Content Menu
● Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
>> Properties of Tungsten Carbide
● Production Process Overview
>> Challenges of Making Tungsten Carbide at Home
● Theoretical Steps for Making Tungsten Carbide at Home
>> Step 1: Acquiring Raw Materials
>> Step 2: Mixing the Powders
>> Step 3: Compacting the Mixture
>> Step 4: Sintering
>> Step 5: Machining
● Advanced Techniques and Considerations
>> Using Alternative Binders
>> Enhancing Thermal Conductivity
>> Recycling Tungsten Carbide
● Safety Precautions
● Applications of Tungsten Carbide
● Future Developments
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the primary components of tungsten carbide?
>> 2. Why is tungsten carbide so hard?
>> 3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
>> 4. What are some common applications of tungsten carbide?
>> 5. Is it safe to handle tungsten carbide powders at home?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is a highly sought-after material due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal properties. It is widely used in industrial applications, including cutting tools, wear components, and even in the aerospace and oil industries. However, making tungsten carbide at home is not a straightforward process and requires careful consideration of safety, equipment, and materials. This article will guide you through the theoretical process of producing tungsten carbide, highlighting the challenges and limitations of attempting this at home.

Introduction to Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a chemical compound consisting of tungsten and carbon atoms. It is typically combined with a metallic binder, such as cobalt or nickel, to enhance its toughness and ductility. The resulting cermet (ceramic-metallic composite) offers superior hardness and wear resistance compared to most metals and alloys.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Hardness and Wear Resistance: Tungsten carbide is renowned for its hardness, which is second only to diamond. This property makes it ideal for cutting tools and wear components.
- Thermal Properties: It has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to maintain its structural integrity in high-temperature environments.
- Chemical Resistance: Tungsten carbide exhibits excellent resistance to acids and alkaline solutions, making it suitable for applications in corrosive environments.
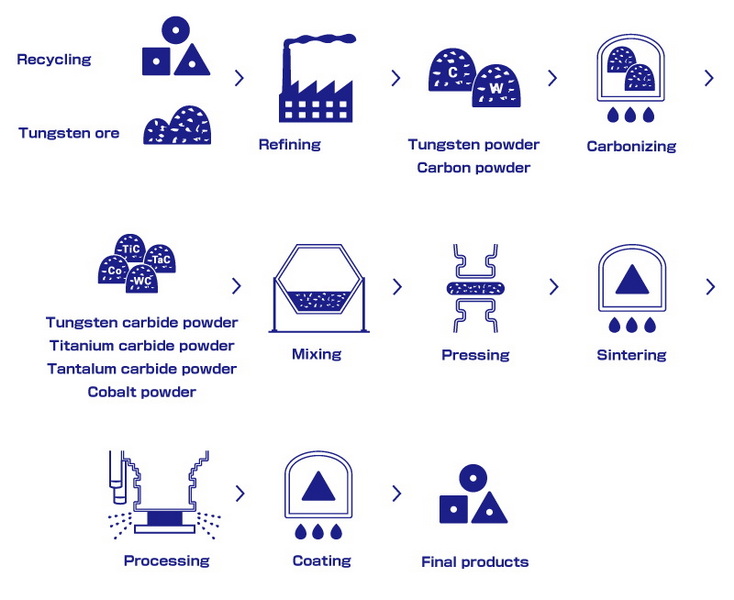
Production Process Overview
The industrial production of tungsten carbide involves several complex steps:
1. Raw Material Preparation: Tungsten and carbon powders are mixed with a binder material like cobalt or nickel.
2. Sintering: The mixture is then sintered at high temperatures (typically around 1400°C) in a vacuum or hydrogen atmosphere to form a solid tungsten carbide structure.
3. Machining: The sintered carbide is machined into the desired shape using diamond tools.
4. Coating (Optional): Additional coatings may be applied to enhance wear resistance and other properties.
Challenges of Making Tungsten Carbide at Home
While it is theoretically possible to attempt making tungsten carbide at home, several challenges arise:
- Safety Concerns: Handling tungsten and carbon powders requires proper safety equipment to avoid inhalation risks.
- Equipment Limitations: Achieving the high temperatures required for sintering is difficult without specialized furnaces.
- Material Quality: Ensuring the purity and consistency of raw materials is crucial for producing high-quality tungsten carbide.
Theoretical Steps for Making Tungsten Carbide at Home
Step 1: Acquiring Raw Materials
You would need to obtain tungsten powder, carbon powder (e.g., graphite), and a binder material like cobalt or nickel. These materials can be sourced from chemical suppliers, but ensuring their purity is essential.
Step 2: Mixing the Powders
Mix the tungsten, carbon, and binder powders in a specific ratio. This step requires careful handling to avoid contamination and ensure uniform distribution.
Step 3: Compacting the Mixture
Use a press or mold to compact the powder mixture into a shape that can be sintered. This step requires significant force to achieve the desired density.
Step 4: Sintering
Sintering requires heating the compacted mixture to a high temperature (around 1400°C) in a controlled atmosphere. This step is the most challenging to replicate at home due to the need for specialized furnaces.
Step 5: Machining
After sintering, the tungsten carbide needs to be machined into the desired shape using diamond tools. This step requires precision and specialized equipment.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
Using Alternative Binders
In industrial settings, various binders are used to enhance specific properties of tungsten carbide. For example, cobalt is commonly used for its ability to improve toughness, while nickel can enhance corrosion resistance.
Enhancing Thermal Conductivity
Tungsten carbide's thermal conductivity can be improved by optimizing the sintering process and using additives that enhance heat transfer properties.
Recycling Tungsten Carbide
Recycling tungsten carbide is an important aspect of its lifecycle. It involves collecting and processing used carbide tools to extract tungsten and other valuable materials, which can then be reused in new products.
Safety Precautions
When handling tungsten carbide powders, it is crucial to wear protective gear, including masks, gloves, and safety glasses. Inhaling these powders can pose serious health risks, and proper ventilation is essential.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is used in a wide range of applications due to its unique properties:
- Cutting Tools: Tungsten carbide is used in drill bits, saw blades, and other cutting tools for its ability to withstand high wear and maintain sharpness.
- Wear Components: It is used in parts that are subject to high friction and wear, such as bearings and bushings.
- Aerospace Industry: Tungsten carbide is used in rocket nozzles and other components due to its high melting point and resistance to extreme conditions.
- Oil and Gas Industry: It is used in drilling equipment for its hardness and resistance to corrosion.
Future Developments
Research into tungsten carbide continues to explore new applications and improvements in production techniques. Advances in sintering technologies and the development of new binders are expected to enhance its properties further.
Conclusion
While it is theoretically possible to outline the steps for making tungsten carbide at home, the practical challenges and safety concerns make it highly impractical. The process requires specialized equipment and expertise, making industrial production the most viable option for high-quality tungsten carbide. However, understanding the process can provide valuable insights into the properties and applications of this versatile material.

FAQ
1. What are the primary components of tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide primarily consists of tungsten and carbon atoms, often combined with a metallic binder like cobalt or nickel to enhance toughness.
2. Why is tungsten carbide so hard?
Tungsten carbide's hardness is due to the strong bond between tungsten and carbon atoms, which creates a rigid crystal structure.
3. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled. It is one of the best candidates for recycling due to its high value and the ability to reuse it in various applications.
4. What are some common applications of tungsten carbide?
Tungsten carbide is commonly used in cutting tools, wear components, aerospace, oil drilling equipment, and even in surgical instruments due to its hardness and corrosion resistance.
5. Is it safe to handle tungsten carbide powders at home?
Handling tungsten and carbon powders requires proper safety equipment to avoid inhalation risks. It is not recommended to handle these materials without adequate protective gear.
Citations:
[1] https://www.tool-tool.com/news/201202/cutting-tool-manufacturing-process/index.html
[2] https://www.linde-amt.com/resource-library/articles/tungsten-carbide
[3] https://www.carbide-products.com/blog/tungsten-carbide-production-process/
[4] https://carbideprocessors.com/pages/carbide-parts/tungsten-carbide-properties.html
[5] https://www.allied-material.co.jp/en/techinfo/tungsten_carbide/process.html
[6] https://www.tungco.com/insights/blog/5-tungsten-carbide-applications/
[7] https://www.refractorymetal.org/tungsten-carbide-production-method.html
[8] https://www.carbide-usa.com/top-5-uses-for-tungsten-carbide/
[9] https://www.carbide-products.com/blog/how-tungsten-carbide-parts-made/
















