Content Menu
● The Nature of Tungsten Carbide
>> Chemical Composition
>> Physical Properties
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
>> Industrial Applications
>> Specialized Applications
>> Consumer Applications
● Tungsten Carbide vs. Pure Tungsten
>> Key Differences
>> Comparative Applications
● Manufacturing Process
● Environmental and Economic Considerations
>> Recycling
>> Economic Impact
● Future Prospects
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the main difference between tungsten carbide and pure tungsten?
>> 2. Why is tungsten carbide used in cutting tools?
>> 3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
>> 4. Is tungsten carbide suitable for jewelry?
>> 5. What are some emerging applications for tungsten carbide?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide, a remarkable compound of tungsten and carbon, is often mistaken for pure tungsten due to its similar properties and applications. However, these two materials are distinct, each with unique characteristics and uses. This article will explore the nature of tungsten carbide, its properties, applications, and how it differs from pure tungsten.

The Nature of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a chemical compound consisting of equal parts tungsten and carbon atoms[1]. It is not pure tungsten, but rather an alloy that combines the strengths of both elements. This compound is known for its exceptional hardness, density, and heat resistance, making it a valuable material in various industries.
Chemical Composition
The chemical formula for tungsten carbide is WC. In this compound:
- W represents tungsten
- C represents carbon
The bonding between these atoms results in a material that is significantly harder than pure tungsten while retaining many of its desirable properties.
Physical Properties
Tungsten carbide boasts an impressive array of physical properties:
1. Hardness: With a hardness second only to diamond, tungsten carbide is extremely resistant to wear and deformation[4].
2. Density: It has approximately double the density of steel, contributing to its strength and durability[1].
3. Melting Point: While not as high as pure tungsten, tungsten carbide still has a very high melting point, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
4. Electrical Conductivity: Tungsten carbide can be formed to conduct electricity, adding to its versatility[4].
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
The unique properties of tungsten carbide make it an invaluable material in numerous industries and applications.
Industrial Applications
1. Cutting Tools: Tungsten carbide is extensively used in the manufacture of cutting tools such as drills, milling cutters, and saw blades[10]. Its hardness and wear resistance allow these tools to cut through tough materials like steel and titanium efficiently.
2. Mining and Drilling: The material's durability makes it ideal for drill bits and other equipment used in mining and foundation drilling[5].
3. Wear Parts: Industries such as oil and gas, mining, and pulp and paper use tungsten carbide parts in machinery subjected to high stress and wear[10].
4. Injection Molding: Precision molds for plastic injection molding often use tungsten carbide due to its high precision and durability[10].
Specialized Applications
1. Ammunition: Tungsten carbide's density and hardness make it suitable for armor-piercing rounds[1][4].
2. Nuclear Industry: The material's properties make it useful in various applications within the nuclear sector[5].
3. Aerospace: Tungsten carbide finds use in the aerospace industry due to its heat resistance and strength[4].
4. Electronics: The compound is used in various electrical components, including light bulbs, due to its heat-resistant properties[4].
Consumer Applications
1. Jewelry: Tungsten carbide's scratch resistance and lustrous appearance have made it popular in jewelry making[4][7].
2. Sports Equipment: Golf club heads often incorporate tungsten carbide for improved performance[4].
3. Writing Instruments: The tips of ballpoint pens frequently use tungsten carbide due to its durability[4].
Tungsten Carbide vs. Pure Tungsten
While tungsten carbide and pure tungsten share some similarities, they are distinct materials with different properties and applications.
Key Differences
1. Hardness: Tungsten carbide is significantly harder than pure tungsten.
2. Brittleness: Pure tungsten is more ductile, while tungsten carbide is more brittle.
3. Melting Point: Pure tungsten has a higher melting point than tungsten carbide.
4. Electrical Conductivity: Pure tungsten is a better electrical conductor than tungsten carbide.
Comparative Applications
Some applications where the choice between tungsten carbide and pure tungsten matters:
1. Cutting Tools: Tungsten carbide is preferred due to its superior hardness and wear resistance.
2. Electrical Contacts: Pure tungsten is often chosen for its better electrical conductivity.
3. High-Temperature Applications: While both materials perform well, pure tungsten's higher melting point makes it preferable in extreme heat situations.、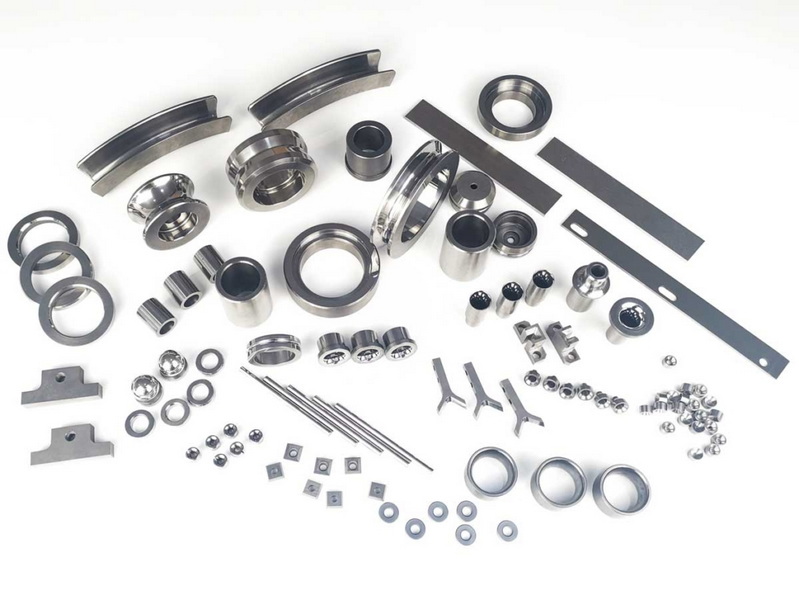
Manufacturing Process
The production of tungsten carbide involves several steps:
1. Powder Production: Tungsten and carbon powders are mixed in precise ratios.
2. Pressing: The powder mixture is compressed into the desired shape.
3. Sintering: The pressed shape is heated to high temperatures, causing the particles to bond.
4. Finishing: The sintered product may undergo additional machining or polishing.
This process, known as powder metallurgy, allows for the creation of complex shapes with high precision.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
Recycling
Tungsten carbide is highly recyclable, which is beneficial both economically and environmentally[4]. The recycling process helps to conserve the limited tungsten resources and reduce energy consumption in production.
Economic Impact
The versatility and durability of tungsten carbide make it a valuable material in many industries. Its use can lead to:
- Increased tool life
- Improved manufacturing efficiency
- Reduced material waste
These factors contribute to cost savings and productivity improvements across various sectors.
Future Prospects
As technology advances, new applications for tungsten carbide continue to emerge. Some areas of potential growth include:
1. Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing with tungsten carbide powders could enable the creation of complex, high-performance parts.
2. Nanotechnology: Tungsten carbide nanoparticles may find use in advanced catalysts and sensors.
3. Sustainable Energy: The material's properties could make it valuable in certain renewable energy technologies.
Conclusion
Tungsten carbide, while not pure tungsten, is a remarkable compound that combines the best properties of tungsten and carbon. Its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat tolerance make it an indispensable material in numerous industries. From cutting tools and mining equipment to jewelry and sports gear, tungsten carbide's applications are diverse and continually expanding.
As we look to the future, the importance of tungsten carbide is likely to grow. Its recyclability and the ongoing development of new applications ensure that this versatile material will continue to play a crucial role in technological advancement and industrial efficiency.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between tungsten carbide and pure tungsten?
The main difference lies in their composition and properties. Tungsten carbide is a compound of tungsten and carbon, while pure tungsten is an element. Tungsten carbide is significantly harder but more brittle than pure tungsten, which is more ductile. Tungsten carbide also has a lower melting point compared to pure tungsten.
2. Why is tungsten carbide used in cutting tools?
Tungsten carbide is used in cutting tools due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. These properties allow tungsten carbide tools to maintain their sharp edges for longer periods, even when cutting through tough materials like steel or titanium. This results in improved efficiency and longer tool life compared to tools made from other materials.
3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide is highly recyclable. The recycling process helps conserve limited tungsten resources and reduces energy consumption in production. This recyclability makes tungsten carbide an environmentally friendly choice for many applications, contributing to its economic value and sustainability.
4. Is tungsten carbide suitable for jewelry?
Tungsten carbide has become increasingly popular in jewelry making, particularly for wedding bands and men's jewelry. Its popularity stems from its scratch resistance, durability, and lustrous appearance. However, it's important to note that due to its hardness, tungsten carbide jewelry cannot be resized like traditional gold or silver rings.
5. What are some emerging applications for tungsten carbide?
Emerging applications for tungsten carbide include its use in additive manufacturing (3D printing), where tungsten carbide powders could be used to create complex, high-performance parts. In nanotechnology, tungsten carbide nanoparticles show promise for use in advanced catalysts and sensors. Additionally, the material's unique properties may make it valuable in certain sustainable energy technologies, though specific applications are still being researched and developed.
Citations:
[1] https://eurobalt.net/blog/2022/03/28/all-the-applications-of-tungsten-carbide/
[2] https://www.itia.info/applications-markets/
[3] https://www.acadbox.com/writing-skills-for-english-papers/
[4] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[6] https://www.iikx.com/news/article/11047.html
[7] https://www.carbide-usa.com/top-5-uses-for-tungsten-carbide/
[8] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/use.html
[9] https://jdn.ucas.ac.cn/public/uploads/files/621b288368bc8.pdf
[10] https://www.sollex.se/en/blog/post/about-cemented-tungsten-carbide-applications-part-1
[11] https://web.xidian.edu.cn/ysxu/files/6266402e5ec45.pdf
















