Content Menu
● Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
● Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
● Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
● Environmental and Health Considerations
● Recycling of Tungsten Carbide
● Future Developments and Innovations
● Economic Impact of Tungsten Carbide
● Global Market Trends
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What is Tungsten Carbide?
>> 2. Is Tungsten Carbide an Alloy?
>> 3. What are the Primary Applications of Tungsten Carbide?
>> 4. How is Tungsten Carbide Manufactured?
>> 5. Can Tungsten Carbide be Recycled?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide, with the chemical formula WC, is a compound made from equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. It is renowned for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and durability, making it an indispensable material in various industrial applications. However, the question of whether tungsten carbide is an element often arises due to its unique properties and uses. In this article, we will delve into the nature of tungsten carbide, its properties, applications, and clarify its classification as a compound rather than an element.

Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is not an element but a chemical compound. Elements are substances that consist of only one type of atom, whereas compounds are formed when atoms of different elements bond together. Tungsten carbide is composed of tungsten (W) and carbon (C) atoms in a 1:1 ratio, making it a compound rather than an element.
The chemical structure of tungsten carbide is crucial for its properties. It has a hexagonal crystal structure, which contributes to its high hardness and stability. This structure is vital for its applications in cutting tools and wear-resistant parts.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is known for its remarkable properties, which make it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications:
- Hardness: Tungsten carbide ranks about 9.0–9.5 on the Mohs scale, comparable to diamond in terms of hardness. This makes it ideal for cutting through hard materials like steel and titanium.
- Wear Resistance: It offers excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools and machinery parts that are subject to high friction and abrasion.
- Thermal Conductivity: Tungsten carbide has a high thermal conductivity of about 110 W/(m·K), which is beneficial for heat dissipation in high-temperature applications.
- Density: With a density of approximately 15.6 g/cm³, it is significantly denser than many other materials like steel or titanium.
These properties combined make tungsten carbide a versatile material that can withstand extreme conditions.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties:
- Cutting Tools: It is used in the manufacture of drills, milling cutters, taps, and saw blades for cutting difficult materials like steel and titanium. The high hardness and wear resistance ensure that these tools maintain their cutting efficiency over time.
- Injection Molding Tools: Precision molds for plastic injection molding are made from tungsten carbide due to its high precision and durability. This ensures that the molds can withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the molding process.
- Wear and Corrosion-Resistant Parts: Tungsten carbide is used in the oil and gas, mining, and pulp and paper industries for parts that require high wear resistance and corrosion resistance. These parts include nozzles, valves, and other components that are exposed to harsh environments.
Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
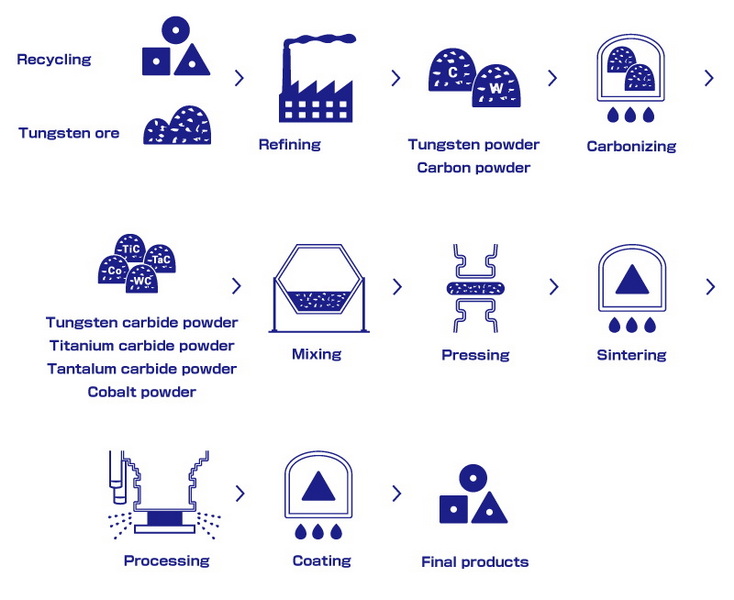
Tungsten carbide is typically produced through a powder metallurgy process:
1. Raw Materials: Tungsten ore is processed into tungsten metal powder, which is then combined with carbon sources like graphite or soot.
2. Carburization: The tungsten metal powder is converted into tungsten carbide through a high-temperature carburization process. This step involves heating the mixture in a furnace to form the WC compound.
3. Sintering: The tungsten carbide powder is mixed with a metallic binder (usually cobalt) and then sintered at high temperatures to form a solid composite. The cobalt binder helps to improve the toughness and ductility of the final product.
The sintering process is critical as it determines the final properties of the tungsten carbide product. Adjusting the sintering conditions can optimize the material's performance for specific applications.
Environmental and Health Considerations
While tungsten carbide is a valuable material, its production and use also raise environmental and health concerns:
- Environmental Impact: The mining of tungsten can have significant environmental impacts, including deforestation and water pollution. Efforts are being made to improve mining practices and reduce waste.
- Health Risks: Workers involved in the production of tungsten carbide may be exposed to dust and other hazardous materials. Proper safety measures, such as ventilation systems and protective gear, are essential to mitigate these risks.
Recycling of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide can be recycled, which is important for conserving resources and reducing waste. Worn-out tools and scrap material can be reclaimed and reused, reducing the need for new raw materials. This recycling process involves collecting and sorting the scrap, followed by a refining process to extract the tungsten and other valuable metals.
Recycling not only helps in reducing environmental impacts but also supports sustainable practices in industries that rely heavily on tungsten carbide.
Future Developments and Innovations
Research into tungsten carbide continues to explore new applications and improvements in manufacturing techniques. Advances in nanotechnology and composite materials are expected to enhance the performance of tungsten carbide products further. Additionally, efforts to develop more sustainable production methods and reduce environmental impacts are ongoing.
These innovations will likely expand the use of tungsten carbide into new fields, such as aerospace and biomedical applications, where its unique properties can offer significant advantages.
Economic Impact of Tungsten Carbide
The economic impact of tungsten carbide is substantial, as it plays a critical role in various industries. The demand for tungsten carbide is driven by its applications in manufacturing and construction, which are essential sectors of many economies. Moreover, the recycling of tungsten carbide contributes to cost savings and resource conservation, further enhancing its economic benefits.
Global Market Trends
The global market for tungsten carbide is influenced by factors such as supply chain dynamics, technological advancements, and regulatory policies. The market is expected to grow as demand increases from emerging industries and applications. However, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and environmental regulations must be addressed to sustain this growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tungsten carbide is not an element but a compound composed of tungsten and carbon atoms. Its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal properties make it a crucial material in various industrial applications, from cutting tools to wear-resistant parts. Understanding its properties and applications helps clarify its role in modern industry.

FAQs
1. What is Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide is a chemical compound made from equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. It is renowned for its hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools and machinery parts.
2. Is Tungsten Carbide an Alloy?
No, tungsten carbide is not an alloy. It is a compound formed by the chemical bonding of tungsten and carbon atoms. Alloys are mixtures of metals, whereas tungsten carbide is a distinct compound with covalent bonds between its constituent atoms.
3. What are the Primary Applications of Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide is primarily used in cutting tools, injection molding tools, and wear-resistant parts in industries such as oil and gas, mining, and pulp and paper.
4. How is Tungsten Carbide Manufactured?
Tungsten carbide is manufactured through a powder metallurgy process involving carburization and sintering with a metallic binder like cobalt.
5. Can Tungsten Carbide be Recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled. Worn-out tools and scrap material can be reclaimed and reused, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Citations:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[2] https://www.sollex.se/en/blog/post/about-cemented-tungsten-carbide-applications-part-1
[3] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/90_how-is-tungsten-carbide-made-.html
[4] https://www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/9whr5d/is_tungsten_carbide_an_alloy/
[5] https://www.istockphoto.com/photos/tungsten-carbide
[6] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/tungsten-carbide.html
[7] https://www.retopz.com/57-frequently-asked-questions-faqs-about-tungsten-carbide/
[8] https://www.thermalspray.com/questions-tungsten-carbide/
[9] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/features.html
[10] https://www.linde-amt.com/resource-library/articles/tungsten-carbide
[11] https://tuncomfg.com/about/faq/
[12] https://www.hit-tw.com/newsdetails.aspx?nid=298
[13] https://carbideprocessors.com/pages/carbide-parts/tungsten-carbide-properties.html
[14] https://www.dymetalloys.co.uk/what-is-tungsten-carbide
[15] https://www.azom.com/properties.aspx?ArticleID=1203
[16] https://www.webelements.com/compounds/tungsten/tungsten_carbide.html
[17] https://consolidatedresources.com/blog/10-facts-about-tungsten-carbide/
[18] https://periodic-table.rsc.org/element/74/tungsten
[19] https://www.gettyimages.hk/%E5%9C%96%E7%89%87/tungsten-carbide?page=3
[20] https://www.shutterstock.com/search/tungsten-carbide
[21] https://www.istockphoto.com/photos/tungsten-carbide?page=2
[22] https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/tungsten
[23] https://www.shutterstock.com/search/%22tungsten-carbide%22?page=3
[24] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/frequently-asked-questions-used-tungsten-carbide-inserts/
[25] https://www.tungstenringsco.com/faq
[26] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[27] https://www.britannica.com/science/tungsten-carbide
[28] https://eurobalt.net/blog/2022/03/28/all-the-applications-of-tungsten-carbide/
[29] https://www.hyperionmt.com/en/products/Carbide-Rolls/grade-data/
[30] https://www.cbceratizit.com/en/product-566387/Tungsten-Carbide-Grade.html
[31] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten
[32] https://periodictable.com/Elements/074/pictures.html
[33] https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/tungsten-carbide
[34] http://picture.chinatungsten.com/list-18.html
















