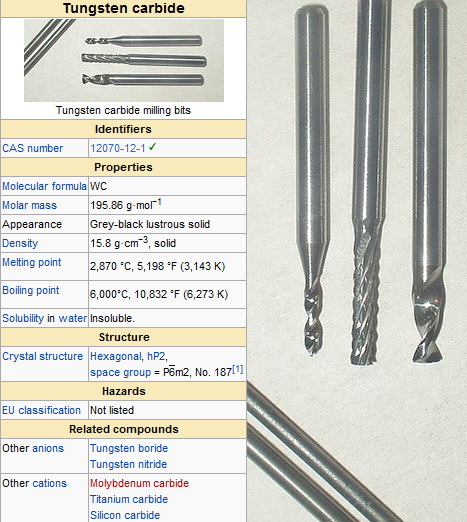
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a chemical compound that consists of equal parts tungsten (W) and carbon (C). It is primarily known for its hardness, which ranks between 9 and 9.5 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond. Due to this unique property, tungsten carbide is widely used in various applications, including cutting tools, mining equipment, jewelry, and industrial machinery.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Density: Tungsten carbide has a density of approximately 15.63 g/cm³.
- Hardness: It typically exhibits a hardness of about 18-22 GPa.
- Melting Point: The melting point of tungsten carbide is around 2,870 °C (5,200 °F).
- Thermal Conductivity: It has a thermal conductivity of about 110 W/m·K.
These properties make tungsten carbide an ideal material for high-stress applications where durability and resistance to wear are crucial.
The Magnetic Properties of Tungsten Carbide
The magnetic behavior of tungsten carbide is influenced by several factors:
- Composition: Pure tungsten itself is not magnetic; it exhibits weak paramagnetic properties. However, when combined with carbon to form tungsten carbide, the material's magnetic characteristics can change depending on the binder used during manufacturing.
- Binder Metals: Tungsten carbide is often produced using binder metals such as cobalt or nickel. Cobalt is ferromagnetic and can impart magnetic properties to tungsten carbide if present in significant amounts. Conversely, nickel-bound tungsten carbide tends to be less magnetic due to nickel's lower susceptibility to magnetism compared to cobalt.
- Grade Variations: Different grades of tungsten carbide contain varying amounts of binder materials. For instance:
- Pure Tungsten Carbide: Non-magnetic.
- Tungsten Carbide with Cobalt (6-15%): Weakly magnetic.
- Tungsten Carbide with Higher Cobalt Content (15-30%): More noticeably magnetic.
- Tungsten Carbide with Nickel: Generally non-magnetic or weakly magnetic.
Why Is This Important?
Understanding whether tungsten carbide is magnetic is crucial for various industries and applications:
- Jewelry: Many people are concerned about the magnetism of tungsten carbide rings, especially for MRI safety. Rings made from pure tungsten carbide without ferromagnetic binders are safe for MRI environments.
- Industrial Applications: In manufacturing settings where magnetic fields are present, selecting the appropriate grade of tungsten carbide can prevent unwanted interactions with machinery or electronic components.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Due to its remarkable properties, tungsten carbide finds applications in numerous fields:
1. Cutting Tools: Used in drills, saw blades, and milling tools due to its hardness and wear resistance. Its cutting speed is significantly higher than that of carbon steel.
2. Mining Equipment: Essential for drill bits and other tools that require extreme durability against abrasive materials. More than half of the tungsten carbide produced goes into mining and drilling applications.
3. Jewelry: Increasingly popular for wedding bands and other decorative items due to its scratch resistance and aesthetic appeal.
4. Industrial Machinery: Employed in components that face high wear and tear, including pumps, valves, and compressors.
5. Aerospace and Defense: Utilized in armor-piercing ammunition and other high-stress applications due to its density and hardness.
6. Medical Tools: Surgical instruments often feature tungsten carbide tips or blades because they can maintain sharp edges longer than stainless steel or titanium counterparts.
7. Wear Parts: Widely used in manufacturing wear-resistant parts such as wire drawing dies and mechanical components that experience high friction.
8. Chemical Processing Equipment: Its chemical inertness makes it suitable for use in environments where corrosion resistance is critical.
9. Precision Instruments: Due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, tungsten carbide maintains dimensional stability under varying temperatures, making it ideal for precision engineering applications.
Comparison with Other Materials
When evaluating materials for specific applications, it's essential to compare tungsten carbide with alternatives like titanium carbide or high-speed steel:
| Property | Tungsten Carbide | Titanium Carbide | High-Speed Steel |
| Hardness | 18-22 GPa | 28-35 GPa | 7-8 GPa |
| Toughness | High | Moderate | High |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
Tungsten carbide stands out due to its combination of hardness and toughness, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications where other materials may fail.
Conclusion
In summary, tungsten carbide itself is not inherently magnetic; however, its magnetic properties can vary significantly based on the binder metals used during its production. Cobalt-bound tungsten carbide exhibits more pronounced magnetic characteristics than nickel-bound variants. Understanding these nuances helps in selecting the right type of tungsten carbide for specific applications across various industries.

FAQ
1. Is pure tungsten magnetic?
No, pure tungsten is not magnetic; it exhibits weak paramagnetic properties.
2. What affects the magnetism of tungsten carbide?
The magnetism of tungsten carbide is influenced by the type and amount of binder metals used during manufacturing, such as cobalt or nickel.
3. Can tungsten carbide be used safely in MRI environments?
Yes, pure tungsten carbide without ferromagnetic binders (like cobalt) is safe for MRI environments.
4. What are the main applications of tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is used in cutting tools, mining equipment, jewelry, industrial machinery, medical tools, wear parts, chemical processing equipment, and precision instruments.
5. How does cobalt affect the properties of tungsten carbide?
Cobalt is ferromagnetic; thus, higher cobalt content in tungsten carbide increases its magnetic properties compared to nickel-bound variants.
Citations:
[1] https://www.refractorymetal.org/tungsten-carbide-uses-properties.html
[2] https://blog.goldsupplier.com/is-tungsten-carbide-magnetic/
[3] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/applications-tungsten-carbide-zzbettercarbide
[4] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/79_tungsten-carbide-vs-titanium-carbide.html
[5] https://carbideprocessors.com/pages/carbide-parts/tungsten-carbide-properties.html
[6] https://www.boyiprototyping.com/materials-guide/is-tungsten-magnetic/
[7] https://www.samaterials.com/content/application-of-tungsten-in-modern-industry.html
[8] https://www.samaterials.com/content/cemented-carbide-vs-tungsten-steel.html
[9] https://scienceinfo.com/tungsten-carbide-properties-applications/
[10] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/why-use-tungsten-carbide-over-other-metals/
[11] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[12] https://blog.carbideprocessors.com/tungsten-carbide/tungsten-carbide-and-magnetism/
[13] https://www.carbide-usa.com/top-5-uses-for-tungsten-carbide/
[14] https://grafhartmetall.com/en/what-is-the-difference-between-ceramics-and-tungsten-carbide/
[15] https://eurobalt.net/blog/2022/03/28/all-the-applications-of-tungsten-carbide/
[16] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/tungsten-carbide-magnetic-shijin-lei
[17] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[18] https://ewsllp.in/why-to-choose-tungsten-carbide-over-other-metals/
[19] https://hmaking.com/is-tungsten-magnetic/
[20] https://www.durit.com/industries
[21] https://www.itia.info/applications-markets/
[22] http://www.stratigery.com/posts/tungsten-carbide-magnetism/
[23] https://www.sollex.se/en/blog/post/about-cemented-tungsten-carbide-applications-part-1
















