Content Menu
● The Composition of Tungsten Carbide
● The Role of Cobalt in Tungsten Carbide
● Manufacturing Process
● Properties of Cobalt-Containing Tungsten Carbide
● Applications of Cobalt-Containing Tungsten Carbide
● Alternatives to Cobalt
● Environmental and Health Considerations
● Identifying Genuine Tungsten Carbide
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Is tungsten carbide magnetic?
>> 2. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
>> 3. Is tungsten carbide safe to wear as jewelry?
>> 4. How does tungsten carbide compare to other hard materials like diamond?
>> 5. Can tungsten carbide be resized or repaired?
● Citations:
Tungsten carbide is a remarkable material known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and durability. It has found widespread use in various industries, from cutting tools to jewelry. However, there's often confusion about its composition, particularly regarding the presence of cobalt. This article will explore the nature of genuine genuine tungsten carbide, its composition, and the role of cobalt in its production and properties.

The Composition of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide, in its purest form, is a chemical compound with the formula WC. It consists of equal parts tungsten and carbon atoms[1][2]. This compound is a fine gray powder that can be pressed and formed into various shapes through a process called sintering.
However, when we talk about "tungsten carbide" in most practical applications, we're often referring to a composite material rather than pure WC. This composite typically includes a binder metal, and the most common binder used is cobalt.
The Role of Cobalt in Tungsten Carbide
Cobalt plays a crucial role in the production and properties of tungsten carbide composites, often referred to as cemented carbides or hardmetals. Here's why cobalt is frequently included:
1. Binding Agent: Cobalt acts as a binder, holding the tungsten carbide particles together. During the sintering process, cobalt melts and flows between the WC grains, creating a strong bond[3].
2. Improved Toughness: While pure tungsten carbide is extremely hard, it can be brittle. The addition of cobalt enhances the material's toughness, making it more resistant to cracking and chipping[4].
3. Balancing Properties: The amount of cobalt can be adjusted to balance hardness and toughness for specific applications. Typically, the cobalt content ranges from 3% to 30% by weight[3].
4. Enhanced Workability: Cobalt's presence makes the material more workable, allowing for easier shaping and forming during manufacturing.
Manufacturing Process
The production of cobalt-containing tungsten carbide involves several steps:
1. Powder Preparation: Tungsten carbide powder is mixed with cobalt powder in predetermined proportions.
2. Pressing: The powder mixture is compressed into the desired shape.
3. Sintering: The pressed form is heated to temperatures between 1,400°C and 1,600°C. At these temperatures, cobalt melts and partially dissolves the tungsten carbide grains[5].
4. Cooling: As the material cools, the cobalt solidifies, binding the tungsten carbide particles together.
Properties of Cobalt-Containing Tungsten Carbide
The inclusion of cobalt in tungsten carbide results in a material with remarkable properties:
1. Hardness: While slightly less hard than pure WC, cobalt-containing tungsten carbide is still one of the hardest materials available, with a hardness close to that of diamond[4].
2. Wear Resistance: The material exhibits exceptional resistance to abrasion and wear, making it ideal for cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
3. Toughness: The cobalt binder significantly improves the material's ability to withstand impact and resist fracture.
4. Thermal Stability: Cobalt-containing tungsten carbide retains its properties at high temperatures, making it suitable for high-speed machining applications[4].
5. Density: The density of tungsten carbide with 5.5% to 6.5% cobalt is approximately 14.5 g/cm³[4].
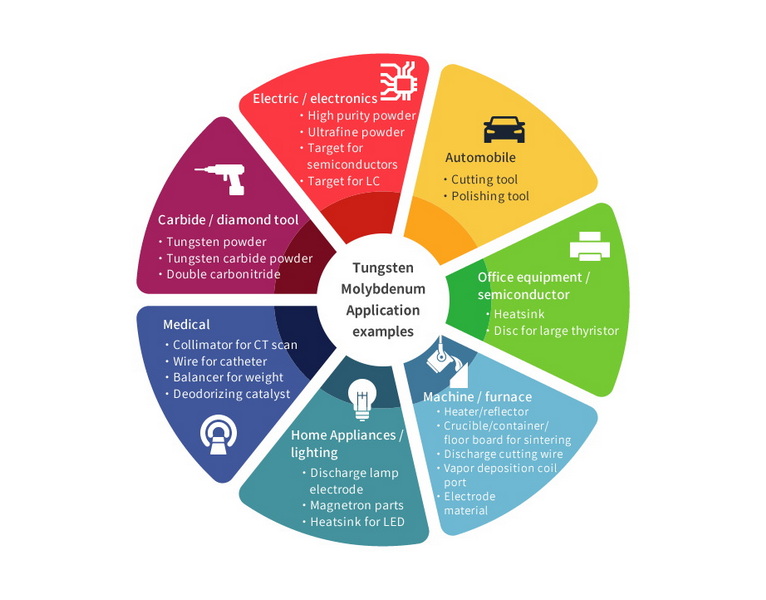
Applications of Cobalt-Containing Tungsten Carbide
The unique combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance makes cobalt-containing tungsten carbide valuable in numerous applications:
1. Cutting Tools: Used in drill bits, end mills, and inserts for machining metals and other hard materials.
2. Mining and Oil Drilling: Components for rock drilling, tunnel boring, and oil well drilling.
3. Wear Parts: Used in manufacturing dies, nozzles, and other components subject to high wear.
4. Armor-Piercing Rounds: Military applications for armor-piercing ammunition.
5. Jewelry: Increasingly popular for wedding bands and other jewelry due to its durability and scratch resistance.
Alternatives to Cobalt
While cobalt is the most common binder for tungsten carbide, there are situations where alternatives are preferred:
1. Nickel: Used in applications requiring better corrosion resistance.
2. Iron: Sometimes used as a lower-cost alternative to cobalt.
3. Nickel-Chromium Alloys: Offer improved toughness and corrosion resistance in certain applications.
4. Cobalt-Free Formulations: Developed for applications where cobalt's magnetic properties are undesirable or where there are concerns about cobalt's toxicity.
Environmental and Health Considerations
The use of cobalt in tungsten carbide has raised some environmental and health concerns:
1. Mining Impact: Cobalt mining can have significant environmental impacts.
2. Occupational Exposure: Workers in tungsten carbide production may be exposed to cobalt dust, which can cause respiratory issues.
3. Recycling Challenges: The presence of cobalt can complicate the recycling process for tungsten carbide products.
4. Toxicity: While the tungsten carbide-cobalt composite is generally stable, there are concerns about potential long-term health effects of cobalt exposure.
Identifying Genuine Tungsten Carbide
Given the value and desirable properties of tungsten carbide, there's a market for imitation products. Here are some ways to distinguish genuine tungsten carbide:
1. Density: Genuine tungsten carbide is very dense. A piece will feel heavier than it looks.
2. Scratch Resistance: It's extremely difficult to scratch tungsten carbide. Common metals won't leave a mark[7].
3. Color: Genuine tungsten carbide has a distinct dark gray color.
4. Magnetism: Due to the cobalt content, many tungsten carbide items are slightly magnetic.
5. Professional Testing: For absolute certainty, professional testing methods like X-ray diffraction can be used.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while pure tungsten carbide (WC) does not contain cobalt, the term "tungsten carbide" in most practical applications refers to a composite material that typically does include cobalt as a binder. This cobalt-containing tungsten carbide is indeed genuine and offers a unique combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance that makes it invaluable in numerous industrial and consumer applications.
The presence of cobalt is not a sign of inferiority or inauthenticity. Rather, it's a crucial component that enhances the material's overall performance and enables its use in a wide range of demanding applications. However, it's important to note that there are also cobalt-free formulations available for specific needs.
As technology advances, we may see new binders and formulations developed, potentially offering even better performance or addressing some of the environmental and health concerns associated with cobalt use. Nonetheless, cobalt-containing tungsten carbide remains a cornerstone material in many industries, testament to its exceptional properties and versatility.

FAQ
1. Is tungsten carbide magnetic?
Tungsten carbide itself is not magnetic. However, the cobalt used as a binder in many tungsten carbide products is magnetic. As a result, many tungsten carbide items will exhibit slight magnetic properties due to their cobalt content.
2. Can tungsten carbide be recycled?
Yes, tungsten carbide can be recycled. However, the process can be complex due to the presence of cobalt and other alloying elements. Specialized recycling facilities use various methods to separate and recover the tungsten and other components.
3. Is tungsten carbide safe to wear as jewelry?
Generally, tungsten carbide jewelry is safe to wear. It's hypoallergenic for most people and doesn't react with skin. However, individuals with extreme sensitivity to metals might react to the nickel sometimes used in the manufacturing process.
4. How does tungsten carbide compare to other hard materials like diamond?
While tungsten carbide is one of the hardest materials available, diamond is still significantly harder. On the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, diamond rates a 10, while tungsten carbide rates around 9 to 9.5. However, tungsten carbide is tougher than diamond, meaning it's less brittle and more resistant to cracking.
5. Can tungsten carbide be resized or repaired?
Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and resistant to deformation, which makes it difficult to resize or repair once it's been formed. This is particularly relevant for jewelry items like rings. If resizing is needed, it's often more practical to replace the item entirely.
Citations:
[1] https://hpvchemicals.oecd.org/ui/handler.axd?id=ed1c76bf-dad9-4baa-8d1b-70fed7f92862
[2] https://heegermaterials.com/blog/90_how-is-tungsten-carbide-made-.html
[3] https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=3358
[4] https://shop.machinemfg.com/c2-tungsten-carbide-physical-and-chemical-properties/
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten_carbide
[6] https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tungsten-carbide-cobalt
[7] https://www.thermalspray.com/how-to-distinguish-real-tungsten-carbide-from-fakes/
[8] https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tungsten-carbide
















